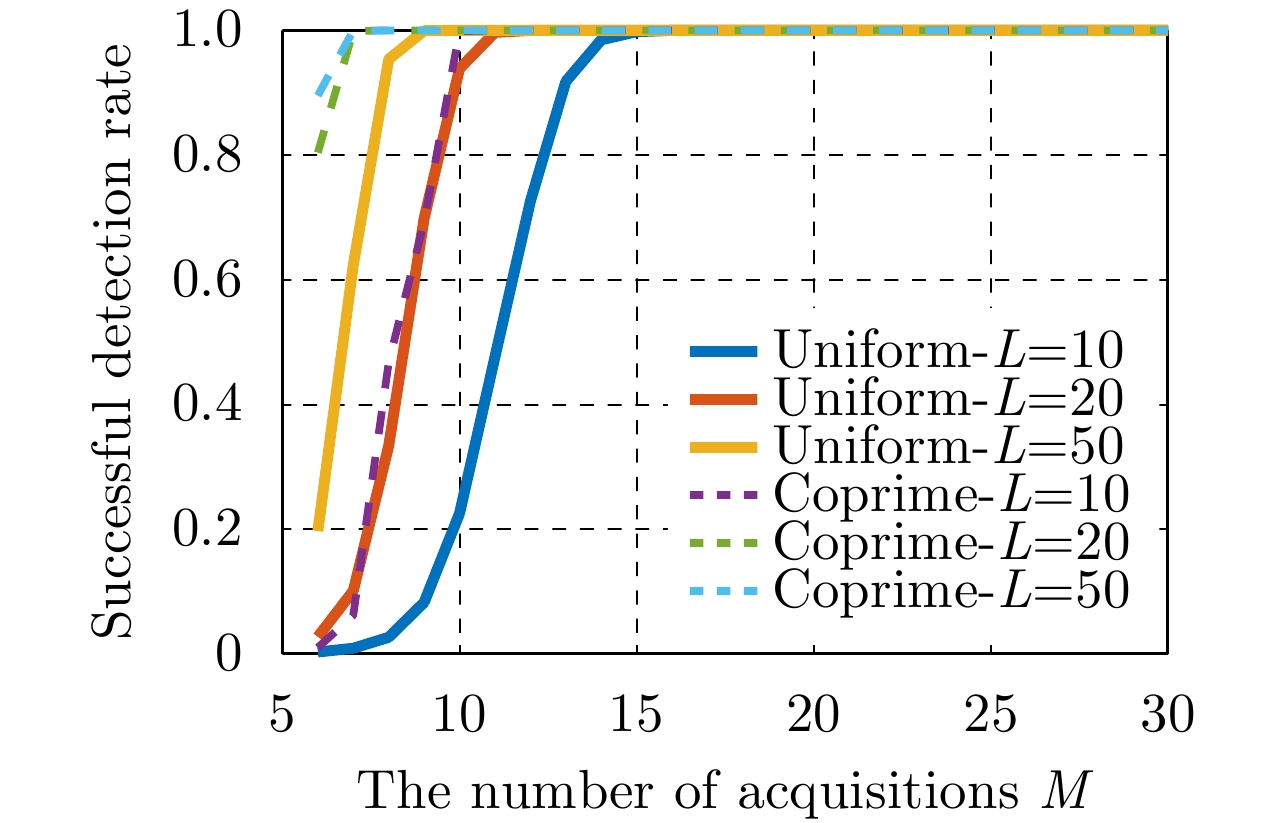
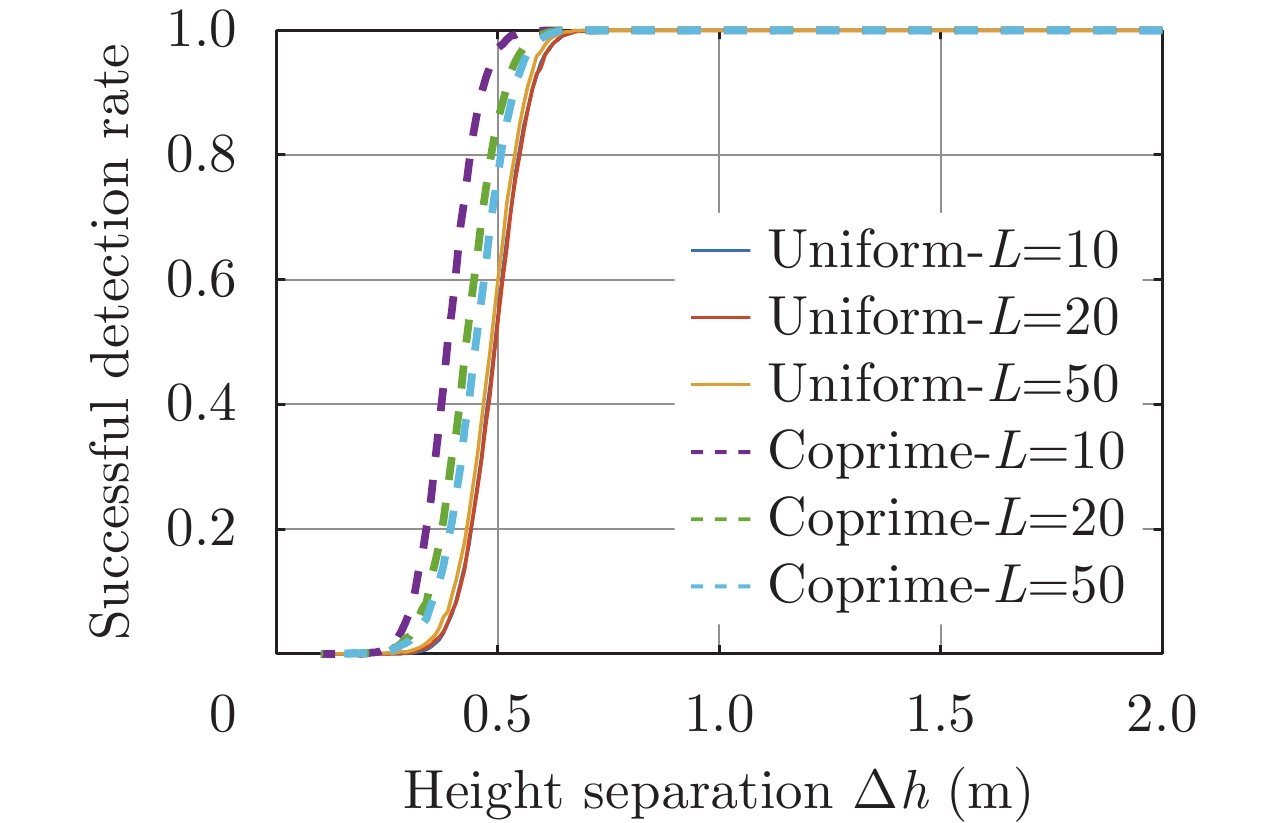
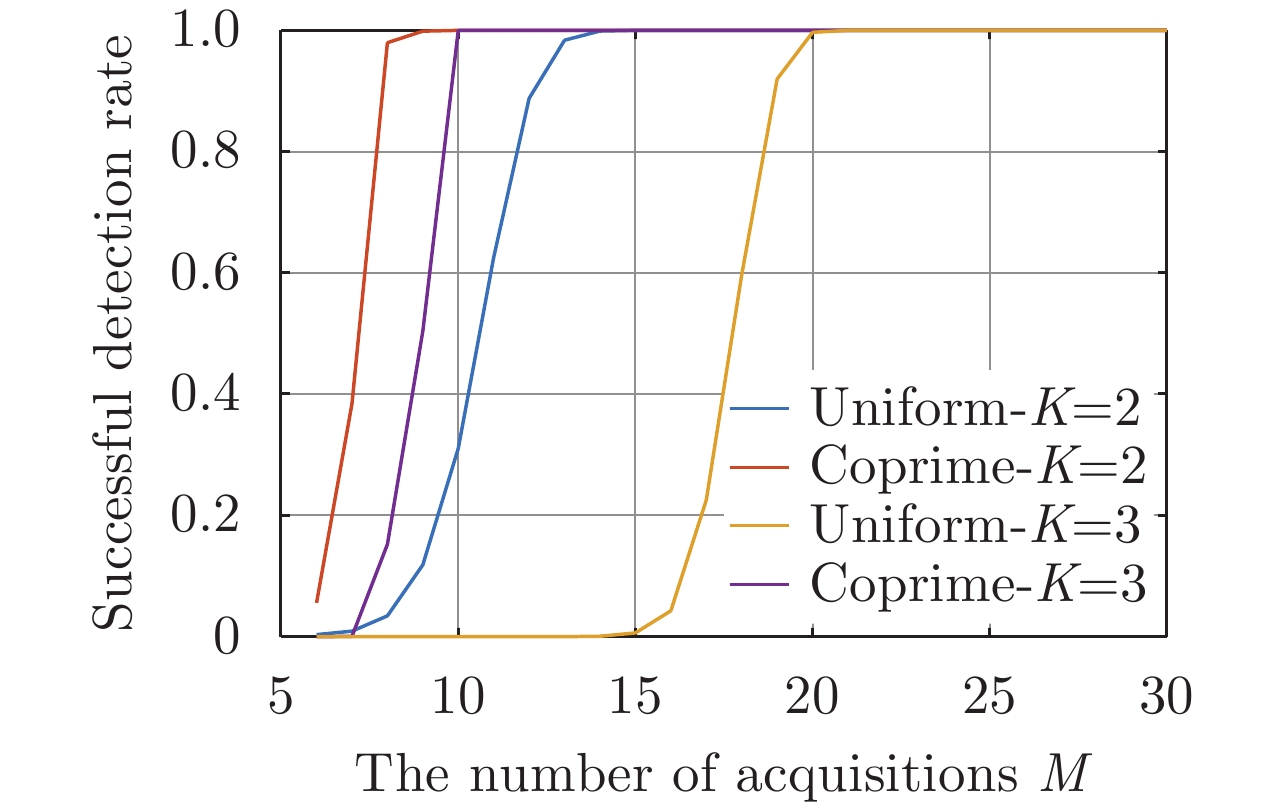
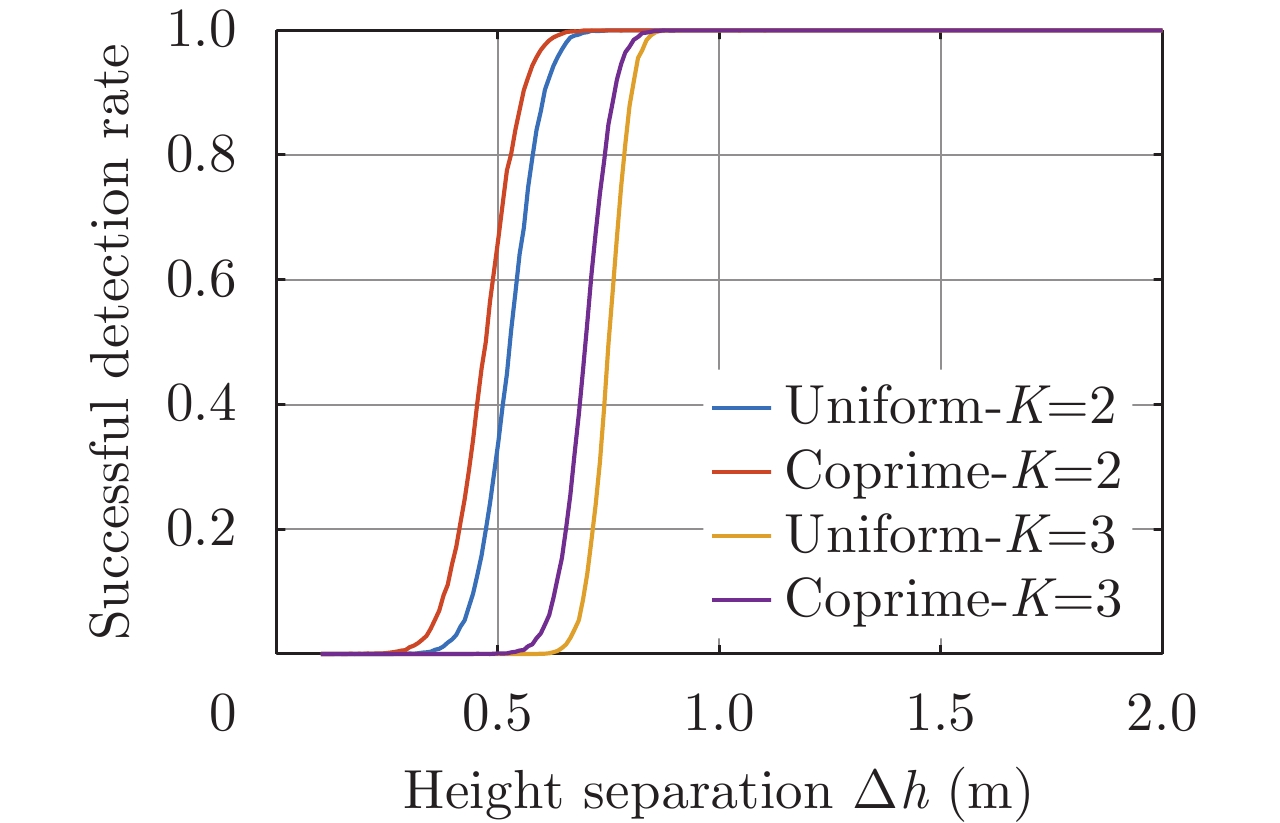
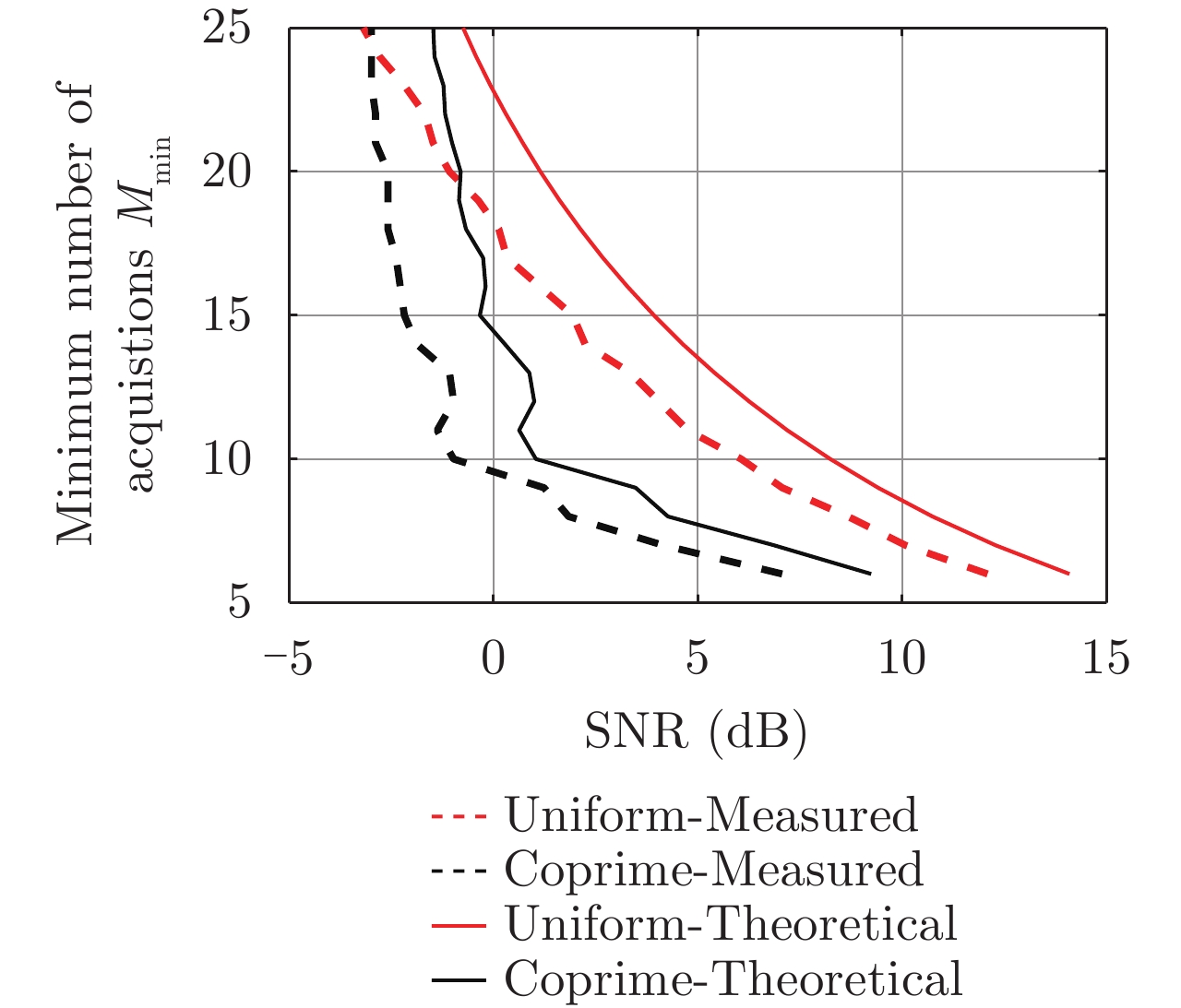
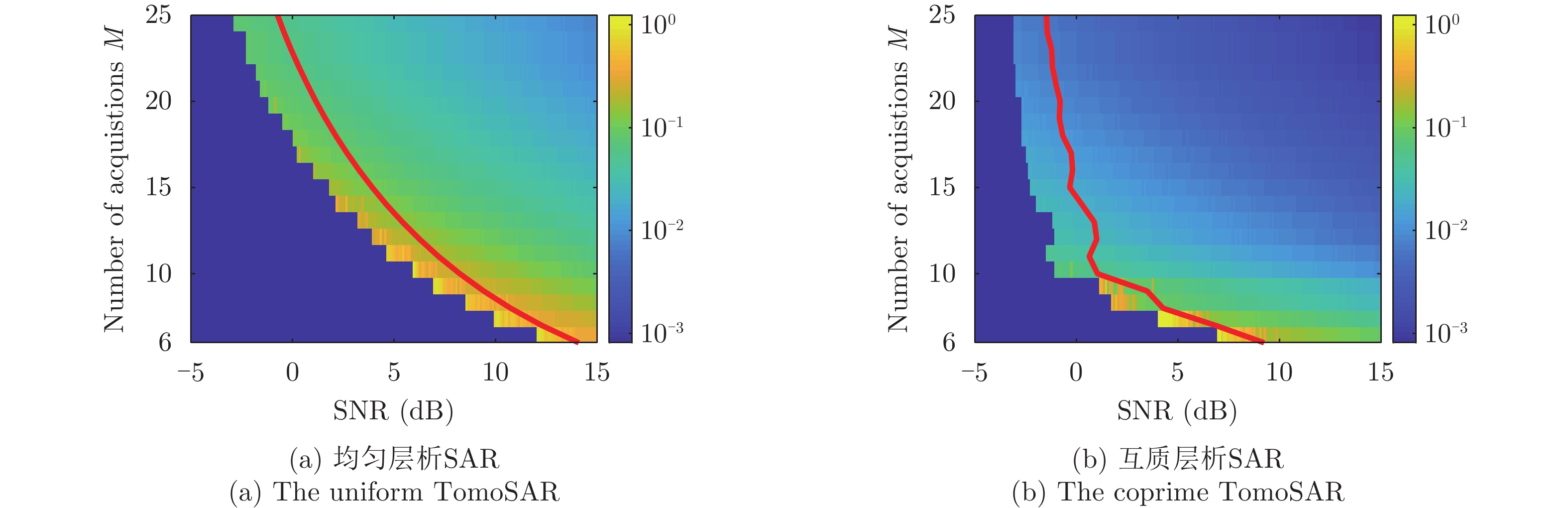
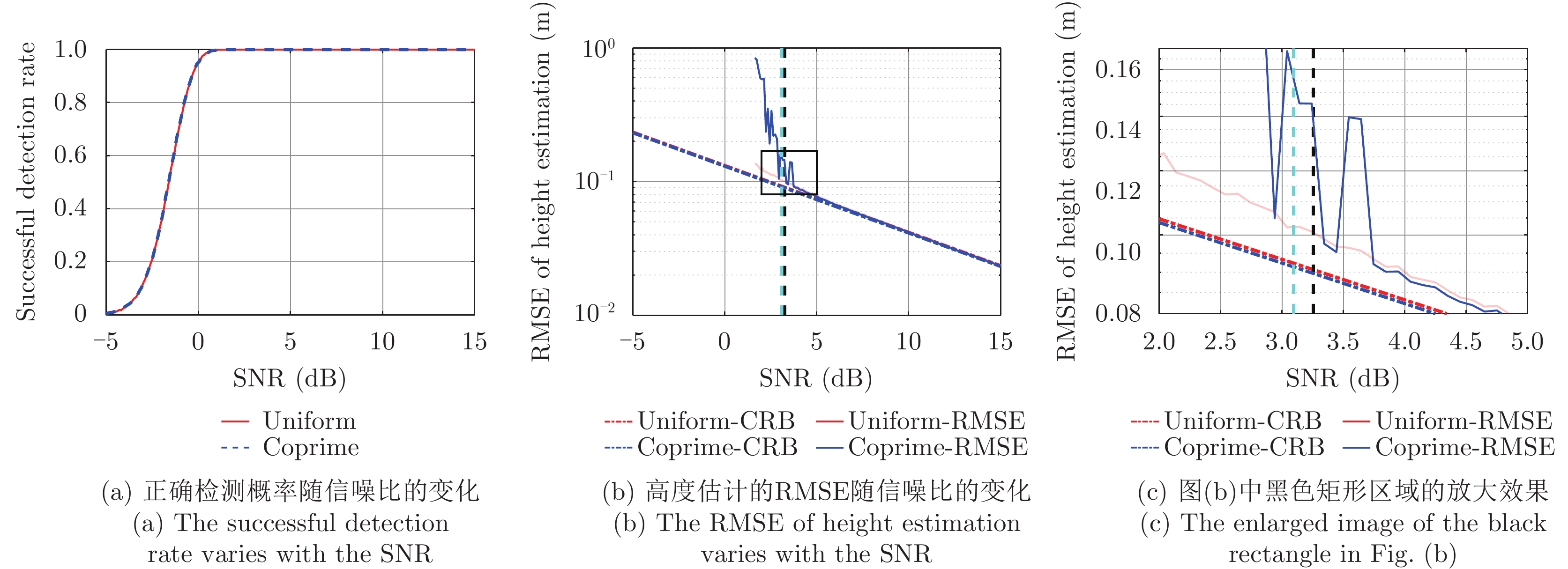
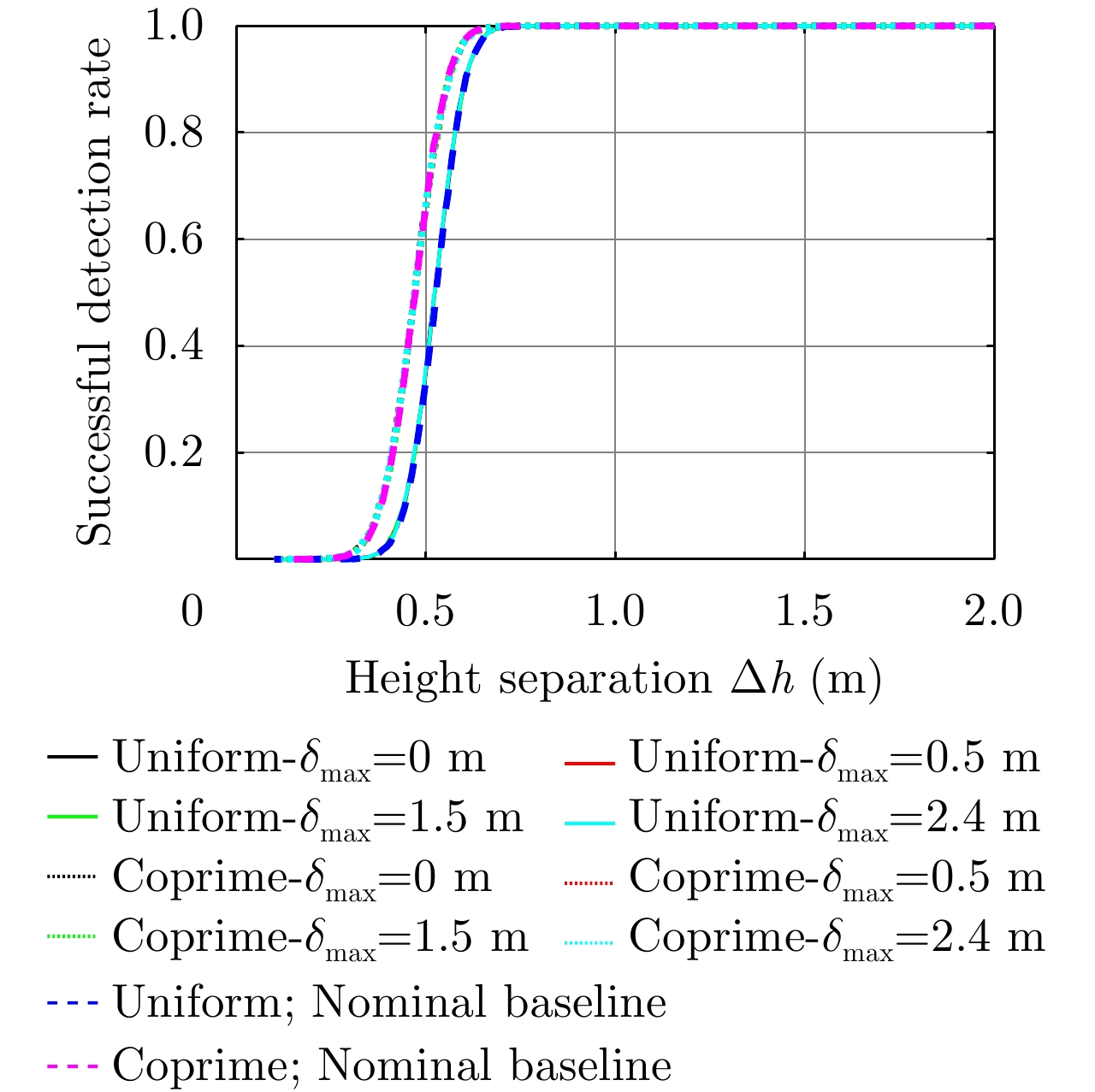
| [1] |
RAMBOUR C, BUDILLON A, JOHNSY A C, et al. From interferometric to tomographic SAR: A review of synthetic aperture radar tomography-processing techniques for scatterer unmixing in urban areas[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(2): 6–29. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2957215 |
| [2] |
REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 |
| [3] |
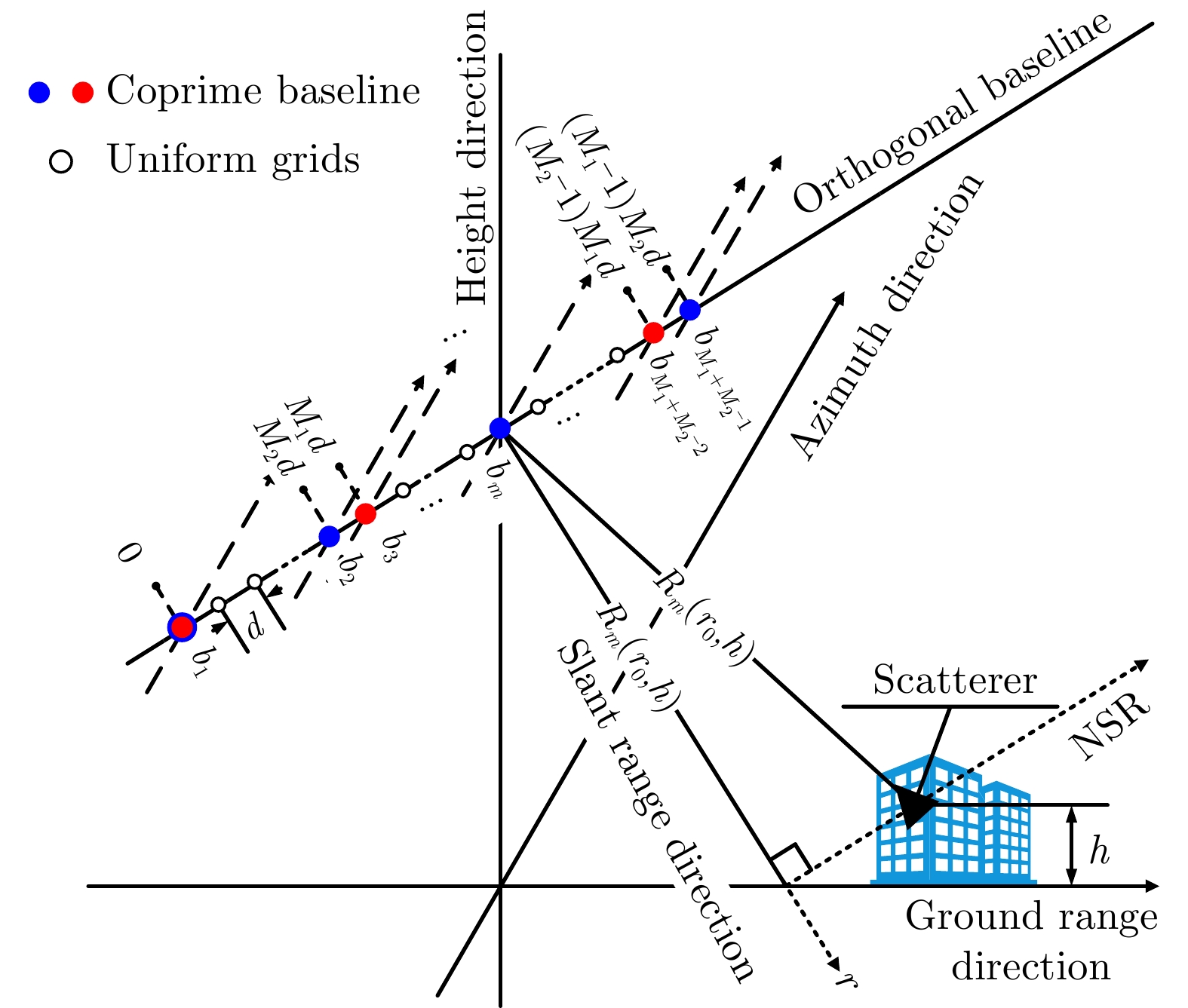
YU Longlong, HUANG Xiaotao, FENG Dong, et al. Coprime synthetic aperture radar tomography[C]. 2021 2nd China International SAR Symposium (CISS), Shanghai, China, 2021: 1–6.
|
| [4] |
YU Longlong, FENG Dong, WANG Jian, et al. An efficient reconstruction approach based on atomic norm minimization for coprime tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4503705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3143662 |
| [5] |
VAIDYANATHAN P P and PAL P. Sparse sensing with Co-prime samplers and arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(2): 573–586. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2089682 |
| [6] |
LOMBARDINI F and PARDINI M. 3-D SAR tomography: The multibaseline sector interpolation approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(4): 630–634. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2001283 |
| [7] |
NANNINI M, REIGBER A, and SCHEIBER R. A study on irregular baseline constellations in SAR tomography[C]. 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 1–4.
|
| [8] |
WEI Lianhuan, FENG Qiuyue, LIU Shanjun, et al. Minimum redundancy array—A baseline optimization strategy for urban SAR tomography[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 3100. doi: 10.3390/rs12183100 |
| [9] |
NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, and MOREIRA A. Estimation of the minimum number of tracks for SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 531–543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2007846 |
| [10] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 |
| [11] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646 |
| [12] |
NADLER B. Finite sample approximation results for principal component analysis: A matrix perturbation approach[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2008, 36(6): 2791–2817. doi: 10.1214/08-aos618 |
| [13] |
NADAKUDITI R R and EDELMAN A. Sample eigenvalue based detection of high-dimensional signals in white noise using relatively few samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(7): 2625–2638. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.917356 |
| [14] |
FORNARO G, VERDE S, REALE D, et al. CAESAR: An approach based on covariance matrix decomposition to improve multibaseline-multitemporal interferometric SAR processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2050–2065. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2352853 |
| [15] |
NAVNEET S, KIM J W, and LU Zhong. A new InSAR persistent scatterer selection technique using top eigenvalue of coherence matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 1969–1978. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2771386 |
| [16] |
PAUCIULLO A, REALE D, FRANZÉ W, et al. Multi-look in GLRT-based detection of single and double persistent scatterers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5125–5137. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2809538 |
| [17] |
D’HONDT O, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, GUILLASO S, et al. Nonlocal filtering applied to 3-D reconstruction of tomographic SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 272–285. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2746420 |
| [18] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based TomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 |
| [19] |
JOHNSON B A, ABRAMOVICH Y I, and MESTRE X. MUSIC, G-MUSIC, and maximum-likelihood performance breakdown[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3944–3958. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.921729 |
| [20] |
SHAGHAGHI M and VOROBYOV S A. Subspace leakage analysis and improved DOA estimation with small sample size[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(12): 3251–3265. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422675 |
| [21] |
FRIEDLANDER B. The root-MUSIC algorithm for direction finding with interpolated arrays[J]. Signal Processing, 1993, 30(1): 15–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(93)90048-F |
| [22] |
RUBSAMEN M and GERSHMAN A B. Direction-of-arrival estimation for nonuniform sensor arrays: From manifold separation to fourier domain MUSIC methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 588–599. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2008560 |
| [23] |
STOICA P and NEHORAI A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer-Rao bound[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(5): 720–741. doi: 10.1109/29.17564 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: