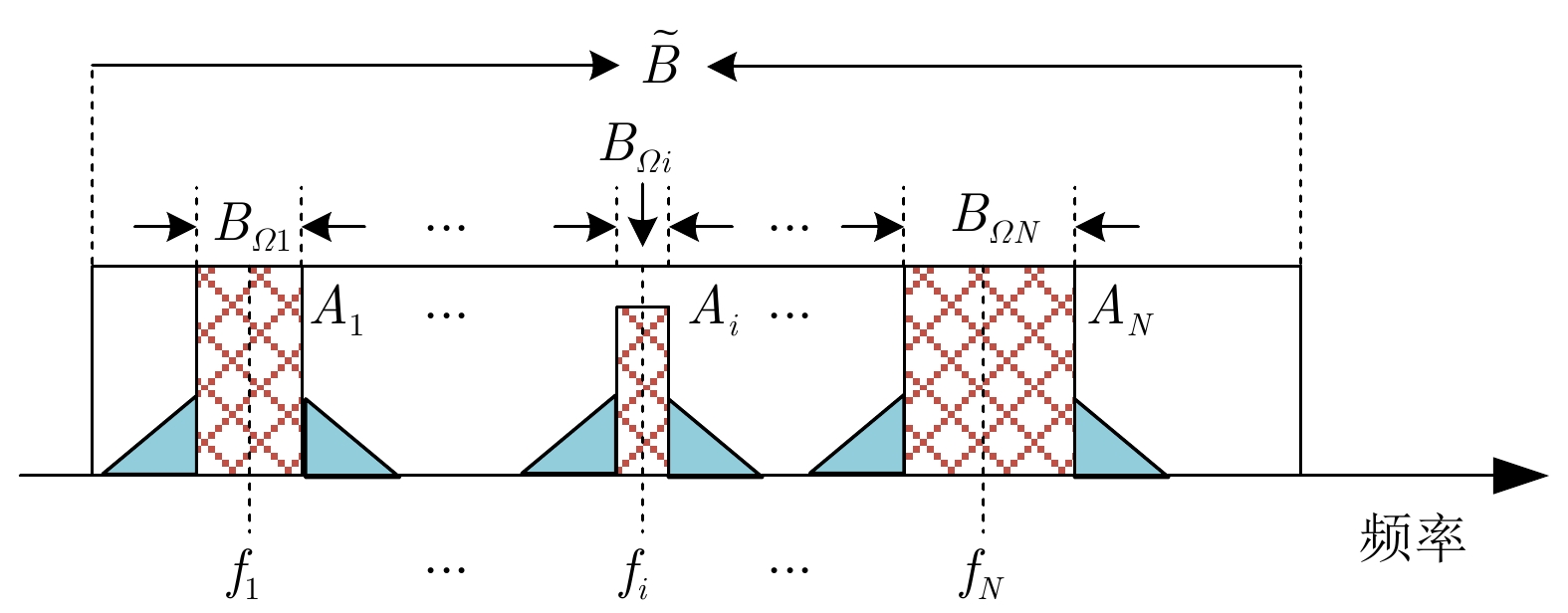
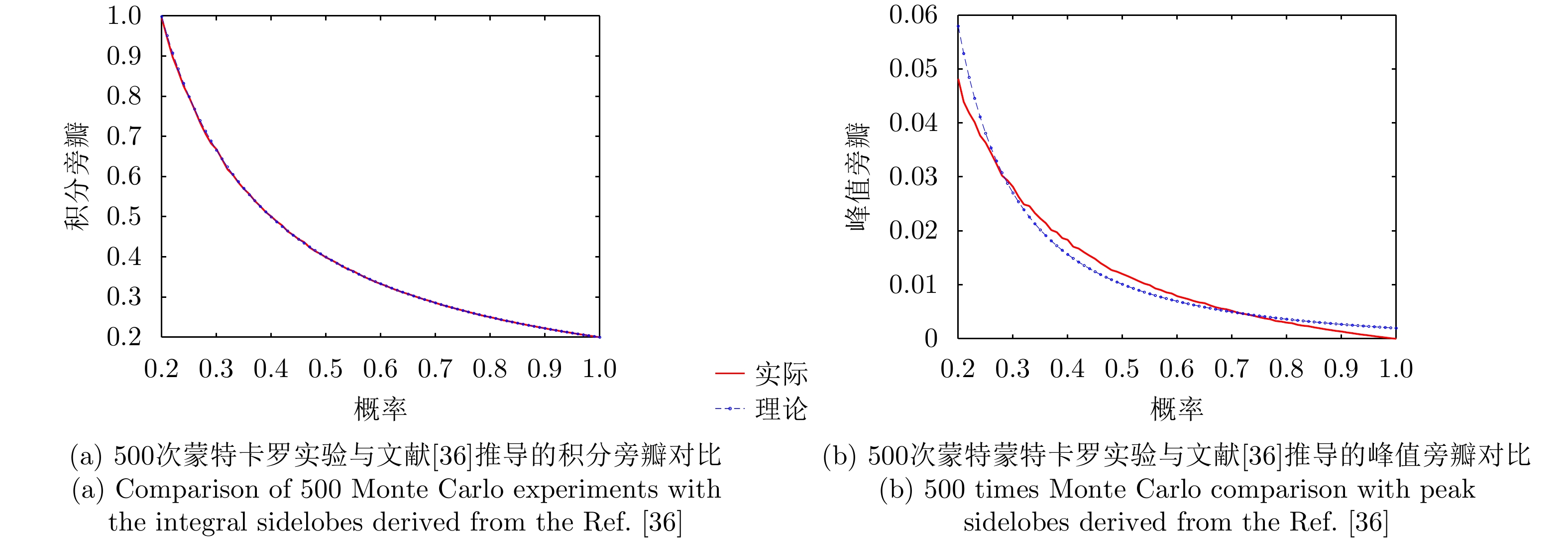
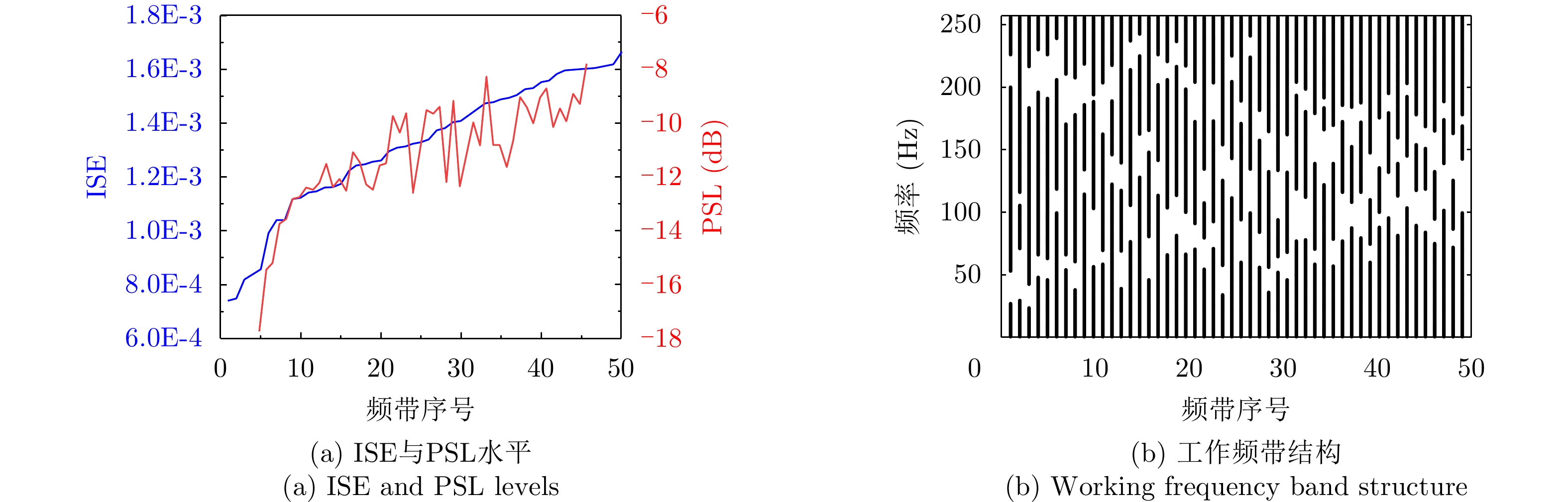
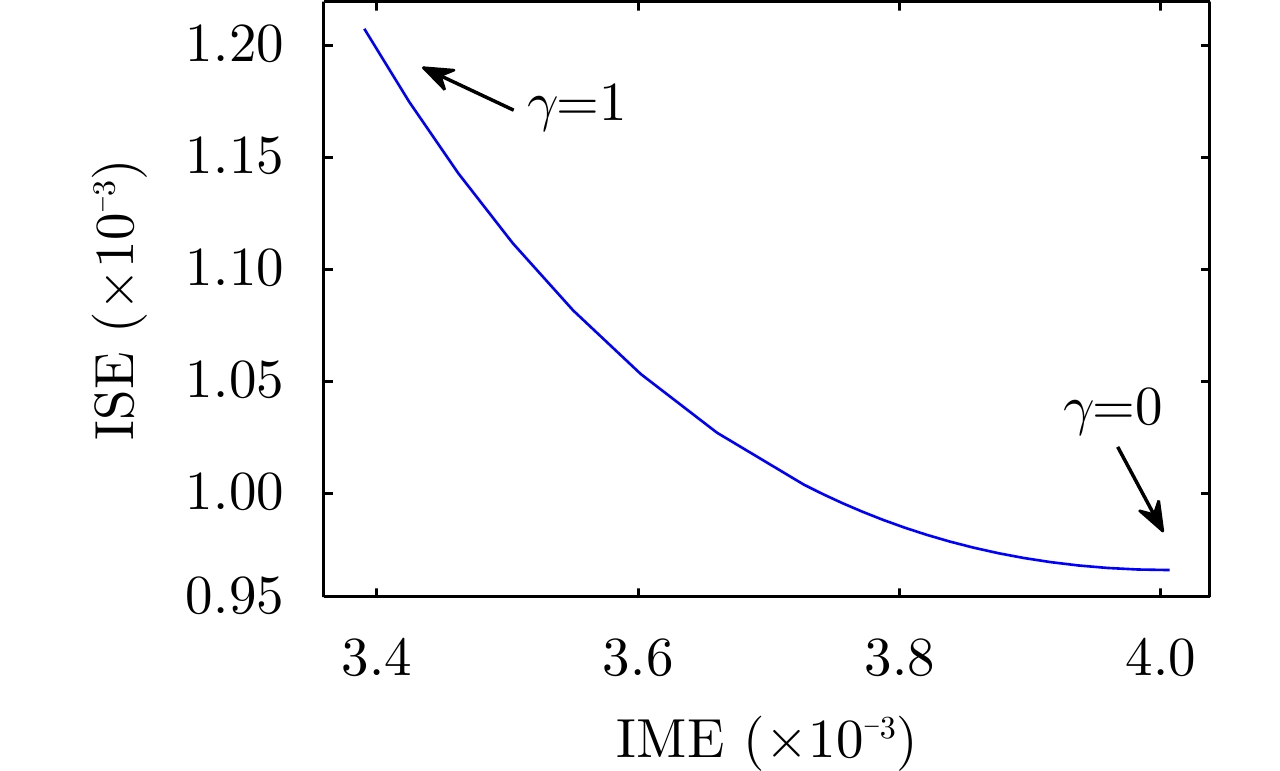
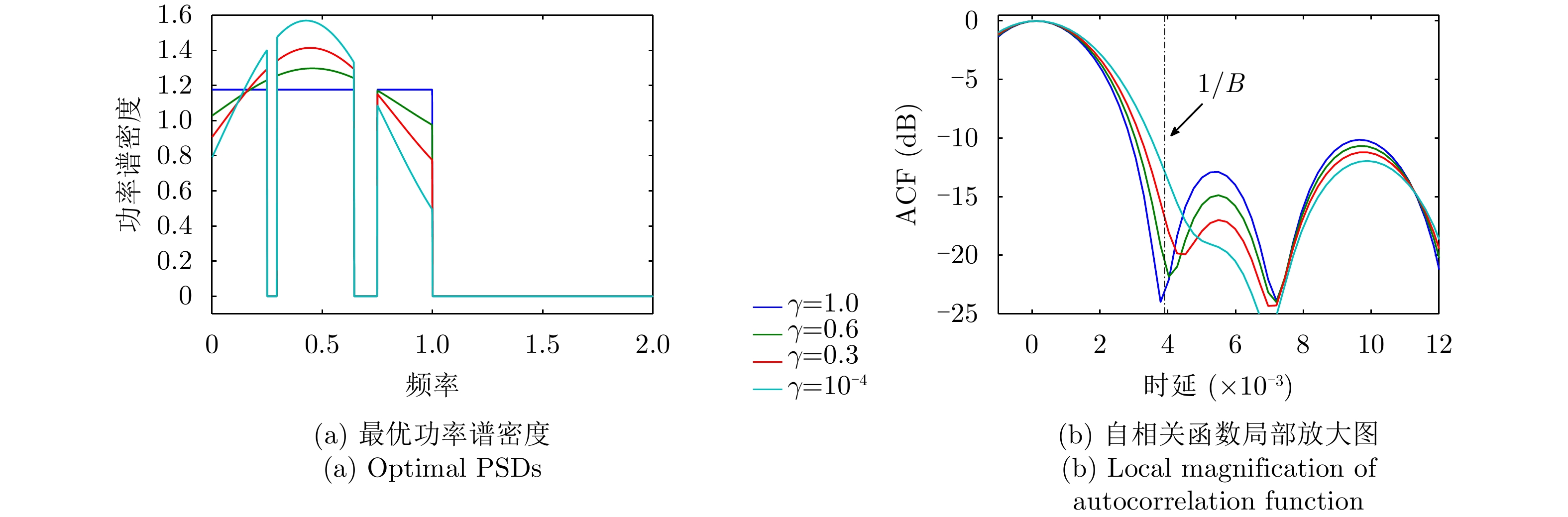
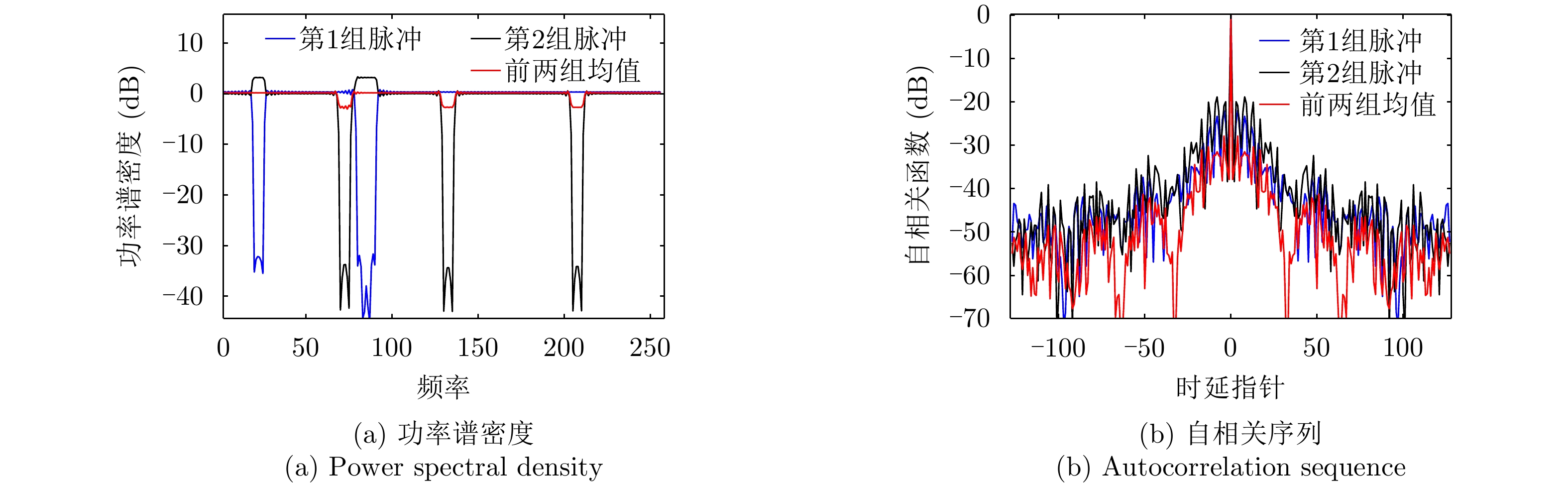
| [1] |
BLUNT S D and MOKOLE E L. Overview of radar waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(11): 2–42. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.160071 |
| [2] |
SALZMAN J, AKAMINE D, and LEFEVRE R. Optimal waveforms and processing for sparse frequency UWB operation[C]. 2001 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2001: 105–110.
|
| [3] |
LEONG H W and DAWE B. Channel availability for east coast high frequency surface wave radar systems[R]. Defence Research Establishment Ottawa (Ontario), 2001.
|
| [4] |
GREEN S D and KINGSLEY S P. Investigation of wide bandwidth HF radar waveforms[C]. IEE Colloquium on Advanced Transmission Waveforms, London, UK, 1995.
|
| [5] |
KUTUZOV V M. Synthesis of non-regular multitone signals and algorithms of their processing[C]. Third International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 1996.
|
| [6] |
GREEN S D and KINGSLEY S P. Improving the range/time sidelobes of large bandwidth discontinuous spectra HF radar waveforms[C]. International Conference on Hf Radio Systems and Techniques, Nottingham, UK, 1997.
|
| [7] |
WEI Yinsheng and LIU Yongtan. New anti-jamming waveform designing and processing for HF radar[C]. 2001 CIE International Conference on Radar, Beijing, China, 2001.
|
| [8] |
WEI Yinsheng, LIU Yongtan, and XU Rongqing. A novel 2-D signal processing scheme for quasi-random step frequency signal[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2003, 14(3): 77–80.
|
| [9] |
ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. Signal processing technique for randomly discontinuous spectra HF radar waveforms[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2004, 15(4): 511–515.
|
| [10] |
ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. A sidelobes suppression technique for spectra discontinuous HF radar signal[C]. 7th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2004.
|
| [11] |
ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. A sidelobes suppression technique for spectra discontinuous HF radar signal based on spectra compensation algorithm[C]. 2004 Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, 2004, Qingdao, China, 2004: 242–245.
|
| [12] |
LINDENFELD M J. Sparse frequency transmit-and-receive waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 851–861. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337459 |
| [13] |
LIU Wenxian, LU Yilong, and LESTURGIE M. Optimal sparse waveform design for HFSWR system[C]. International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Pisa, Italy, 2007.
|
| [14] |
ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Hopped-frequency waveform design for range sidelobe suppression in spectral congestion[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 87–94. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0232 |
| [15] |
NUNN C and MOYER L R. Spectrally-compliant waveforms for wideband radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2012, 27(8): 11–15. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2012.6329156 |
| [16] |
YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, GE Peng, et al. Constrained radar waveform design algorithm for spectral coexistence[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(8): 558–560. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4524 |
| [17] |
ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. PCFM radar waveform design with spectral and correlation considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2885–2898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2719359 |
| [18] |
GERLACH K. Thinned spectrum ultrawideband waveforms using stepped-frequency polyphase codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(4): 1356–1361. doi: 10.1109/7.722721 |
| [19] |
FAUST H H, CONNOLLY B, FIRESTONE T M, et al. A spectrally clean transmitting system for solid-state phased-array radars[C]. 2004 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004.
|
| [20] |
DE GRAAF J, FAUST H, ALATISHE J, et al. Generation of spectrally confined transmitted radar waveforms: Experimental results[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006.
|
| [21] |
PAN Mengguan, CHEN Baixiao, and YANG Minglei. A general range-velocity processing scheme for discontinuous spectrum FMCW signal in HFSWR applications[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 2016: 2609873. doi: 10.1155/2016/2609873 |
| [22] |
ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. Range sidelobes suppression for wideband randomly discontinuous spectra OTH-HF radar signal[C]. 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37509), Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 577–581.
|
| [23] |
MISHRA K V, MULLETI S, and ELDAR Y C. RaSSteR: Random sparse step-frequency radar[Z]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.05720, 2020.
|
| [24] |
ZHANG Jie. Study on wideband sparse spectrum waveform for anti-interception and anti-jamming countermeasure[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [25] |
FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, SO H C, et al. Min-max metric for spectrally compatible waveform design via log-exponential smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1075–1090. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2969043 |
| [26] |
YANG J, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Multi-spectrally constrained transceiver design against signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022.
|
| [27] |
AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, PIEZZO M, et al. Radar waveform design in a spectrally crowded environment via nonconvex quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1138–1152. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120731 |
| [28] |
ALHUJAILI K, YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, et al. Spectrally compatible MIMO radar beampattern design under constant modulus constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4749–4766. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3003976 |
| [29] |
王璐璐, 王宏强, 王满喜. 雷达目标检测的最优波形设计综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. doi: 10.12000/JR16084WANG Lulu, WANG Hongqiang, and WANG Manxi. An overview of radar waveform optimization for target detection[J]. Journal of Radar, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. doi: 10.12000/JR16084 |
| [30] |
PATTON L K and RIGLING B D. Autocorrelation constraints in radar waveform optimization for detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 951–968. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178041 |
| [31] |
HAN S H and LEE J H. An overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for multicarrier transmission[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2005, 12(2): 56–65. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2005.1421929 |
| [32] |
LI Jian, GUERCI J R, and XU Luzhou. Signal waveform's optimal-under-restriction design for active sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2006, 13(9): 565–568. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.874465 |
| [33] |
JONES A M, RIGLING B D, and RANGASWAMY M. Subspace approach to performance modelling of range-sidelobe suppressed waveforms[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(3): 466–473. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0283 |
| [34] |
MARČENKO V A and PASTUR L A. Distribution of eigenvalues for some sets of random matrices[J]. Mathematics of the USSR-Sbornik, 1967, 1(4): 457–483. doi: 10.1070/SM1967v001n04ABEH001994 |
| [35] |
GOODMAN N R. The distribution of the determinant of a complex wishart distributed matrix[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1963, 34(1): 178–180. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177704251 |
| [36] |
FROST S W. Performance analysis of radar waveforms for congested spectrums[D]. [Master dissertation], Wright State University, 2011.
|
| [37] |
毛智能. 非连续谱抗模糊波形设计研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.
MAO Zhineng. Research on waveform design foramibgumty suppresson underdiscontinuous spectrum[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2020.002047. |
| [38] |
ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Correlation performance analysis for waveforms with spectral notches[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(11): 1644–1651. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0080 |
| [39] |
WANG Guangtao and LU Yilong. Bounds on generalised integrated sidelobe level in waveforms with stopbands[J]. Electronics Letters, 2010, 46(23): 1561–1562. doi: 10.1049/el.2010.1876 |
| [40] |
WANG Guohua, MAI Chaoyun, SUN Jinping, et al. Sparse frequency waveform analysis and design based on ambiguity function theory[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(4): 707–717. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0270 |
| [41] |
赵德华. 频谱拥堵环境下的自适应雷达波形设计研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.
ZHAO Dehua. Research on waveform desgn for adaptmve radar in spectrum congested environment[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
|
| [42] |
ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Spectrum optimization via fft-based conjugate gradient method for unimodular sequence design[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.07.035 |
| [43] |
GERLACH K, FREY M R, STEINER M J, et al. Spectral nulling on transmit via nonlinear FM radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1507–1515. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751276 |
| [44] |
OECHSLIN R, WELLIG P, HINRICHSEN S, et al. Cognitive radar parameter optimization in a congested spectrum environment[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018.
|
| [45] |
WEITZEL C E. RF power amplifiers for wireless communications[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2000, 1(1): 64. doi: 10.1109/MMW.2000.823830 |
| [46] |
JAKABOSKY J, BLUNT S D, and HIGGINS T. Ultra-low sidelobe waveform design via spectral shaping and LINC transmit architecture[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 2015.
|
| [47] |
KAY S M. Modern Spectral Estimation: Theory and Application[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1988.
|
| [48] |
JACKSON L, KAY S, and VANKAYALAPATI N. Iterative method for nonlinear FM synthesis of radar signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 910–917. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461666 |
| [49] |
ZHUANG Shanna, HE Yapeng, and ZHU Xiaohua. Designing sparse frequency waveform with low range sidelobes for HFSWR[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 596–599.
|
| [50] |
HE Hao, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems: A Computational Approach[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
|
| [51] |
BIŞKIN O T and AKAY O. A new algorithm for designing sequences using stopband and correlation constraints[C]. 2018 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Izmir, Turkey, 2018: 1–4.
|
| [52] |
AUBRY A, CAROTENUTO V, and MAIO A D. Forcing multiple spectral compatibility constraints in radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(4): 483–487. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2532739 |
| [53] |
ALDAYEL O, MONGA V, and RANGASWAMY M. Successive QCQP refinement for MIMO radar waveform design under practical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(14): 3760–3774. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2552501 |
| [54] |
CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, FOGLIA G, et al. Quadratic optimization with similarity constraint for unimodular sequence synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(18): 4756–4769. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2715010 |
| [55] |
YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. Quadratic optimization for unimodular sequence design via an ADPM framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3619–3634. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2998637 |
| [56] |
GE Peng, CUI Guolong, KARBASI S M, et al. Cognitive radar sequence design under the spectral compatibility requirements[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(5): 759–767. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0239 |
| [57] |
YANG Jing, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Waveform design with spectral coexistence[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019.
|
| [58] |
LIANG J, SO H C, LI J, et al. Unimodular sequence design based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5367–5381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597123 |
| [59] |
ROWE W, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Spectrally constrained waveform design [sp Tips&Tricks][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(3): 157–162. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2301792 |
| [60] |
LIANG Junli, SO H C, LEUNG C S, et al. Waveform design with unit modulus and spectral shape constraints via Lagrange programming neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1377–1386. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2464178 |
| [61] |
TANG Bo and LIANG Junli. Efficient algorithms for synthesizing probing waveforms with desired spectral shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(3): 1174–1189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2876585 |
| [62] |
MAO Zhineng and WEI Yinsheng. Waveform optimisation for unambiguous Doppler extension[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(2): 290–299. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5061 |
| [63] |
GLADKOVA I. Analysis of stepped-frequency pulse train design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(4): 1251–1261. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5310296 |
| [64] |
ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Design unimodular sequence train with low central and recurrent autocorrelation sidelobes via FFT-based cyclic algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(19): 1329–1331. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2157 |
| [65] |
AUBRY A, CAROTENUTO V, DE MAIO A, et al. Cognitive radar waveform design for spectral compatibility[C]. 2016 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), Edinburgh, UK, 2016: 1–5.
|
| [66] |
AUBRY A, MAIO A D, HUANG Yongwei, et al. A new radar waveform design algorithm with improved feasibility for spectral coexistence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1029–1038. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140093 |
| [67] |
TANG Bo, LI Jian, and LIANG Junli. Alternating direction method of multipliers for radar waveform design in spectrally crowded environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 398–402. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.08.003 |
| [68] |
CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar with transmit beampattern formation[C]. 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Shanghai, China, 2018.
|
| [69] |
Alaee-Kerahroodi M, RAEI E, KUMAR S, et al. Coexistence of communications and cognitive MIMO radar: Waveform design and prototype[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.11890, 2021.
|
| [70] |
MARTONE A and AMIN M. A view on radar and communication systems coexistence and dual functionality in the era of spectrum sensing[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 119: 103135.
|
| [71] |
DENG M, CHENG Z, and HE Z. Spectrally compatible waveform design for large-scale MIMO radar beampattern synthesis with One-Bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022.
|
| [72] |
CHEN Ningkang, WEI Ping, GAO Lin, et al. Beampattern synthesis and spectral compatibility based MIMO radar waveform design[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 118: 103211. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103211. |
| [73] |
YAO Yu, LIU Haitao, MIAO Pu, et al. MIMO radar design for extended target detection in a spectrally crowded environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3127727 |
| [74] |
CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar in the presence of multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(13): 3543–3555. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2833818 |
| [75] |
SHI Shengnan, WANG Zhaoyi, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar with ISL and PAPR constraints[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(5): 2368–2377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2951740 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: