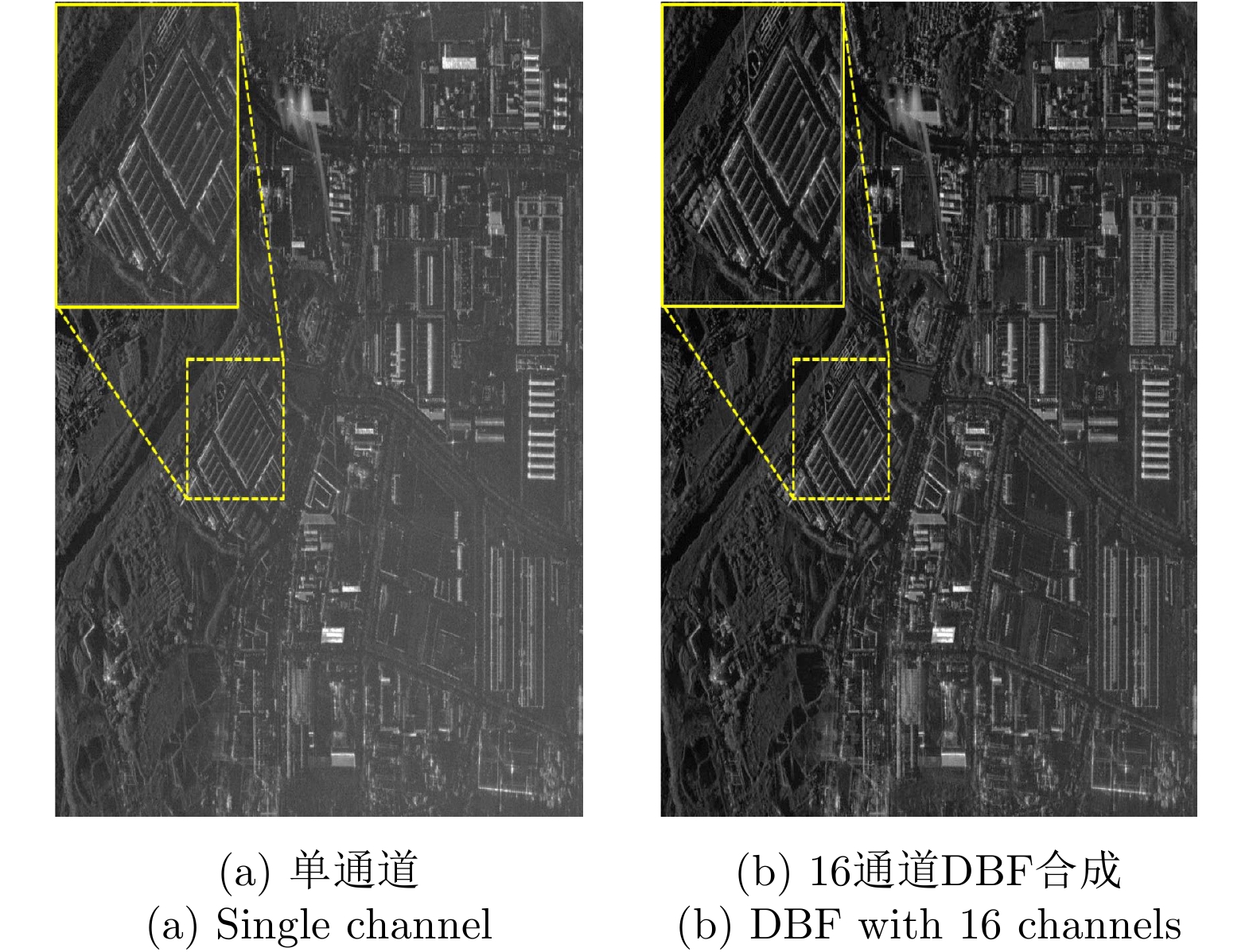
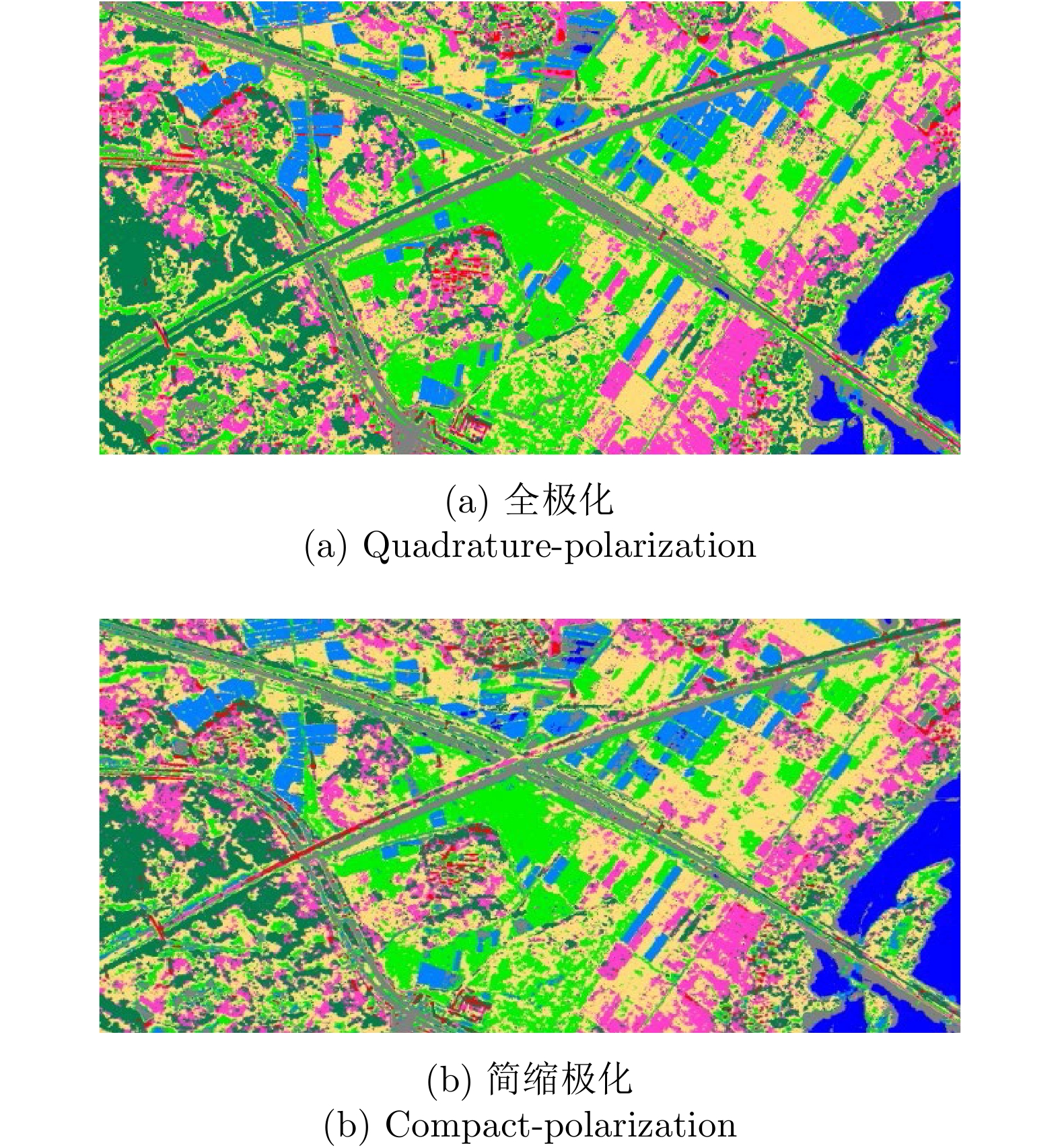
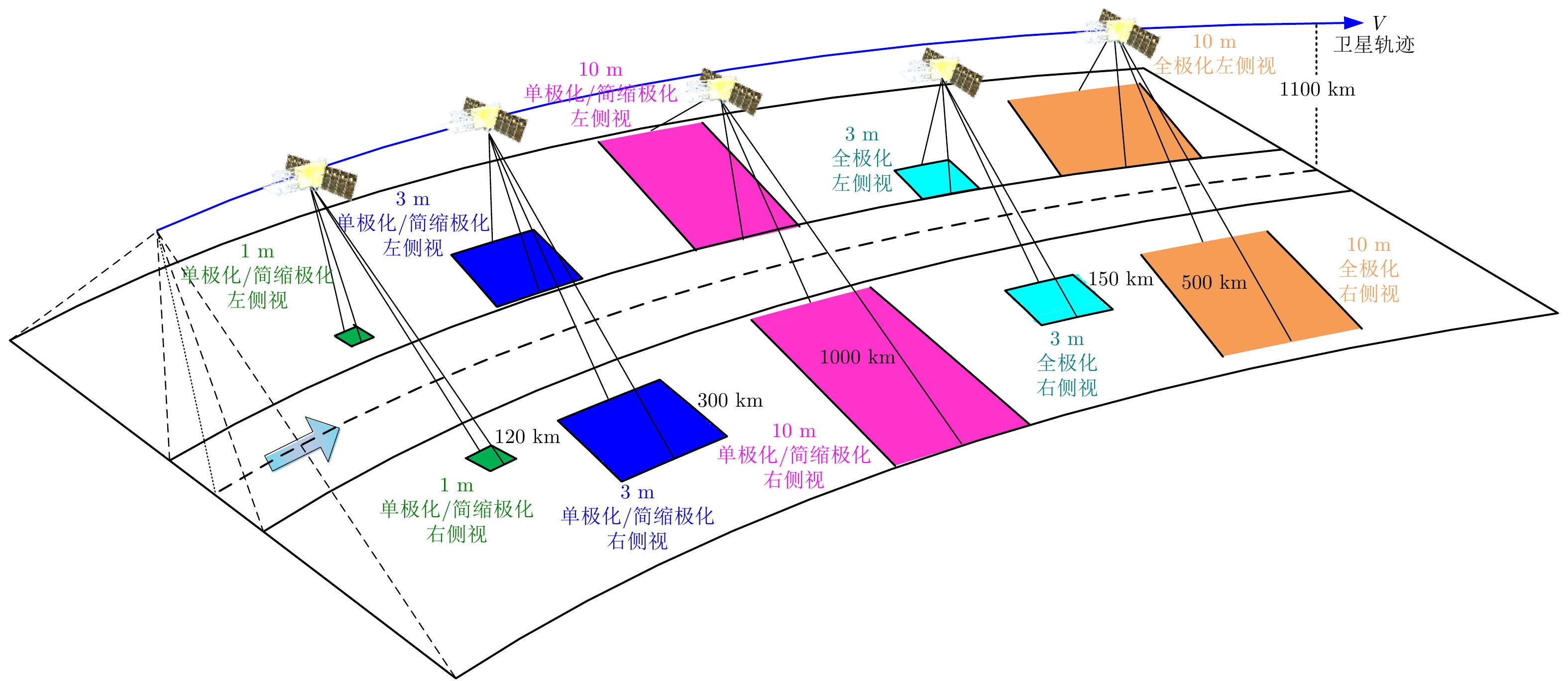
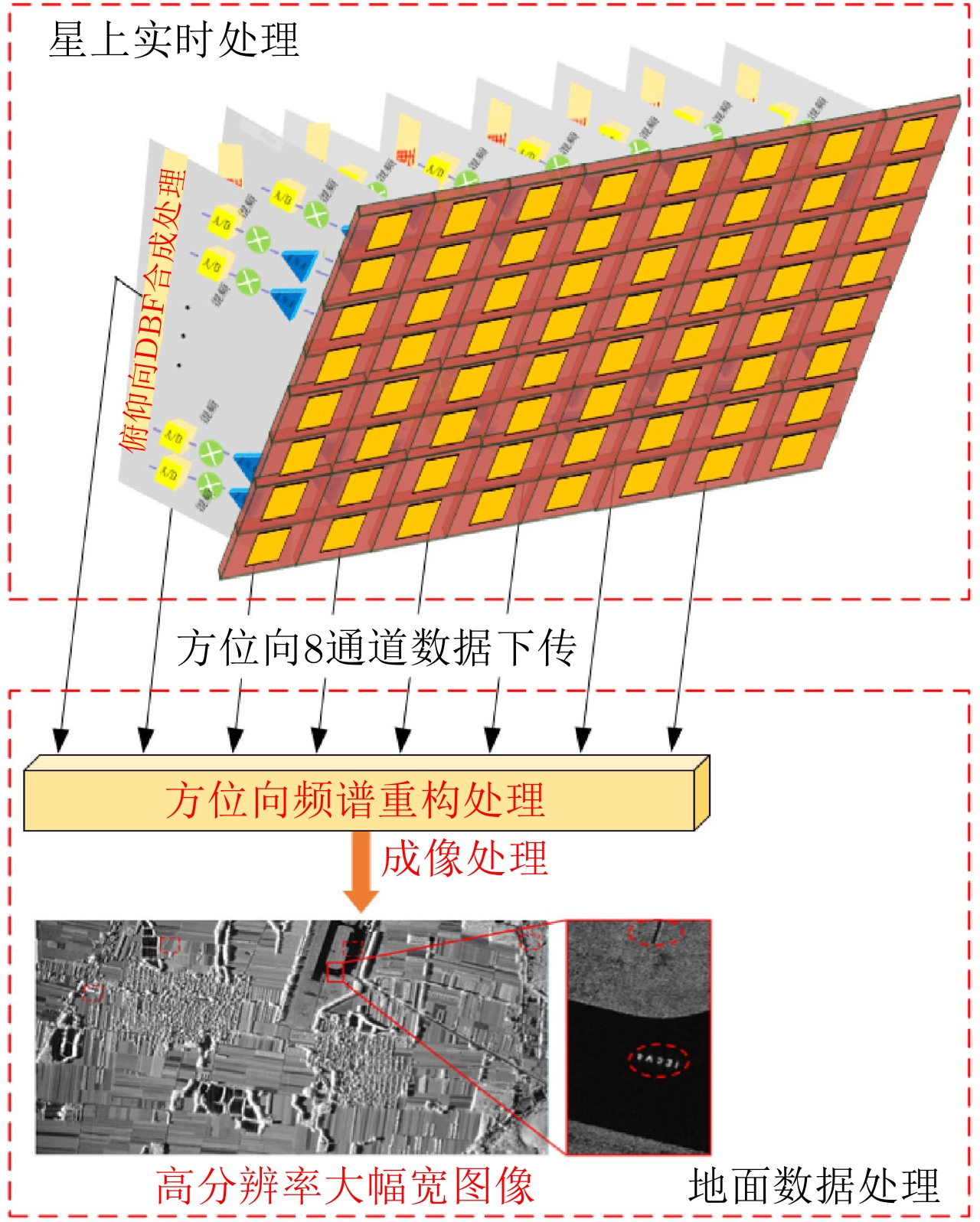
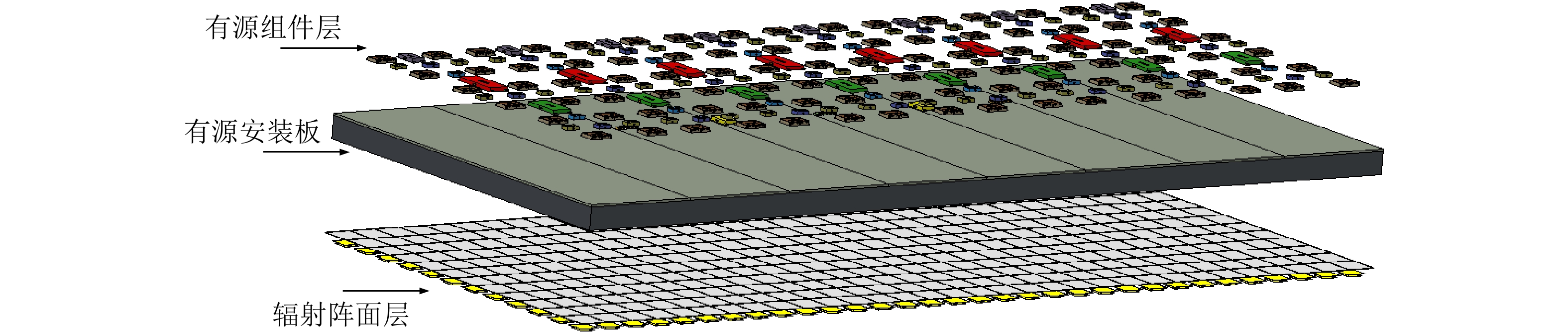
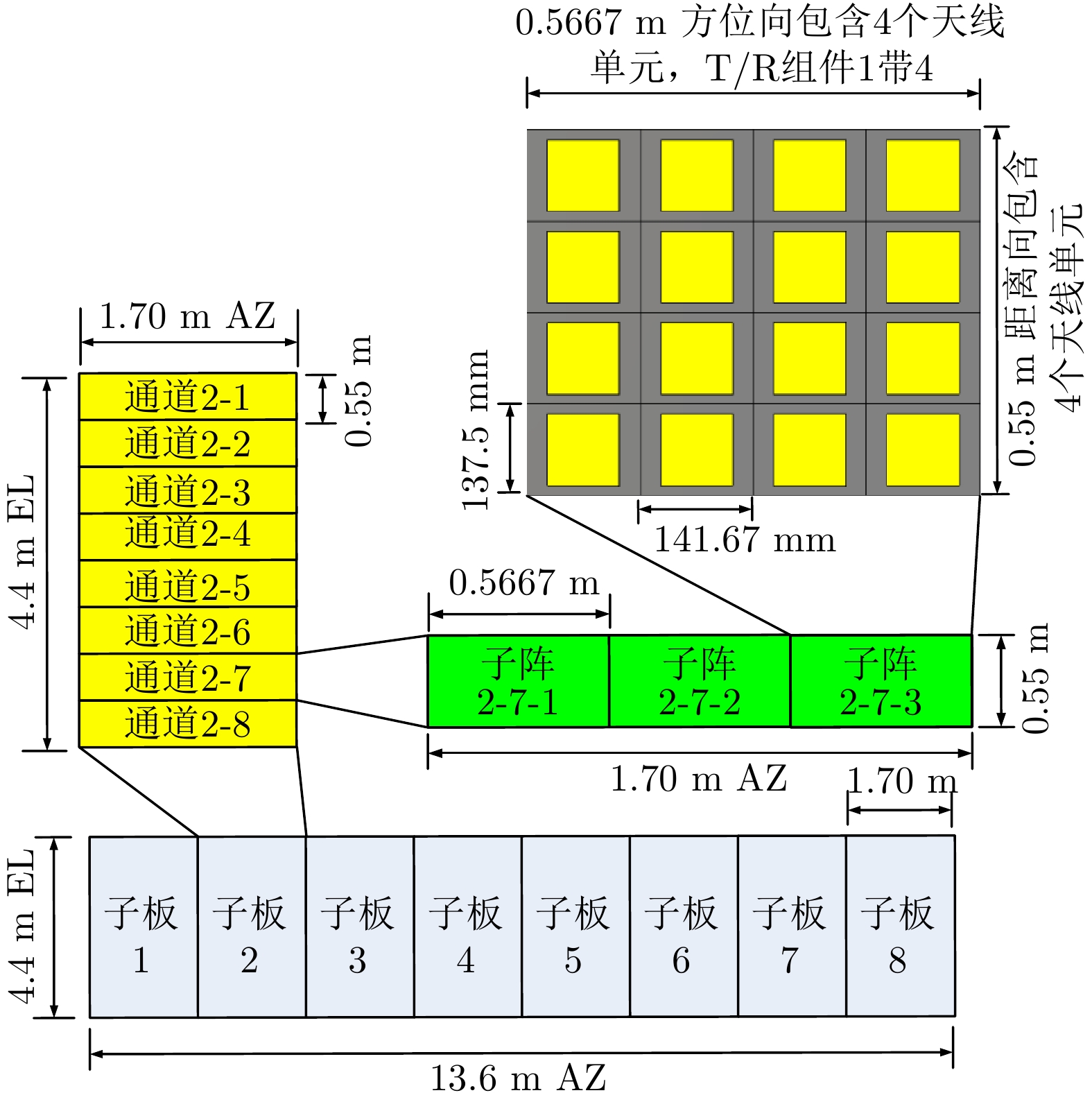
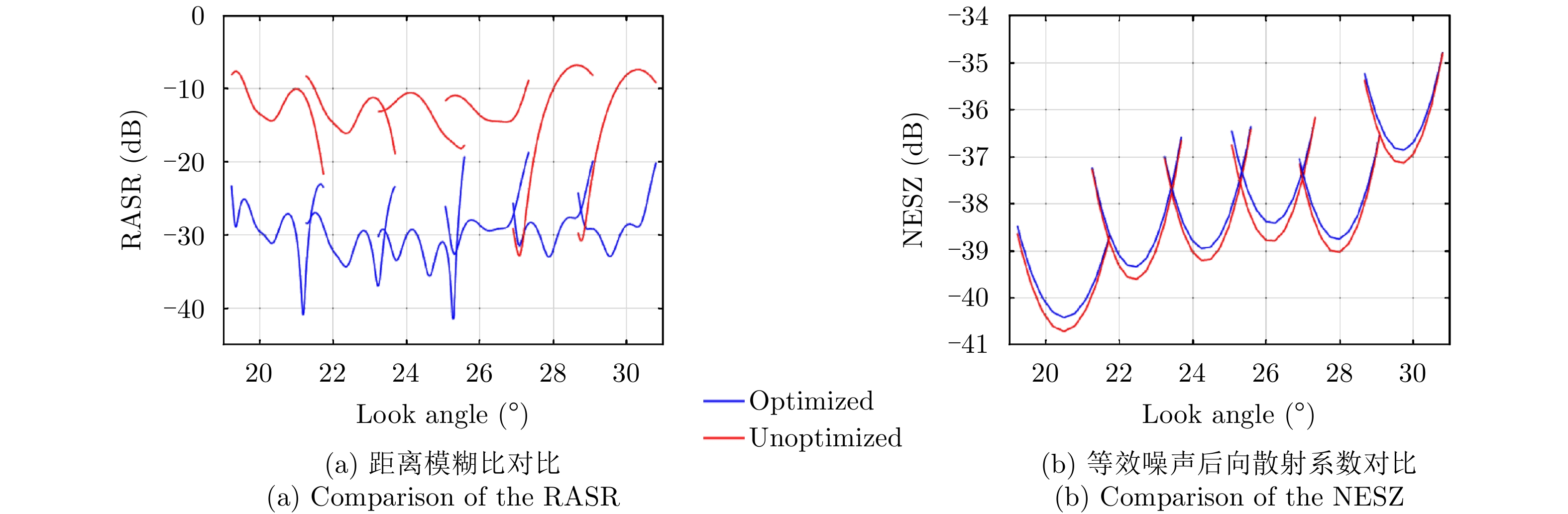
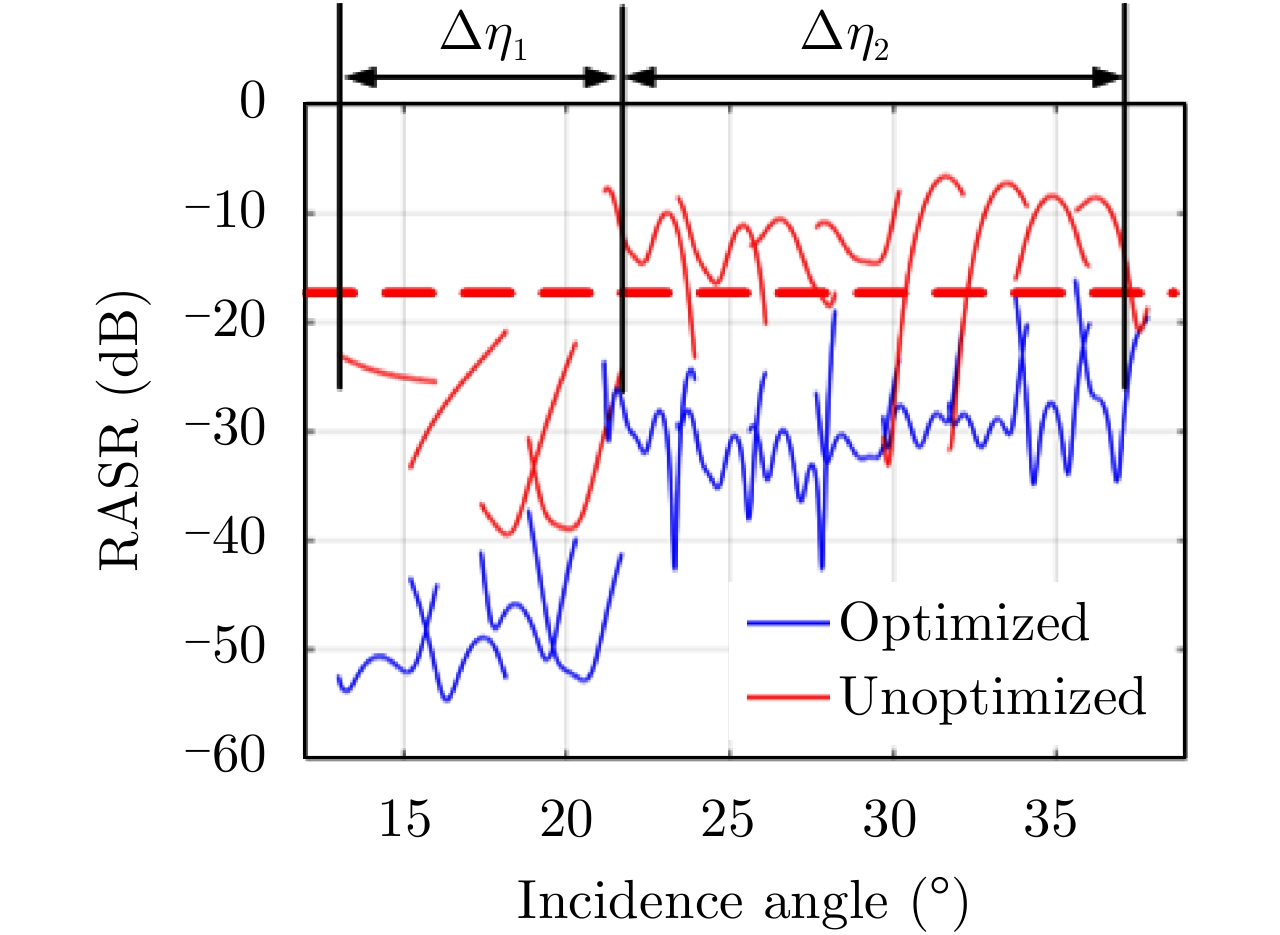
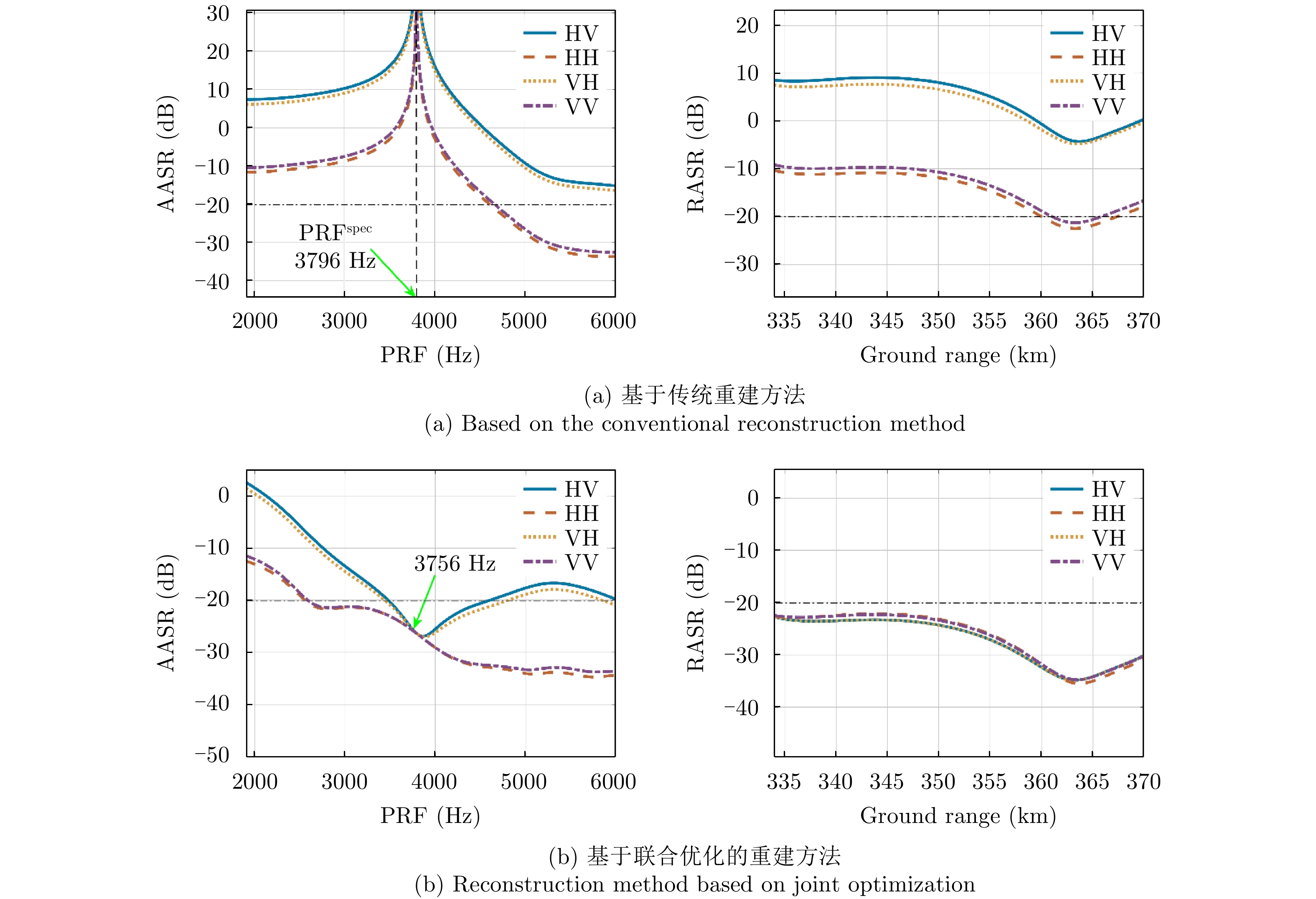
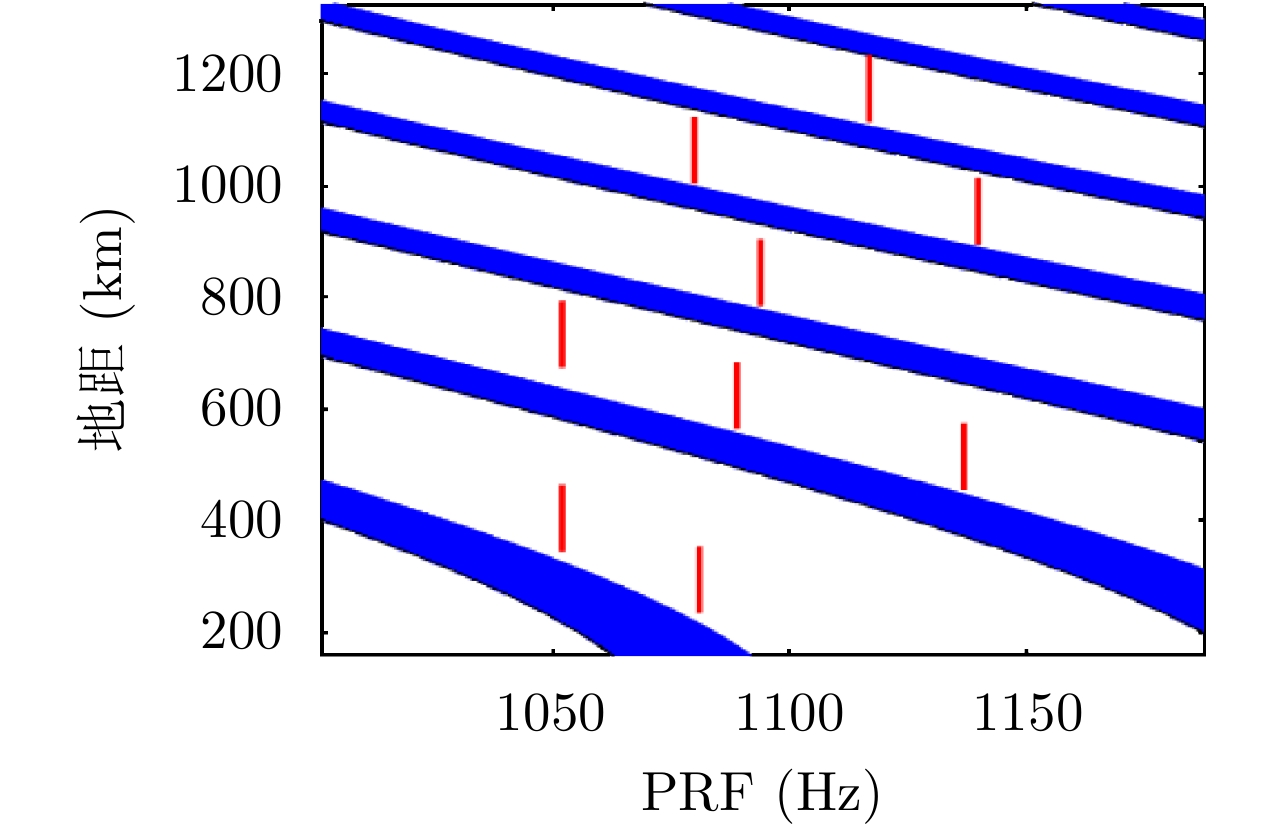
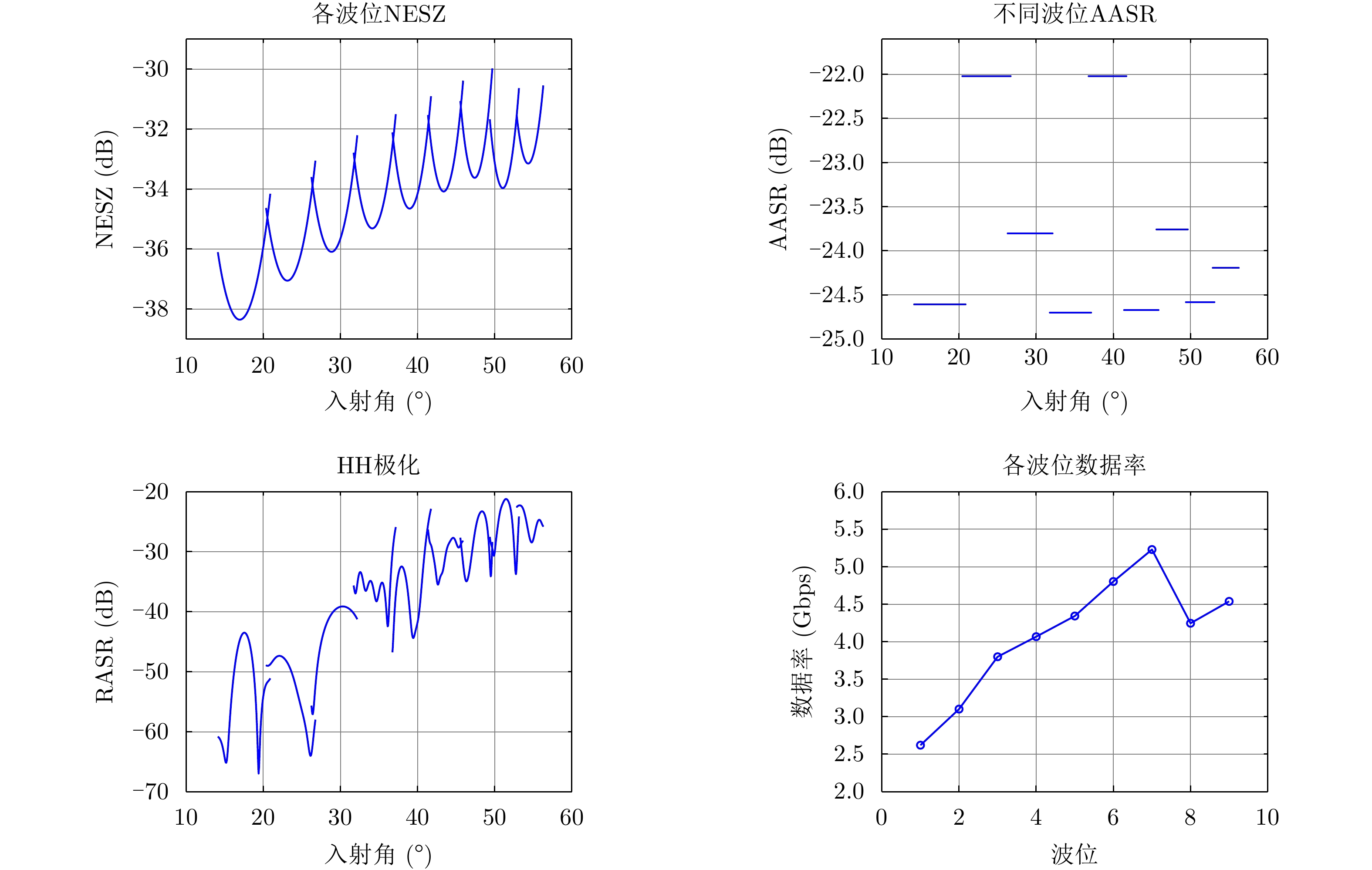
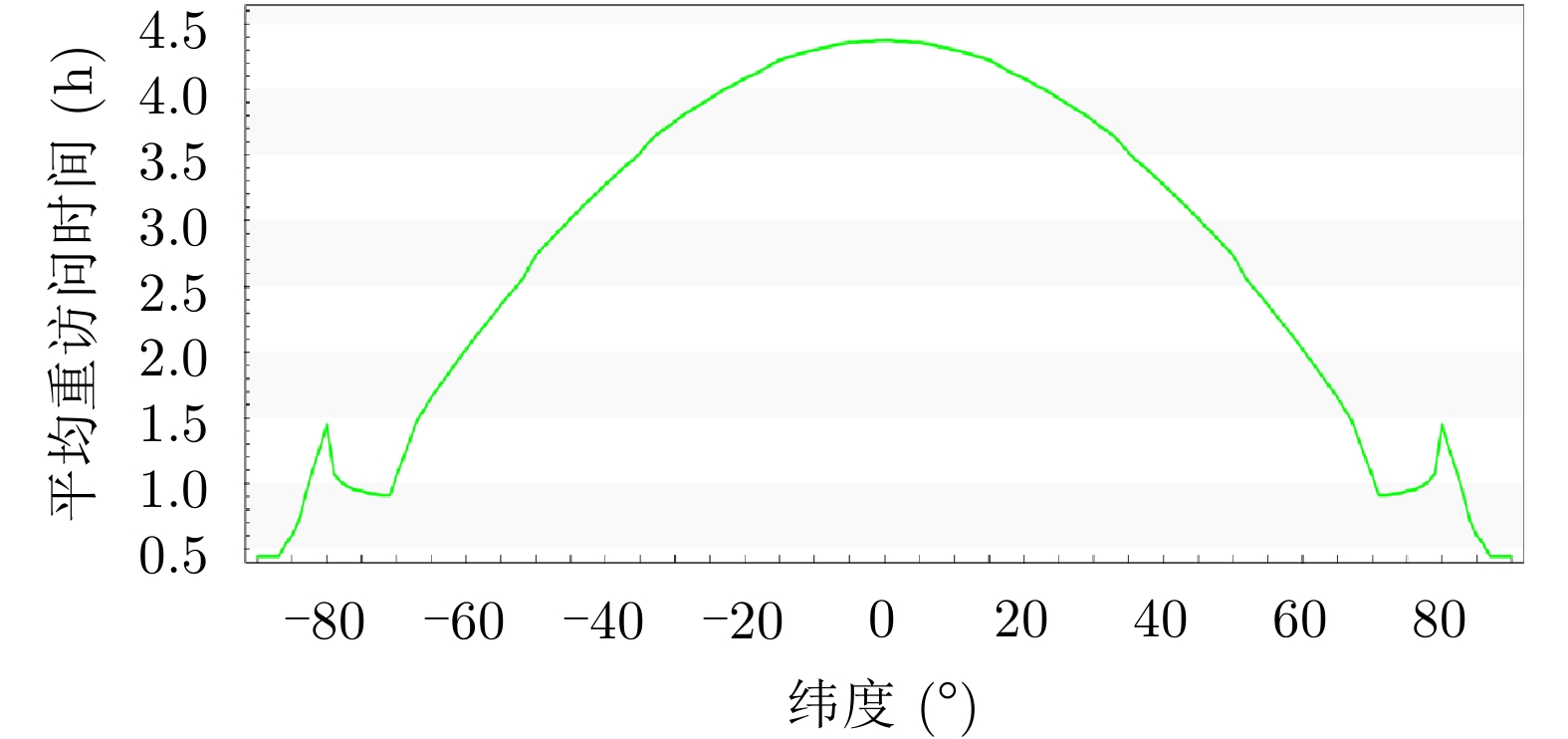
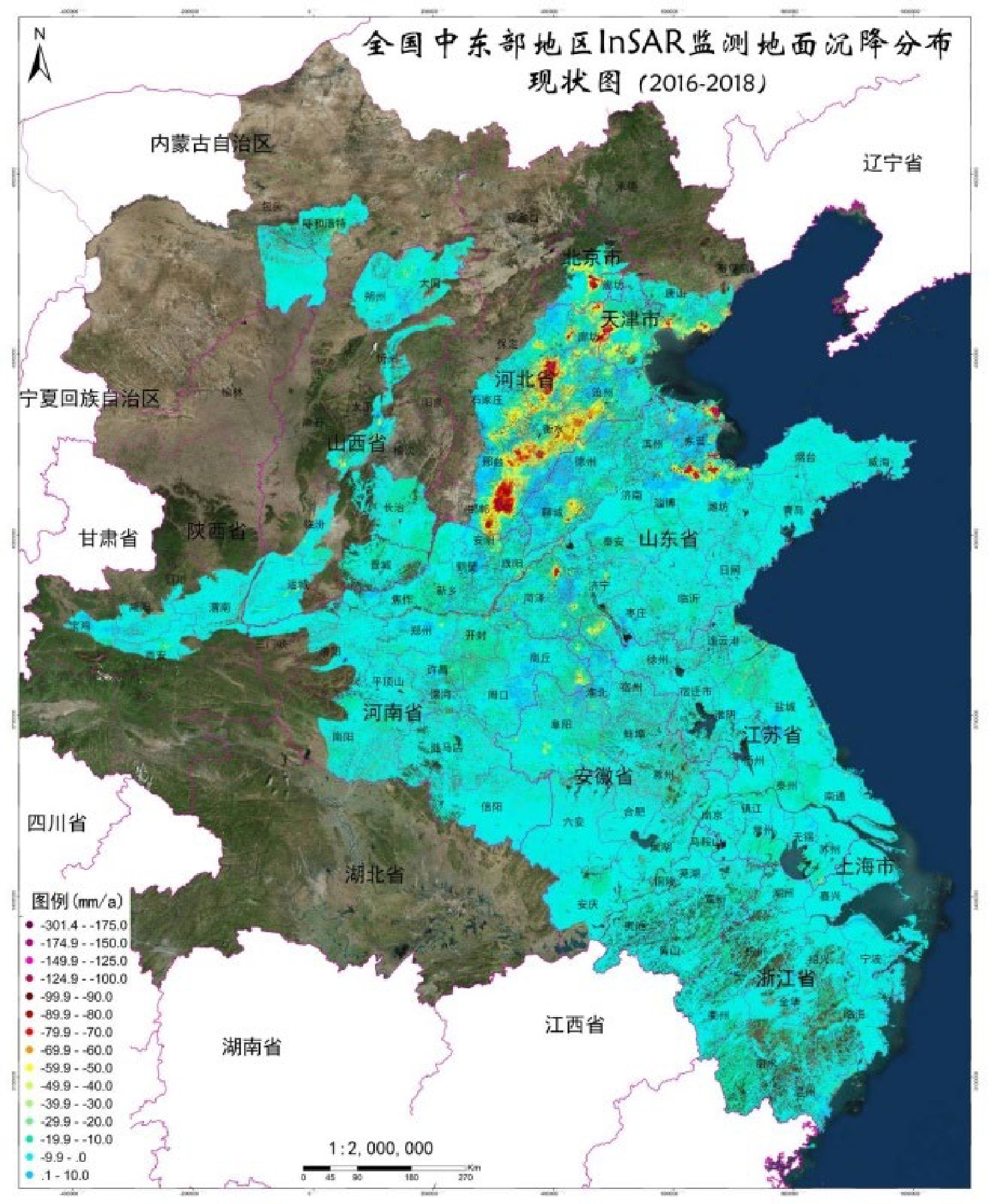
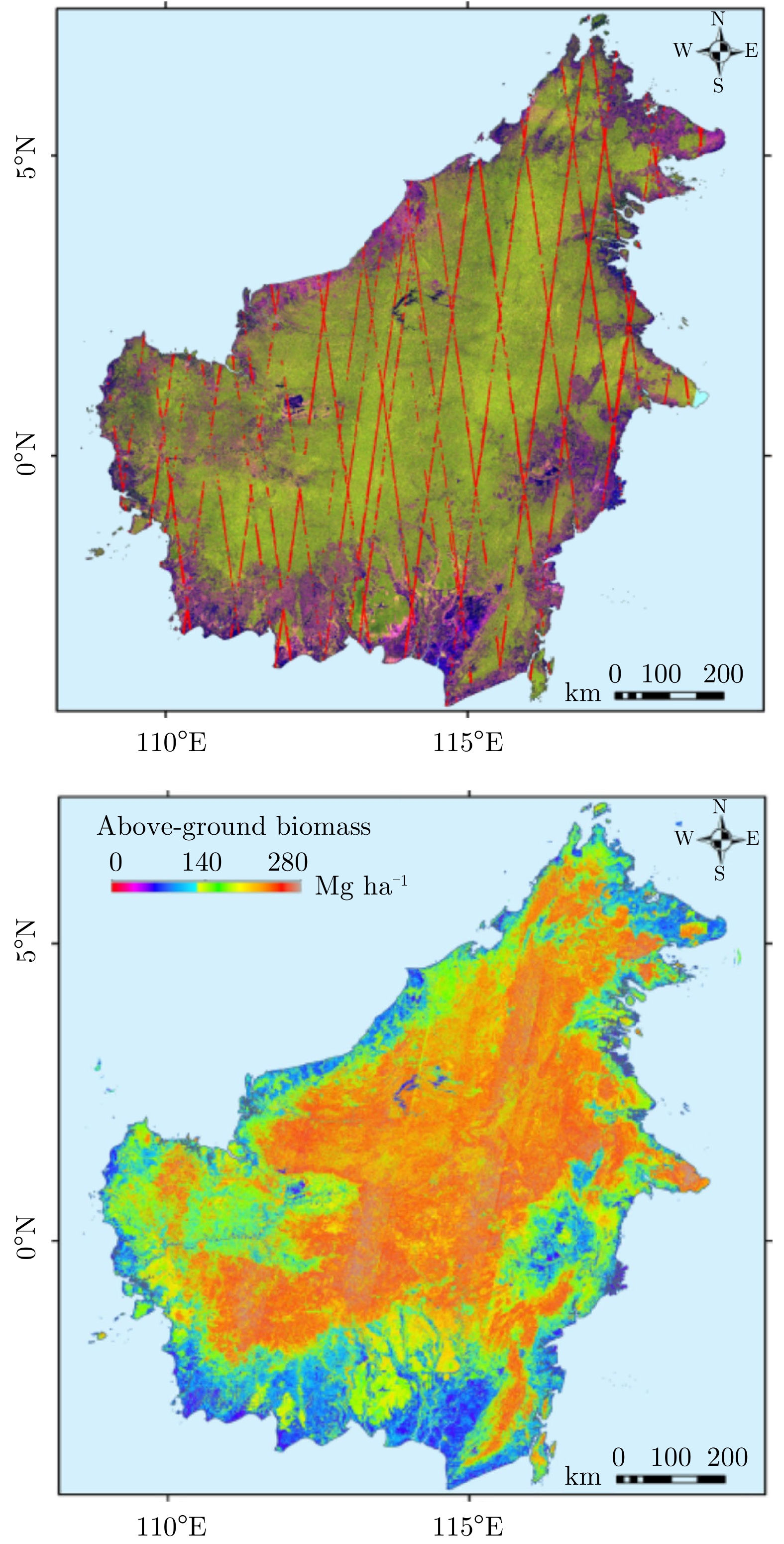
| [1] |
邓云凯, 禹卫东, 张衡, 等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
MOREIRA A, KRIEGER G, HAJNSEK I, et al. Tandem-L: A highly innovative bistatic SAR mission for global observation of dynamic processes on the earth’s surface[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2015, 3(2): 8–23. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2015.2437353 |
| [4] |
Rosen P. Planned data products and science processing paradigm for the proposed NASA-ISRO SAR mission[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2014, 5(5): 486–499.
|
| [5] |
MOTOHKA T, KANKAKU Y, MIURA S, et al. Alos-4 L-band SAR mission and observation[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 5271–5273. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898169. |
| [6] |
KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 260–264. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.832700 |
| [7] |
KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. SAR signal reconstruction from non-uniform displaced phase centre sampling[C]. IGARSS 2004-2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 1763–1766.
|
| [8] |
JING Wei, XING Mengdao, QIU Chengwei, et al. Unambiguous reconstruction and high-resolution imaging for multiple-channel SAR and airborne experiment results[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(1): 102–106. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2008825 |
| [9] |
ZHAO Shuo, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Modifications on multichannel reconstruction algorithm for SAR processing based on periodic nonuniform sampling theory and nonuniform fast Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(11): 4998–5006. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2421303 |
| [10] |
FAN Feng, DANG Hongxing, TAN Xiaomin, et al. An improved scheme of Digital Beam-Forming in elevation for spaceborne SAR[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–6.
|
| [11] |
WANG Wei, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. An improved processing scheme of digital beam-forming in elevation for reducing resource occupation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 309–313. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2508098 |
| [12] |
GEBERT N, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Digital beamforming on receive: Techniques and optimization strategies for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 564–592. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089542 |
| [13] |
ZHAO Qingchao, ZHANG Yi, WANG Wei, et al. On the frequency dispersion in DBF SAR and digital scalloped beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(5): 3619–3632. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958863 |
| [14] |
ZHOU Yashi, WANG Wei, CHEN Zhen, et al. Digital Beamforming synthetic aperture radar (DBSAR): Experiments and performance analysis in support of 16-channel airborne X-band SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6784–6798. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027691 |
| [15] |
WANG R, WANG Wei, SHAO Yunfeng, et al. First bistatic demonstration of digital beamforming in elevation with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 842–849. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2467176 |
| [16] |
HOU Wentao, ZHAO Fengjun, LIU Xiuqing, et al. A unified framework for comparing the classification performance between quad-, compact-, and dual-polarimetric SARs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5204814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3067314 |
| [17] |
ZHAO Pengfei, DENG Yunkai, WANG Wei, et al. Ambiguity suppression based on joint optimization for multichannel hybrid and ± π/4 Quad-Pol SAR systems[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(10): 1907. doi: 10.3390/rs13101907 |
| [18] |
LI Peng, ZHAO Fengjun, LIU Dacheng, et al. First demonstration of hybrid Quad-Pol SAR based on P-band airborne experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–16. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3084959 |
| [19] |
FREEMAN A, JOHNSON W T K, HUNEYCUTT B, et al. The “Myth” of the minimum SAR antenna area constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 320–324. doi: 10.1109/36.823926 |
| [20] |
邓云凯. 星载高分辨率宽幅SAR成像技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020.
DENG Yunkai. Spaceborne High-Resolution Wide-Swath SAR Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020.
|
| [21] |
YOUNIS M, ROMMEL T, BORDONI F, et al. On the pulse extension loss in digital beamforming SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1436–1440. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2406815 |
| [22] |
SUESS M and WIESBECK W. Side-looking synthetic aperture radar system[Z]. Euro Patent EP 1 241 487 A1, 2001.
|
| [23] |
PATYUCHENKO A, ROMMEL T, LASKOWSKI P, et al. Digital beam-forming reconfigurable radar system demonstrator[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 1541–1544. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351103. |
| [24] |
RINCON R F, VEGA M A, BUENFIL M, et al. NASA’s L-band digital beamforming synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3622–3628. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2157971 |
| [25] |
洪文. 基于混合极化架构的极化SAR: 原理与应用(中英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074HONG Wen. Hybrid-polarity architecture based polarimetric SAR: Principles and applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074 |
| [26] |
LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009.
|
| [27] |
RANEY R K, FREEMAN A, and JORDAN R L. Improved range ambiguity performance in Quad-Pol SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(2): 349–356. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2121075 |
| [28] |
SOUYRIS J C and MINGOT S. Polarimetry based on one transmitting and two receiving polarizations: The π/4 mode[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, Canada, 2002: 629–631. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2002.1025127. |
| [29] |
SOUYRIS J C, IMBO P, FJORTOFT R, et al. Compact polarimetry based on symmetry properties of geophysical media: The π/4 mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 634–646. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.842486 |
| [30] |
OHKI M and SHIMADA M. Large-area land use and land cover classification with quad, compact, and dual polarization SAR data by PALSAR-2[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5550–5557. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2819694 |
| [31] |
DABBOOR M, MONTPETIT B, and HOWELL S. Assessment of the high resolution SAR mode of the RADARSAT constellation mission for first year ice and multiyear ice characterization[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 594. doi: 10.3390/rs10040594 |
| [32] |
RANEY R K. Hybrid dual-polarization synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(13): 1521. doi: 10.3390/rs11131521 |
| [33] |
RANEY R K. Comparing compact and quadrature polarimetric SAR performance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 861–864. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2550863 |
| [34] |
YANG Ce, OU Naiming, DENG Yunkai, et al. Pattern synthesis algorithm for range ambiguity suppression in the Lt-1 mission via sequential convex optimizations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099132 |
| [35] |
ISHIMARU A, KUGA Y, LIU Jun, et al. Ionospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar at 100 MHz to 2 GHz[J]. Radio Science, 1999, 34(1): 257–268. doi: 10.1029/1998RS900021 |
| [36] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004: 660.
|
| [37] |
BAMLER R and EINEDER M. Accuracy of differential shift estimation by correlation and split-bandwidth interferometry for wideband and delta-k SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(2): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.843203 |
| [38] |
JAKOWATZ C V JR, EICHEL P H, and GHIGLIA D C. Autofocus of SAR imagery degraded by ionospheric-induced phase errors[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 1101, Millimeter Wave and Synthetic Aperture Radar, Orlando, USA, 1989: 46–52. doi: 10.1117/12.960513. |
| [39] |
KNEPP D L and GROVES K M. The effect of ionospheric scintillation on phase gradient autofocus processing of synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2011 XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 2013: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/URSIGASS.2011.6050878. |
| [40] |
WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752 |
| [41] |
FREEMAN A. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to Faraday rotation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(8): 1617–1624. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.830161 |
| [42] |
QUEGAN S and LOMAS M R. The impact of system effects on estimates of faraday rotation from synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(8): 4284–4298. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2395076 |
| [43] |
JEHLE M, RUEGG M, ZUBERBUHLER L, et al. Measurement of ionospheric faraday rotation in simulated and real spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1512–1523. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2004710 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
HENDERSON F M and LEWIS A J. Radar detection of wetland ecosystems: A review[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2008, 29(20): 5809–5835. doi: 10.1080/01431160801958405 |
| [46] |
LI Zengyuan, ZHAO Lei, LI Kun, et al. A survey of developments on forest resources monitoring technology of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2020, 12(2): 150–158. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.002 |
| [47] |
HAYASHI M, MOTOHKA T, and SAWADA Y. Aboveground biomass mapping using ALOS-2/PALSAR-2 time-series images for Borneo's forest[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(12): 5167–5177. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2957549 |
| [48] |
JIA Hongying, WANG Yingjie, GE Daqing, et al. Improved offset tracking for predisaster deformation monitoring of the 2018 Jinsha River landslide (Tibet, China)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 247: 111899. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111899 |
| [49] |
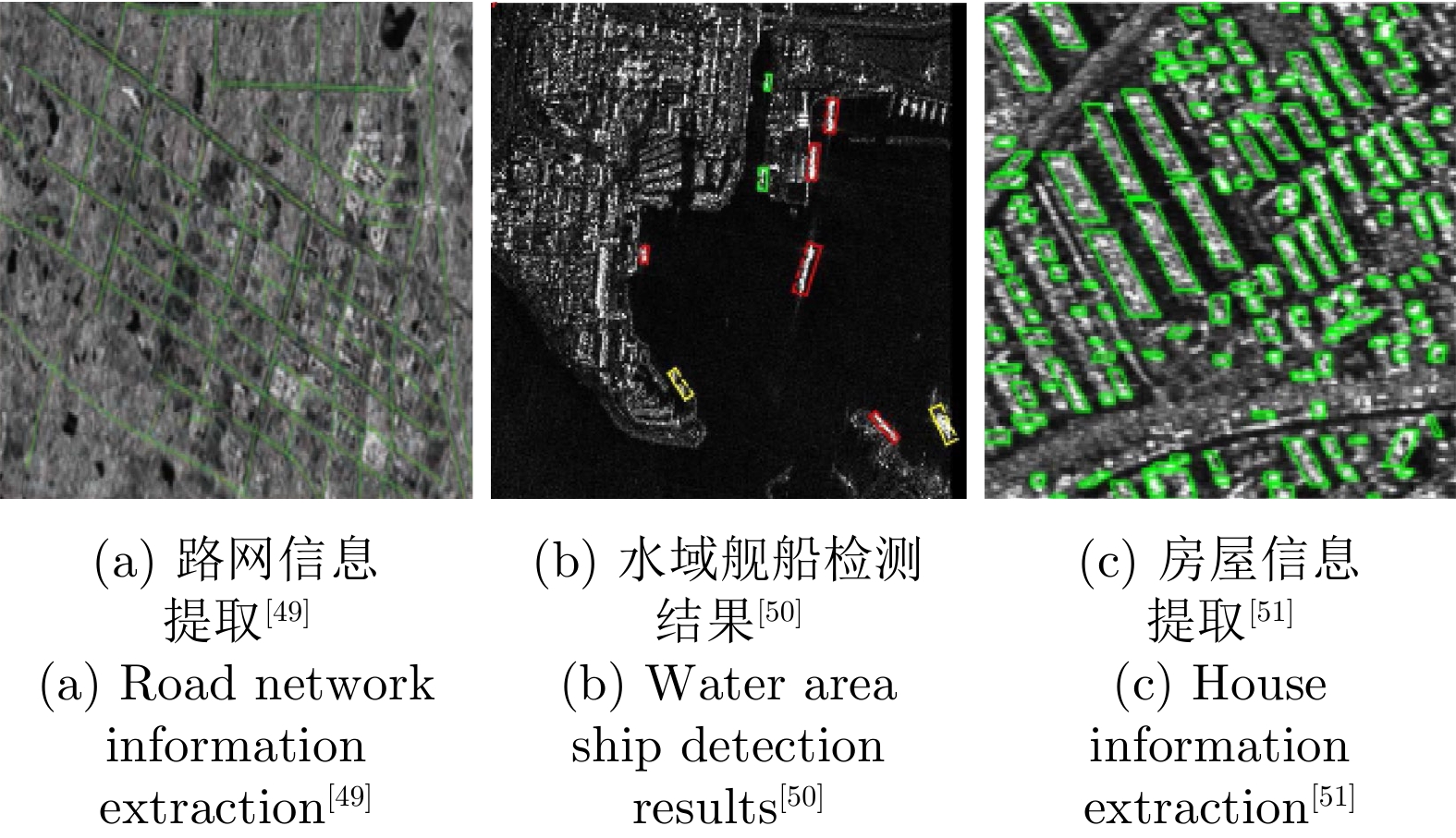
LU Pingping, DU Kangning, YU Weidong, et al. Feature fusion based road extraction for HJ-1-C SAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(3): 352–360. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13059 |
| [50] |
YANG Rong, PAN Zhenru, JIA Xiaoxue, et al. A novel CNN-based detector for ship detection based on rotatable bounding box in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 1938–1958. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3049851 |
| [51] |
CHEN Shanshan, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Automatic recognition of isolated buildings on single-aspect SAR image using range detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(2): 219–223. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2327125 |
| [52] |
LIU Qian, YANG Le, LIU Qinhuo, et al. Review of forest above ground biomass inversion methods based on remote sensing technology[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(1): 62–74. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20154108 |
| [53] |
KRAUS T, KRIEGER G, BACHMANN M, et al. Spaceborne demonstration of distributed SAR imaging with TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(11): 1731–1735. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2907371 |
| [54] |
TOPORKOV J V, PERKOVIC D, FARQUHARSON G, et al. Sea surface velocity vector retrieval using dual-beam interferometry: First demonstration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(11): 2494–2502. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.848603 |
| [55] |
FRASIER S J and CAMPS A J. Dual-beam interferometry for ocean surface current vector mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(2): 401–414. doi: 10.1109/36.905248 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: