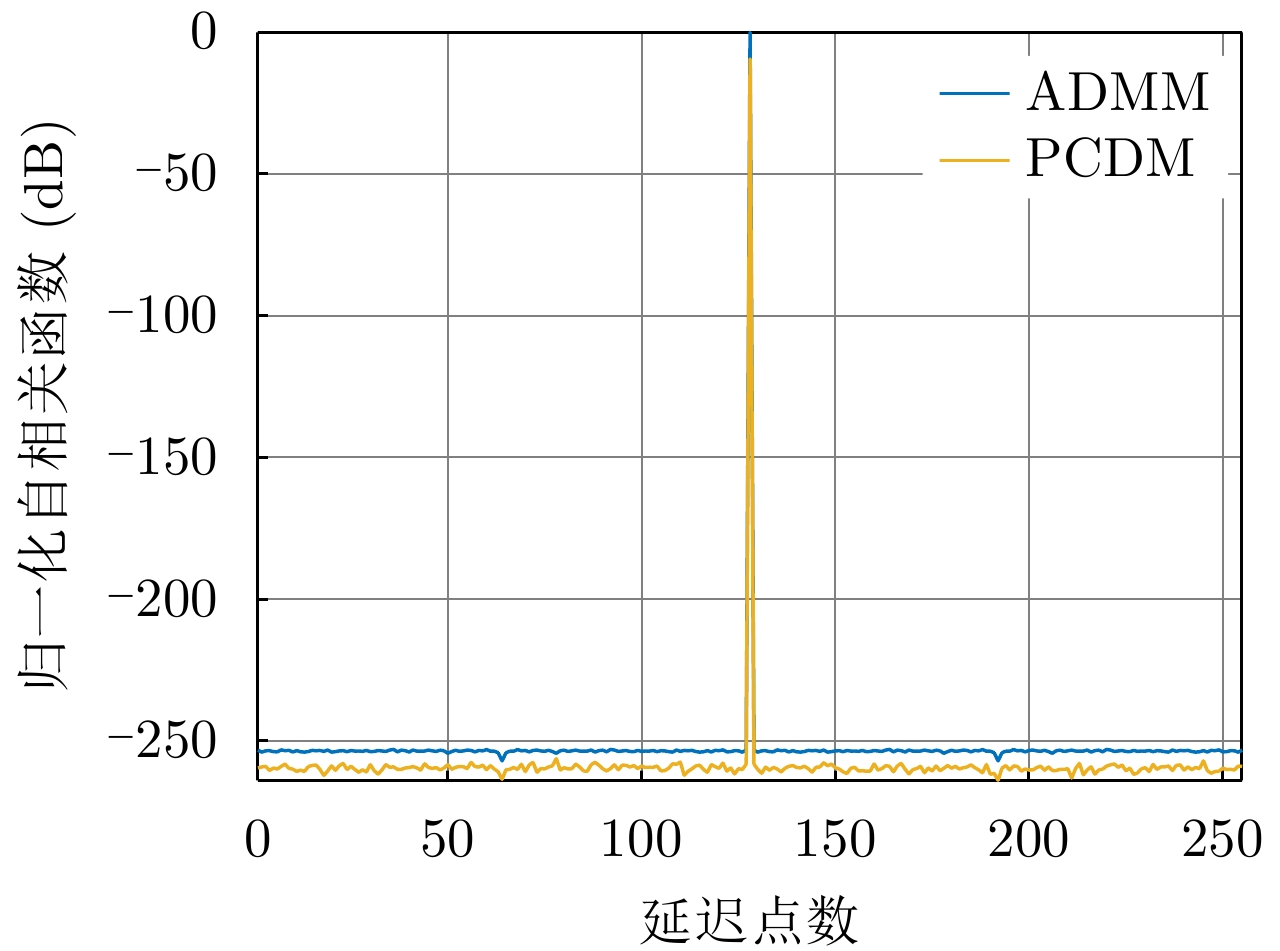
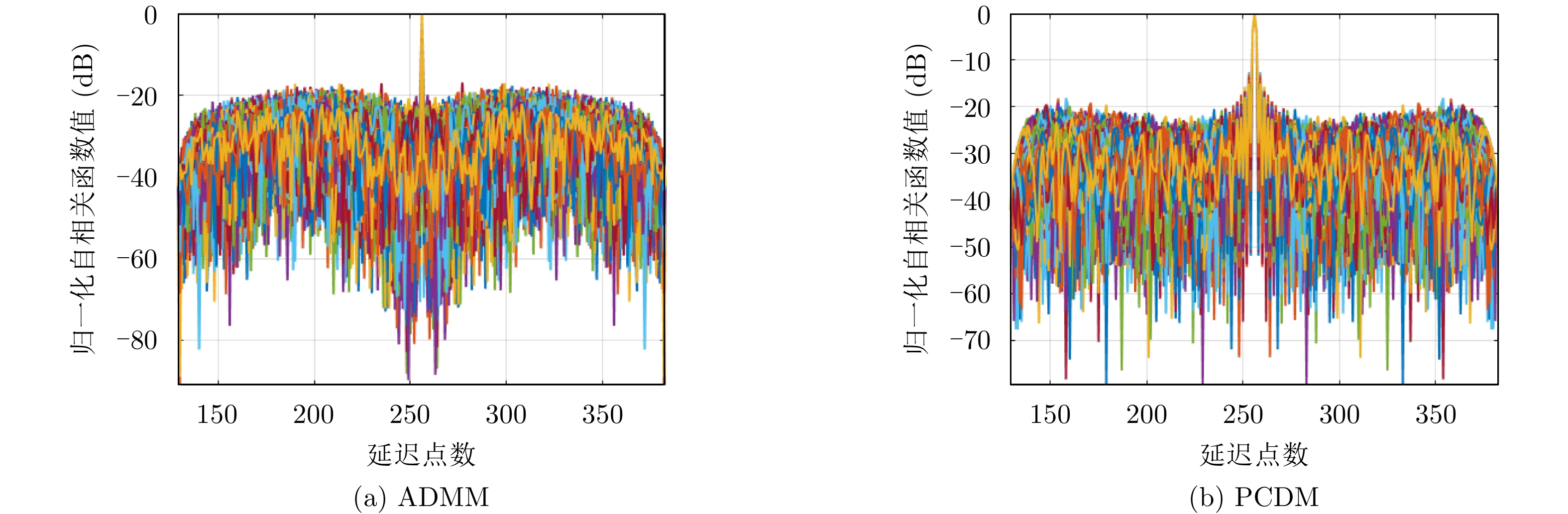
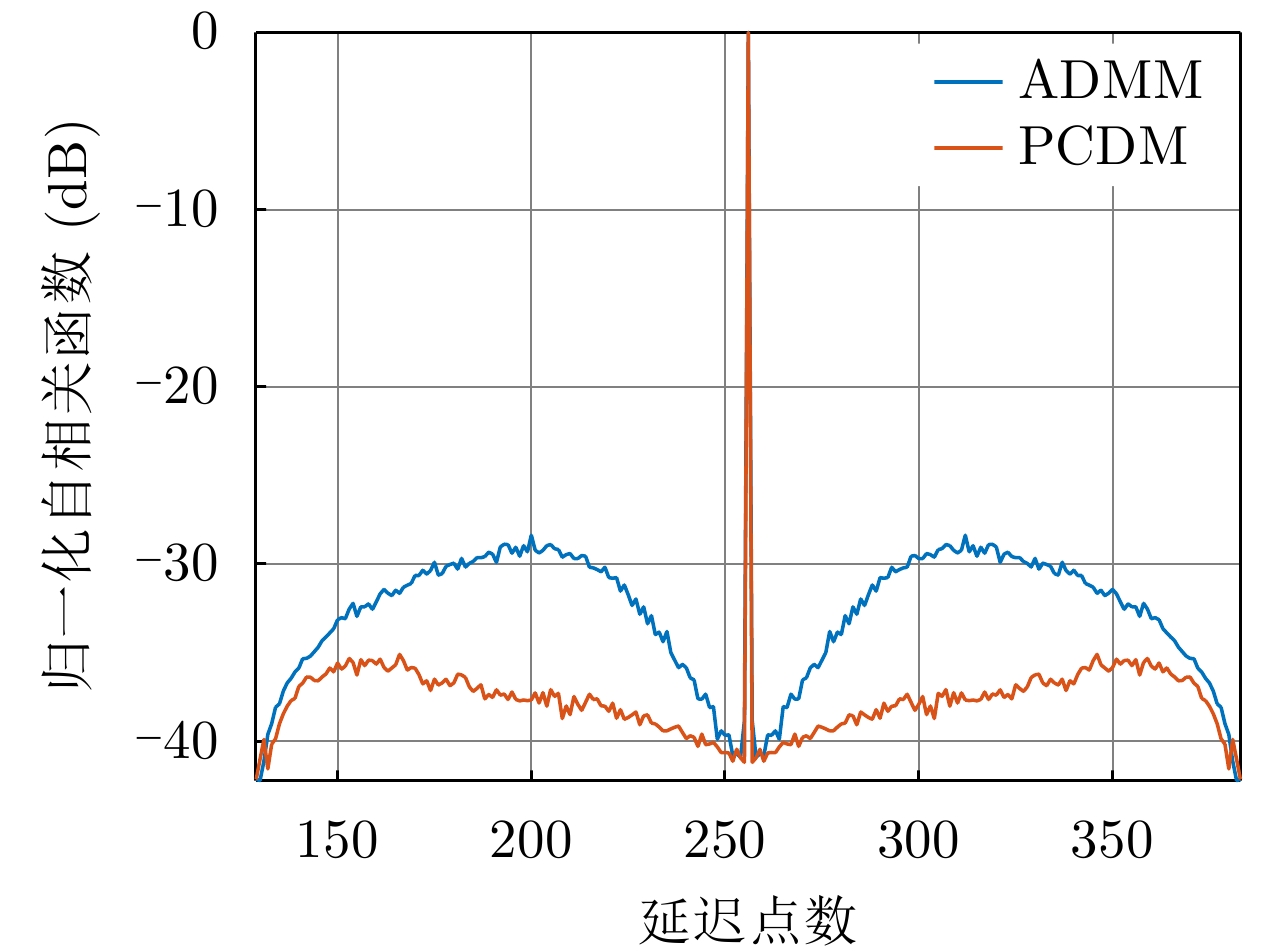
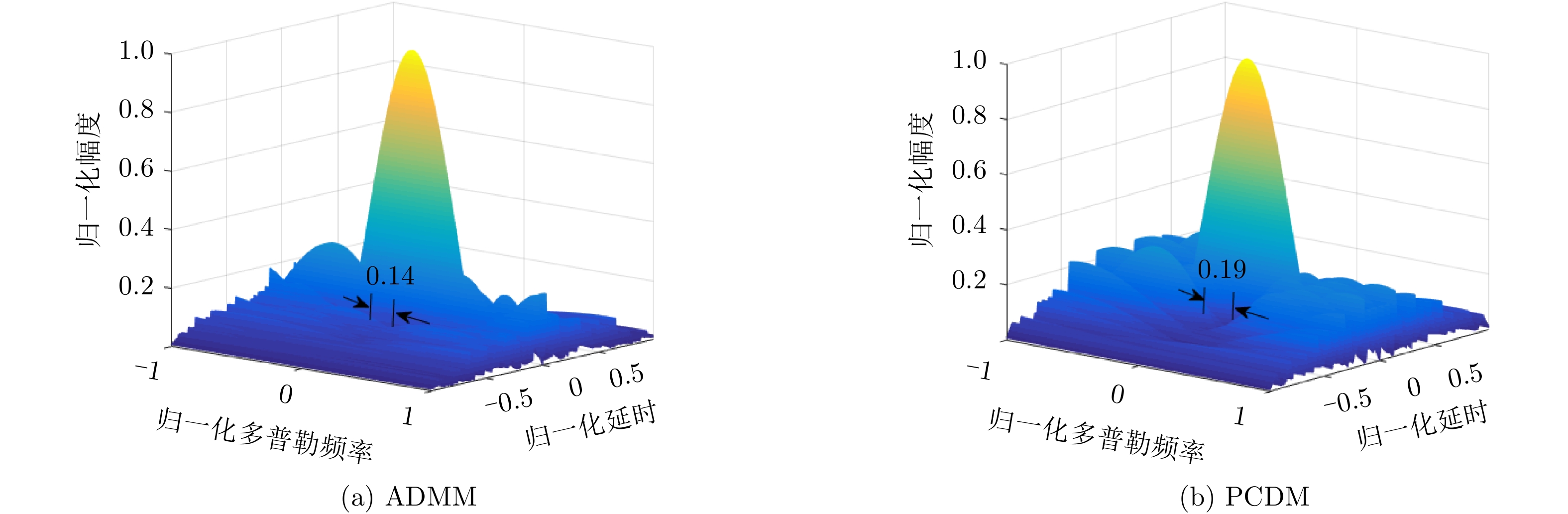
| [1] |
GINI F, DE MAIO A, and PATTON L. Waveform Design and Diversity for Advanced Radar Systems[M]. London, UK: Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2012: 5.
|
| [2] |
SKOLNIK M I. Introduction to Radar Systems[M]. 3rd ed. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill Education (Asia) Co. , 2007. 10–56.
|
| [3] |
WANG Xinhai, ZHANG Gong, ZHANG Yu, et al. Design of spectrally compatible waveform with constant modulus for colocated multiple-input multiple-output radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(8): 1373–1388. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0009 |
| [4] |
DAVIS M E and PILLAI S U. Waveform diversity for ultra-wide band surveillance radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(9): 1226–1233. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0366 |
| [5] |
GOLAY M. A class of finite binary sequences with alternate auto-correlation values equal to zero (Corresp. )[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1972, 18(3): 449–450. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1972.1054797 |
| [6] |
BARKER R H. Group Synchronizing of Binary Digital Systems[M]. JACKSON W. Communication Theory. New York: Academic Press, 1953: 273–287.
|
| [7] |
GOLAY M. Sieves for low autocorrelation binary sequences[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1977, 23(1): 43–51. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1977.1055653 |
| [8] |
MERTENS S. Exhaustive search for low-autocorrelation binary sequences[J]. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 1996, 29(18): L473–L481. doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/29/18/005 |
| [9] |
KOCABAS S E and ATALAR A. Binary sequences with low aperiodic autocorrelation for synchronization purposes[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2003, 7(1): 36–38. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2002.807438 |
| [10] |
JEDWAB J. A survey of the merit factor problem for binary sequences[C]. Third International Conference on Sequences and Their Applications, Seoul, Korea, 2005: 30–55. doi: 10.1007/11423461_2. |
| [11] |
WANG S. Efficient heuristic method of search for binary sequences with good aperiodic autocorrelations[J]. Electronics Letters, 2008, 44(12): 731–732. doi: 10.1049/el:20081058 |
| [12] |
FRANK R. Polyphase codes with good nonperiodic correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1963, 9(1): 43–45. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1963.1057798 |
| [13] |
ZHANG N and GOLOMB S W. Polyphase sequence with low autocorrelations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(3): 1085–1089. doi: 10.1109/18.256535 |
| [14] |
NUNN C J and COXSON G E. Polyphase pulse compression codes with optimal peak and integrated sidelobes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 775–781. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089560 |
| [15] |
DE MAIO A, DE NICOLA S, HUANG Yongwei, et al. Design of phase codes for radar performance optimization with a similarity constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 610–621. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2008247 |
| [16] |
CUI Guolong, JING Ying, LU Shuping, et al. Dual-Use Unimodular Sequence Design via Frequency Nulling Modulation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018(6): 62470–62481. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2876644 |
| [17] |
SOLTANALIAN M and STOICA P. Computational design of sequences with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(5): 2180–2193. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2186134 |
| [18] |
STOICA P, HE Hao, and LI Jian. New algorithms for designing unimodular sequences with good correlation properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(4): 1415–1425. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2012562 |
| [19] |
STOICA P, HE Hao, and LI Jian. On designing sequences with impulse-like periodic correlation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2009, 16(8): 703–706. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2009.2021378 |
| [20] |
SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Optimization methods for designing sequences with low autocorrelation sidelobes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(15): 3998–4009. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2425808 |
| [21] |
BORWEIN P and FERGUSON R. Polyphase sequences with low autocorrelation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2005, 51(4): 1564–1567. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2004.842778 |
| [22] |
LIANG Junli, SO H C, LEUNG C S, et al. Waveform design with unit modulus and spectral shape constraints via Lagrange programming neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1377–1386. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2464178 |
| [23] |
LIANG Junli, SO H C, LI Jian, et al. Unimodular sequence design based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5367–5381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597123 |
| [24] |
BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 |
| [25] |
ZHANG Jindong, ZHU Daiyin, and ZHANG Gong. New antivelocity deception jamming technique using pulses with adaptive initial phases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2): 1290–1300. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494414 |
| [26] |
BONNANS J F, GILBERT J C, LEMARÉCHAL C, et al. Numerical Optimization: Theoretical and Practical Aspects[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006, 67–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-35447-5. |
| [27] |
TANG Liang, ZHU Yongfeng, and FU Qiang. Fast algorithm for designing periodic/aperiodic sequences with good correlation and stopband properties[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2018, 2018(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s13634-018-0579-z |
| [28] |
ESMAEILI-NAJAFABADI H, LEUNG H, and MOO P W. Unimodular waveform design with desired ambiguity function for cognitive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2489–2496. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2942411 |
| [29] |
GRANT M. CVX: MATLAB software for disciplined convex programming[EB/OL]. http://cvxr.com/cvx, 2020. |
| [30] |
PEAUCELLE D, HENRION D, LABIT Y, et al. User’s guide for SEDUMI interface 1.04[J]. Siam Journal on Optimization - SIAMJO, 2002.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: