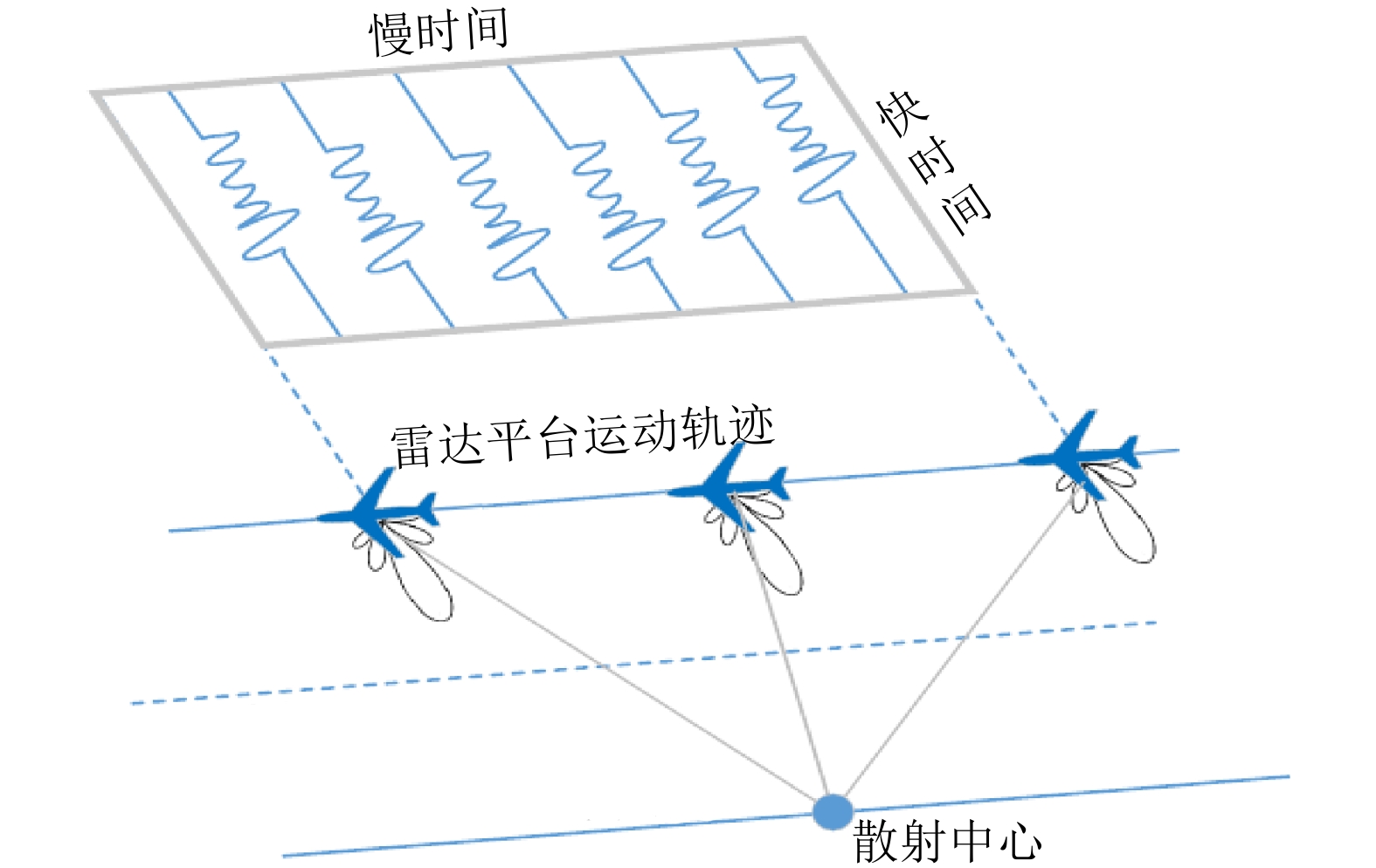
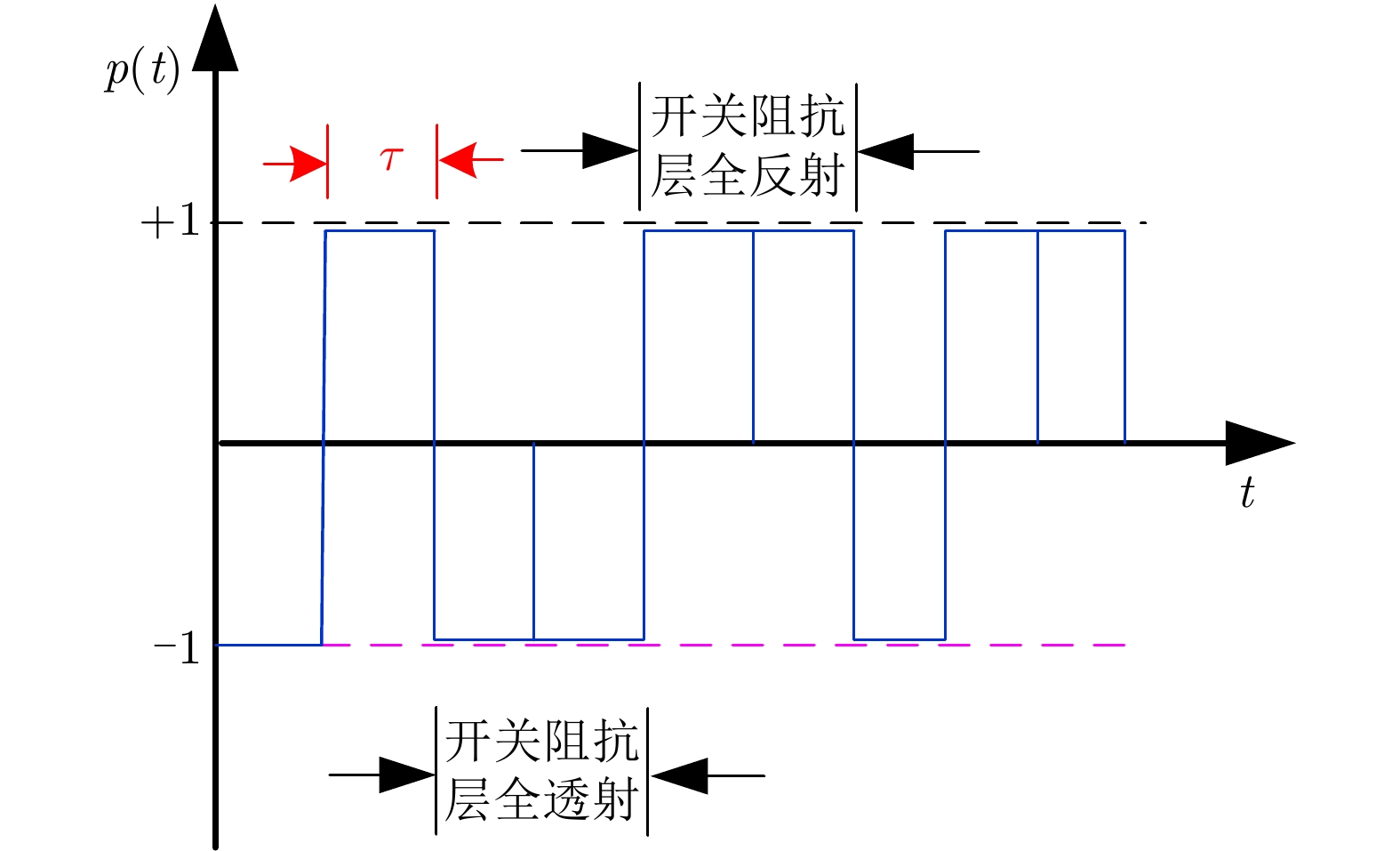
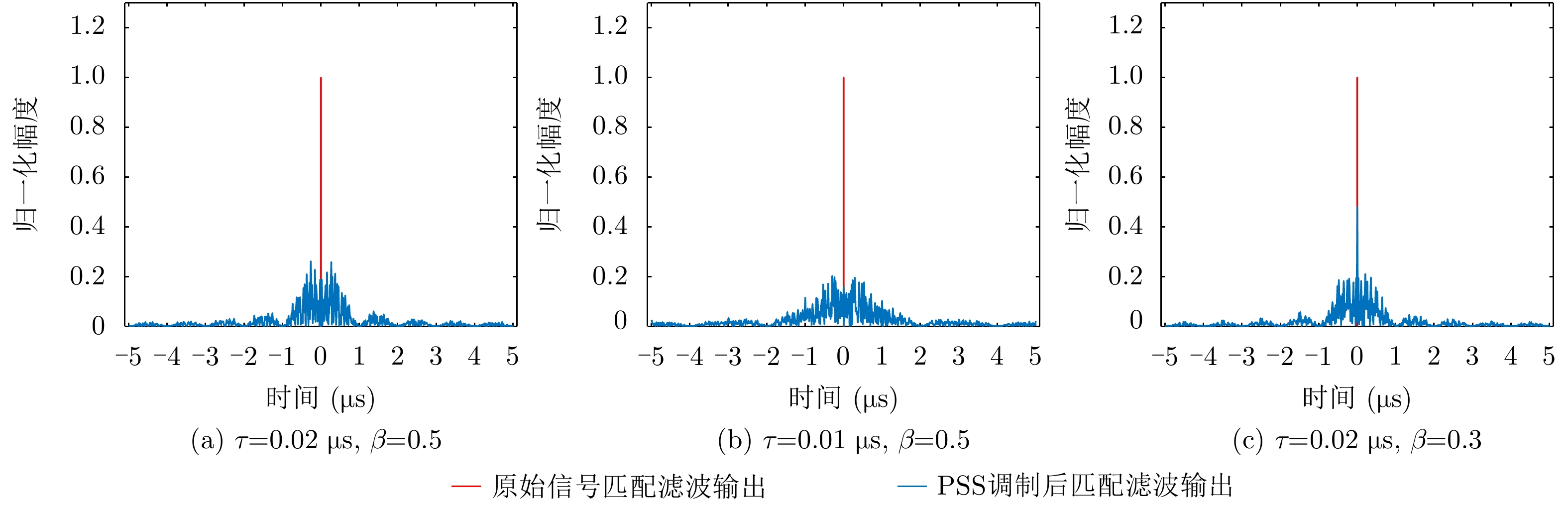
| [1] |
CHEN V C, LI F, HO S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402 |
| [2] |
ZHUANG Zhaowen, LIU Yongxiang, and LI Xiang. The achievements of target characteristic with micro-motion[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 35(3): 520–525. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2007.03.028 |
| [3] |
WU Xiaofang, LIU Yang, WANG Xuesong, et al. Analysis of SAR imaging characteristics of targets with rotational micro-motion[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(4): 1181–1189. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2010.04.039 |
| [4] |
BAI Xueru, SUN Guangcai, ZHOU Feng, et al. A novel ISAR jamming method based on rotating angular reflectors[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2008, 23(5): 867–872. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2008.05.019 |
| [5] |
PENDRY J B. Focus issue: Negative refraction and metamaterials[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(7): 639. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.000639 |
| [6] |
YEN T J, PADILLA W J, FANG N, et al. Terahertz magnetic response from artificial materials[J]. Science, 2004, 303(5663): 1494–1496. doi: 10.1126/science.1094025 |
| [7] |
PADILLA W J. Group theoretical description of artificial electromagnetic metamaterials[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(4): 1639–1646. doi: 10.1364/OE.15.001639 |
| [8] |
TENNANT A and CHAMBERS B. Adaptive radar absorbing structure with PIN diode controlled active frequency selective surface[J]. Smart materials and Structures, 2004, 13(1): 122–125. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/13/1/013 |
| [9] |
HUANG Cheng, ZHAO Bo, SONG Jiakun, et al. Active transmission/absorption frequency selective surface with dynamical modulation of amplitude[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(6): 3593–3598. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3037813 |
| [10] |
CHAMBERS B and TENNANT A. The phase-switched screen[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 2004, 46(6): 23–27. doi: 10.1109/MAP.2004.1396733 |
| [11] |
RAMACCIA D, SOUNAS D L, ALÙ A, et al. Phase-induced frequency conversion and Doppler effect with time-modulated metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(3): 1607–1617. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2952469 |
| [12] |
SAIKIA M, SRIVASTAVA K V, and RAMAKRISHNA A S. Frequency-shifted reflection of electromagnetic waves using a time-modulated active tunable frequency-selective surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(4): 2937–2944. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2951494 |
| [13] |
ZHAO Jie, YANG Xi, DAI Junyan, et al. Programmable time-domain digital-coding metasurface for non-linear harmonic manipulation and new wireless communication systems[J]. National Science Review, 2019, 6(2): 231–238. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy135 |
| [14] |
JIA Yongtao, LIU Ying, GUO Y J, et al. A dual-patch polarization rotation reflective surface and its application to ultra-wideband RCS reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 65(6): 3291–3295. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2694879 |
| [15] |
ZAKER R and SADEGHZADEH A. A low-profile design of polarization rotation reflective surface for wideband RCS reduction[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(9): 1794–1798. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2930130 |
| [16] |
CUI Tiejun, QI Meiqing, WAN Xiang, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.99 |
| [17] |
ZHANG Lei, CHEN Xiaoqing, LIU Shuo, et al. Space-time-coding digital metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4334. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06802-0 |
| [18] |
杨欢欢, 曹祥玉, 高军, 等. 可重构电磁超表面及其应用研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 206–219. doi: 10.12000/JR20137YANG Huanhuan, CAO Xiangyu, GAO Jun, et al. Recent advances in reconfigurable metasurfaces and their applications[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 206–219. doi: 10.12000/JR20137 |
| [19] |
LUO Yong, KIKUTA K, HAN Zhengli, et al. An active metamaterial antenna with mems-modulated scanning radiation beams[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2016, 37(7): 920–923. doi: 10.1109/LED.2016.2565559 |
| [20] |
BRYANT A T, LU Liqing, SANTI E, et al. Physical modeling of fast p-i-n diodes with carrier lifetime zoning, Part I: Device model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electrons, 2008, 23(1): 189–197. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2007.911823 |
| [21] |
XU Letao, FENG Dejun, and WANG Xuesong. Matched-filter properties of linear-frequency-modulation radar signal reflected from a phase-switched screen[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(2): 318–324. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0182 |
| [22] |
XU Letao, FENG Dejun, and WANG Xuesong. High-resolution range profile deception method based on phase-switched screen[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 1665–1668. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2521778 |
| [23] |
WANG Junjie, FENG Dejun, XU Zhiming, et al. Time-domain digital-coding active frequency selective surface absorber/reflector and its imaging characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(6): 3322–3331. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3037757 |
| [24] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 123–134.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technique[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 123–134.
|
| [25] |
YASIR S, 杨国敏, 徐丰. 四叶草形超宽带漫散射编码超表面[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 382–390. doi: 10.12000/JR21061YASIR S, YANG Guomin, and XU Feng. A four-leaf clover-shaped coding metasurface for ultra-wideband diffusion-like scattering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 382–390. doi: 10.12000/JR21061 |
| [26] |
张然, 冯德军, 徐乐涛. 基于Salisbury屏的二面角设计及其极化特性分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 658–665. doi: 10.12000/JR16055ZHANG Ran, FENG Dejun, and XU Letao. Design and polarization characteristics analysis of dihedral based on Salisbury screen[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 658–665. doi: 10.12000/JR16055 |
| [27] |
WEI Yue, SHEN Gangxiang, and BOSE S K. Span-restorable elastic optical networks under different spectrum conversion capabilities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2014, 63(2): 401–411. doi: 10.1109/TR.2014.2313806 |
| [28] |
TENNANT A. Reflection properties of a phase modulating planar screen[J]. Electronics Letters, 1997, 33(21): 1768–1769. doi: 10.1049/el:19971160 |
| [29] |
CHAMBERS B and TENNANT A. Reflection of radar signals from multiple phase-modulated surfaces[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2007, 1(2): 142–148. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20060078 |
| [30] |
SHULMAN N and FEDER M. Random coding techniques for nonrandom codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1999, 45(6): 2101–2104. doi: 10.1109/18.782147 |
| [31] |
TAI Ning, CUI Kaibo, WANG Chao, et al. The design of a novel coherent noise jammer against LFM radar[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2016, 13(21): 1–12. doi: 10.1587/elex.13.20160924 |
| [32] |
WU Qihua, LIU Xiaobin, LIU Jin, et al. A radar imaging method using nonperiodic interrupted sampling linear frequency modulation signal[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(20): 8294–8302. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2865531 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: