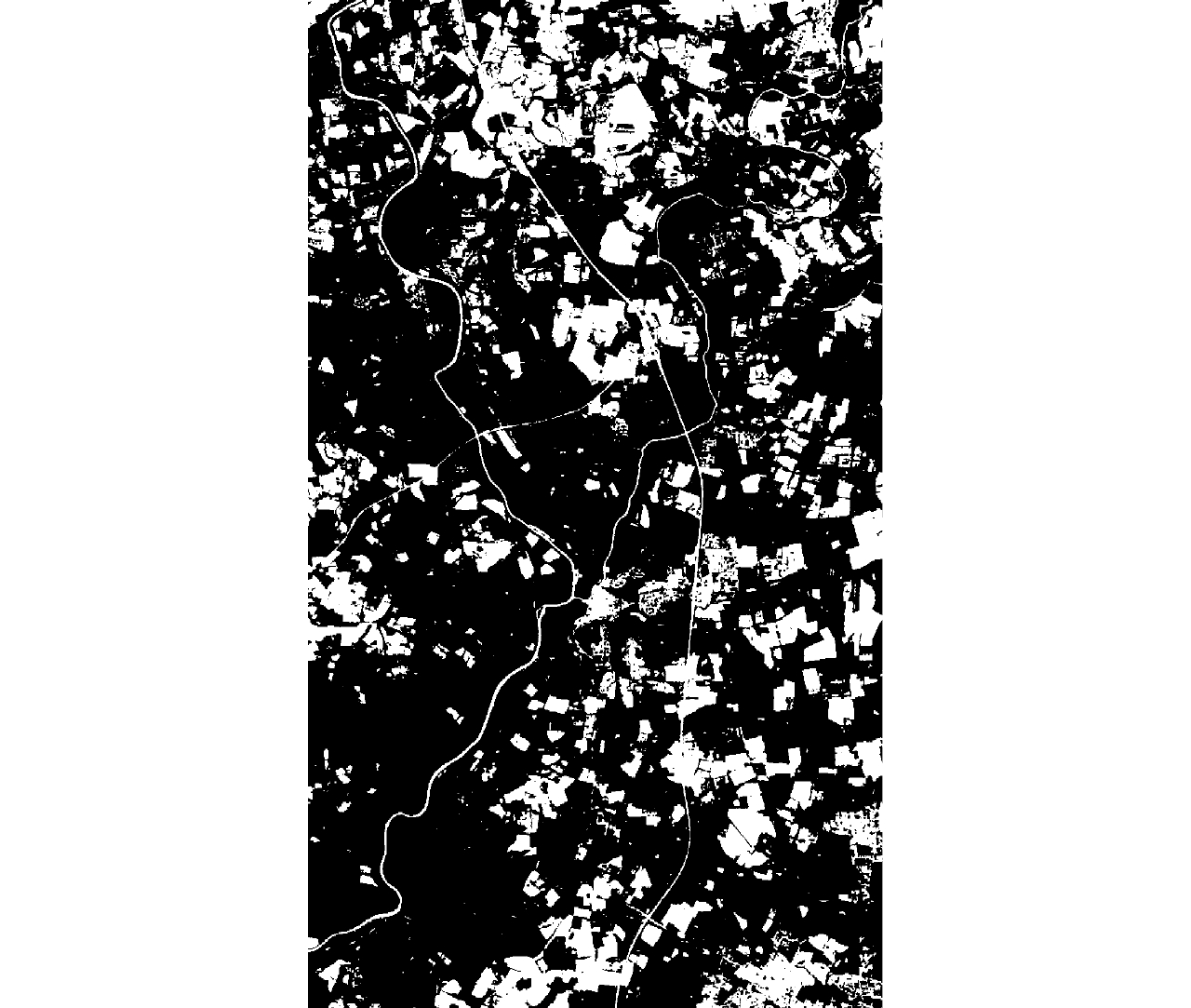
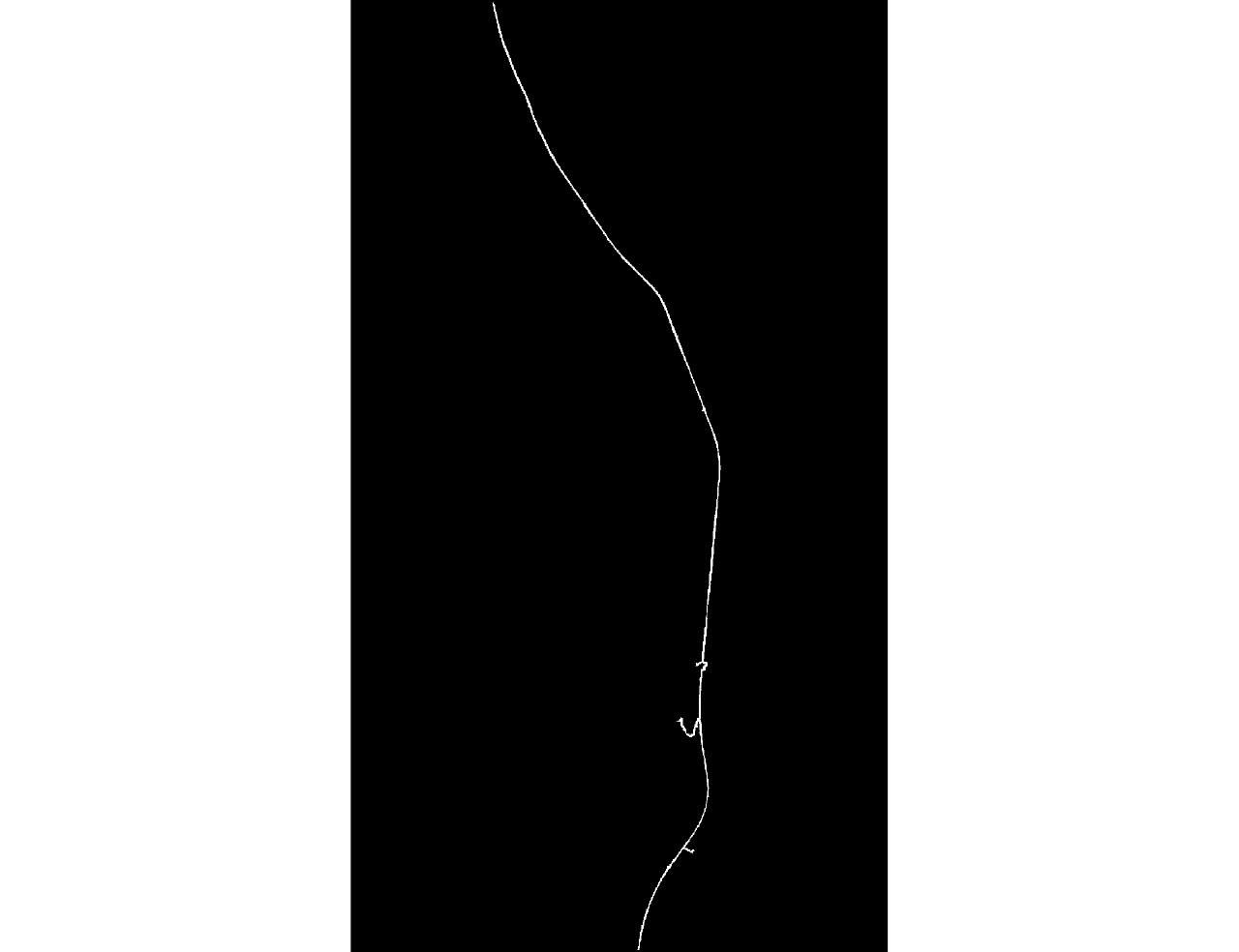
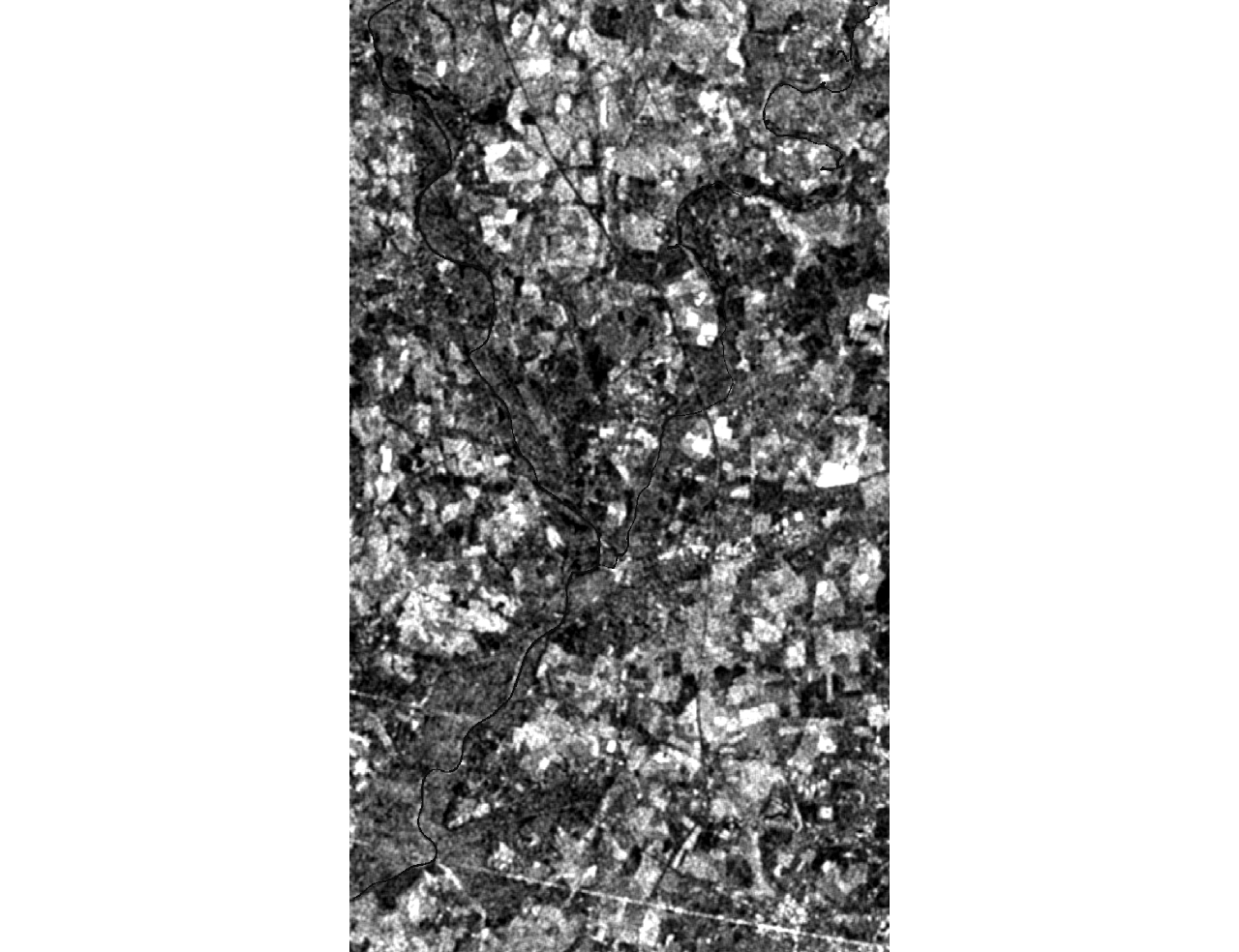
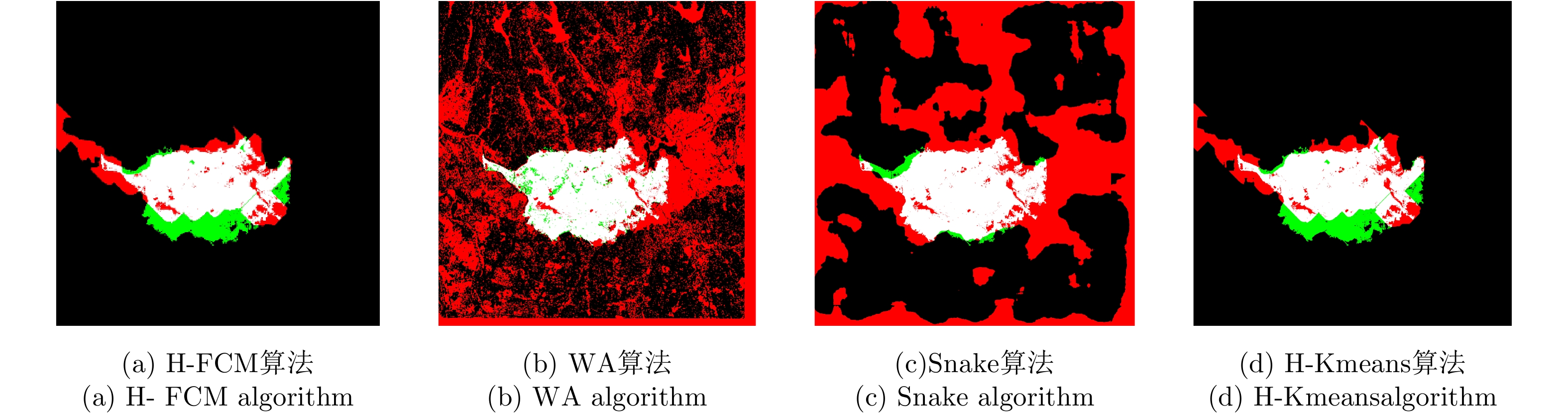
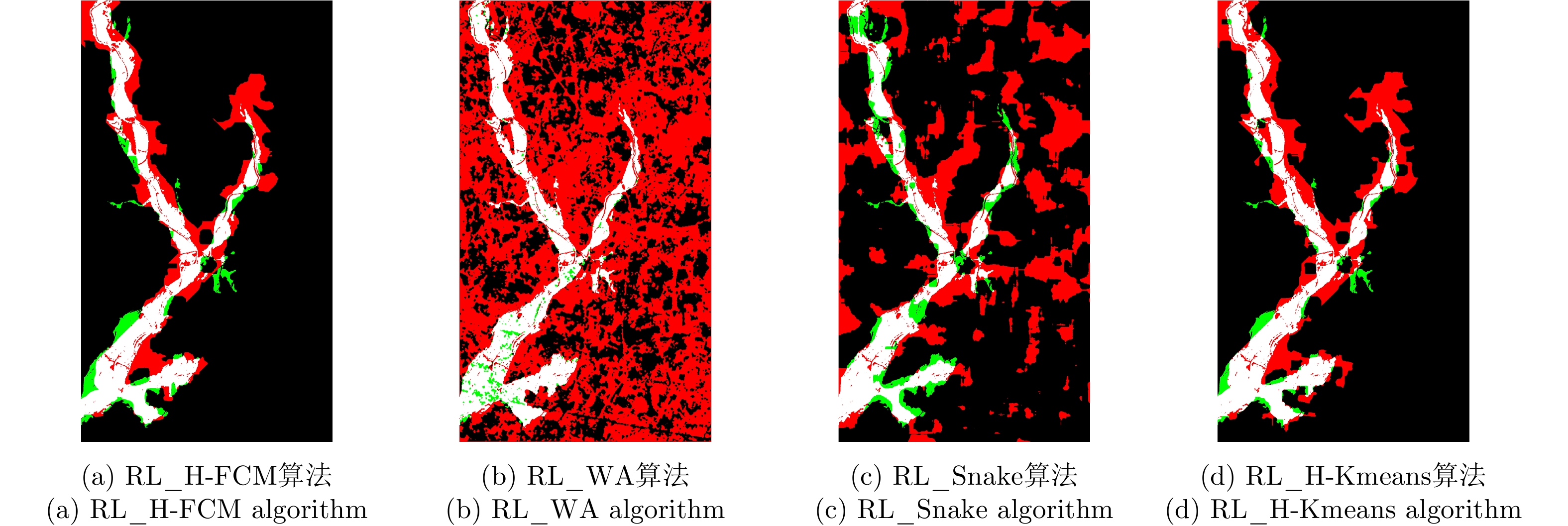
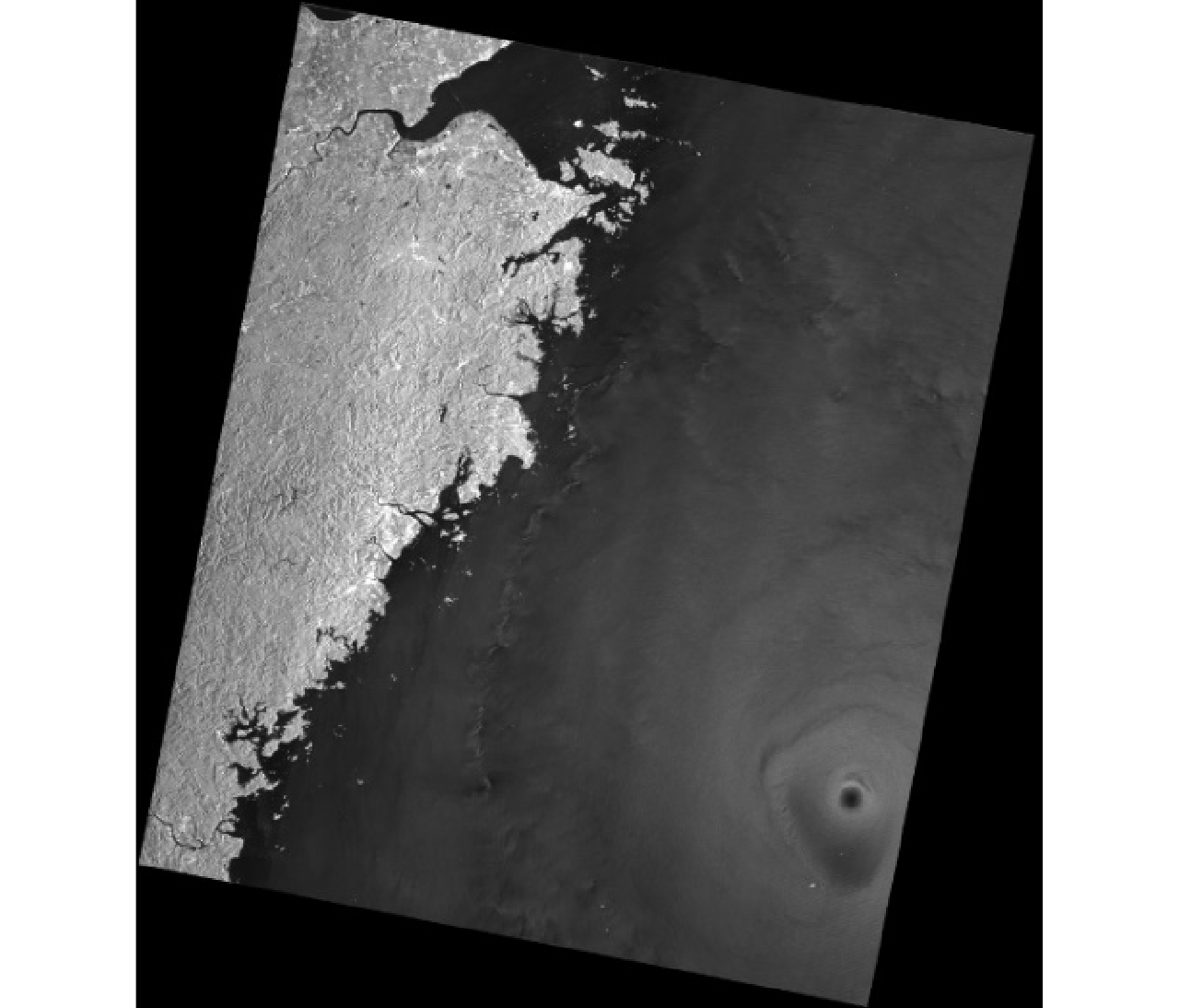
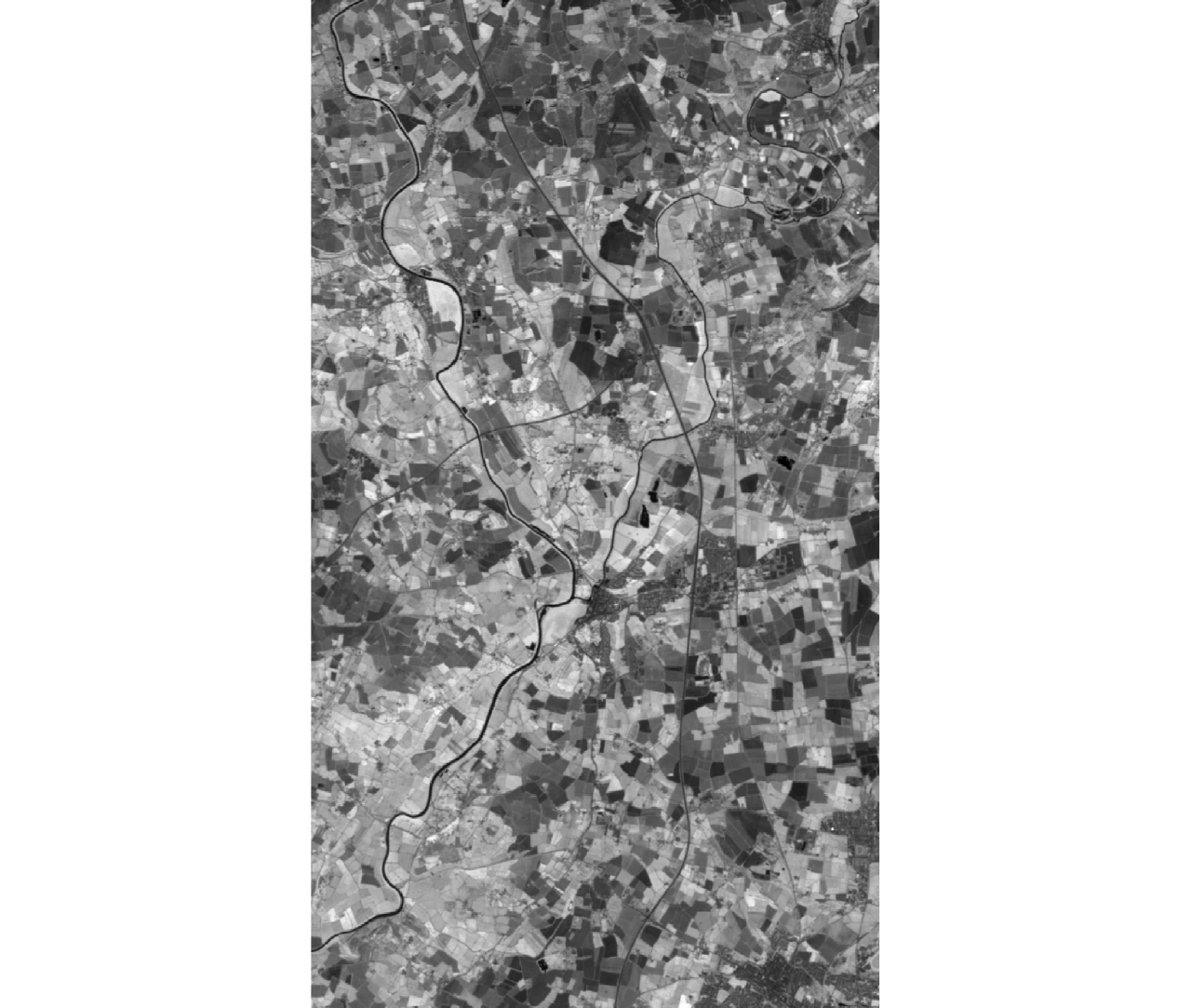
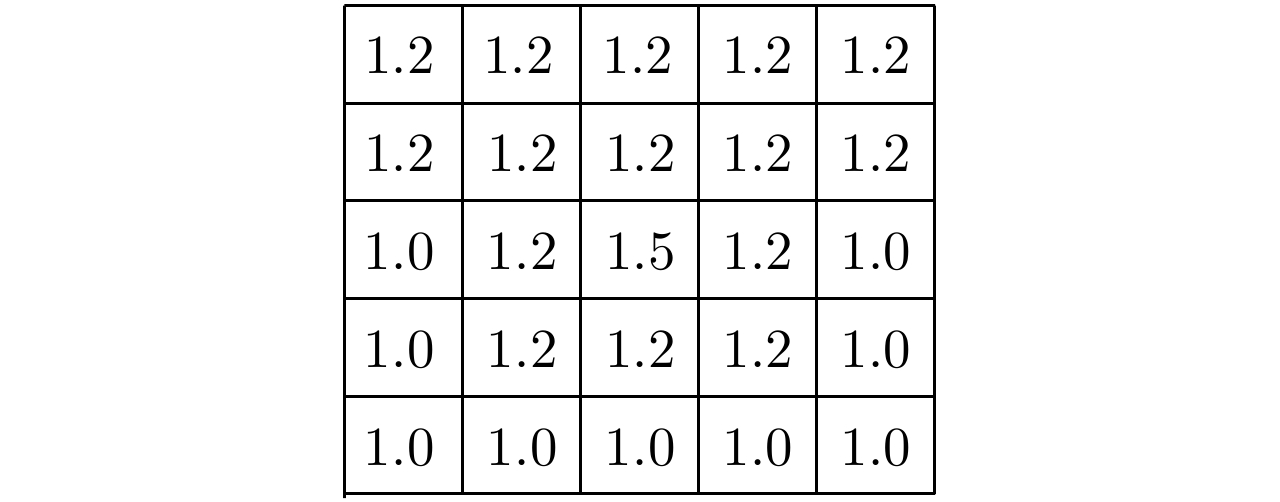
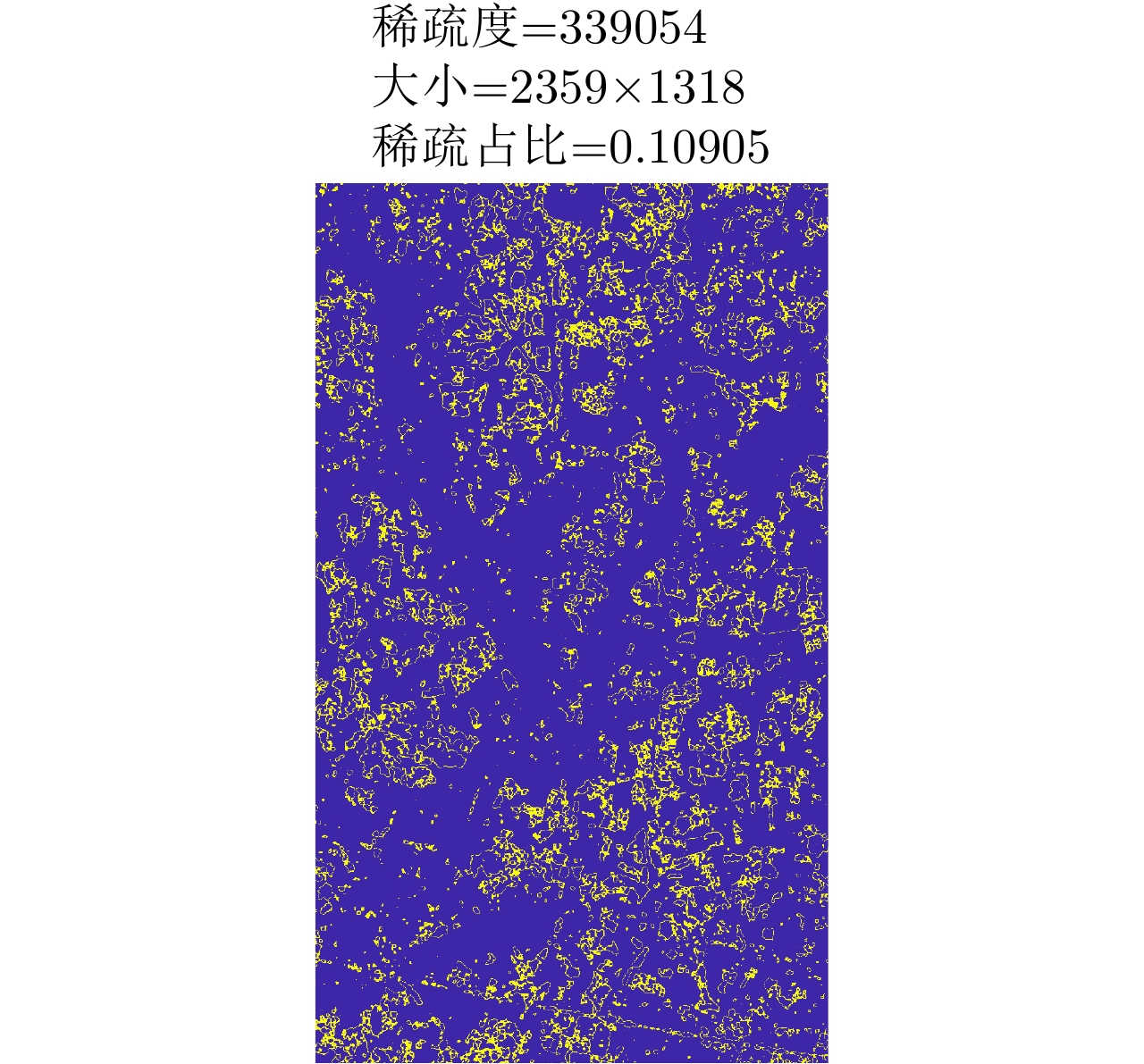
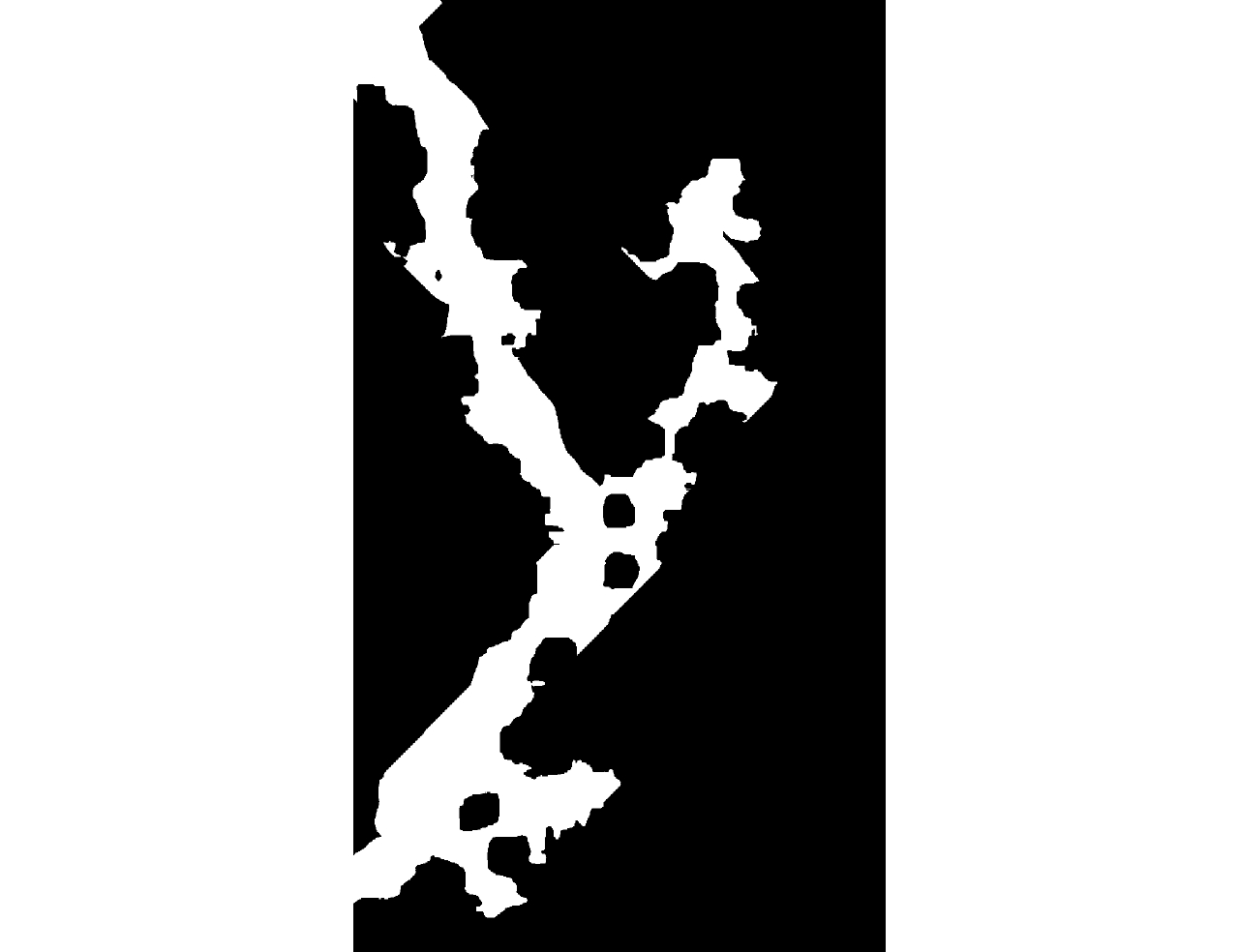
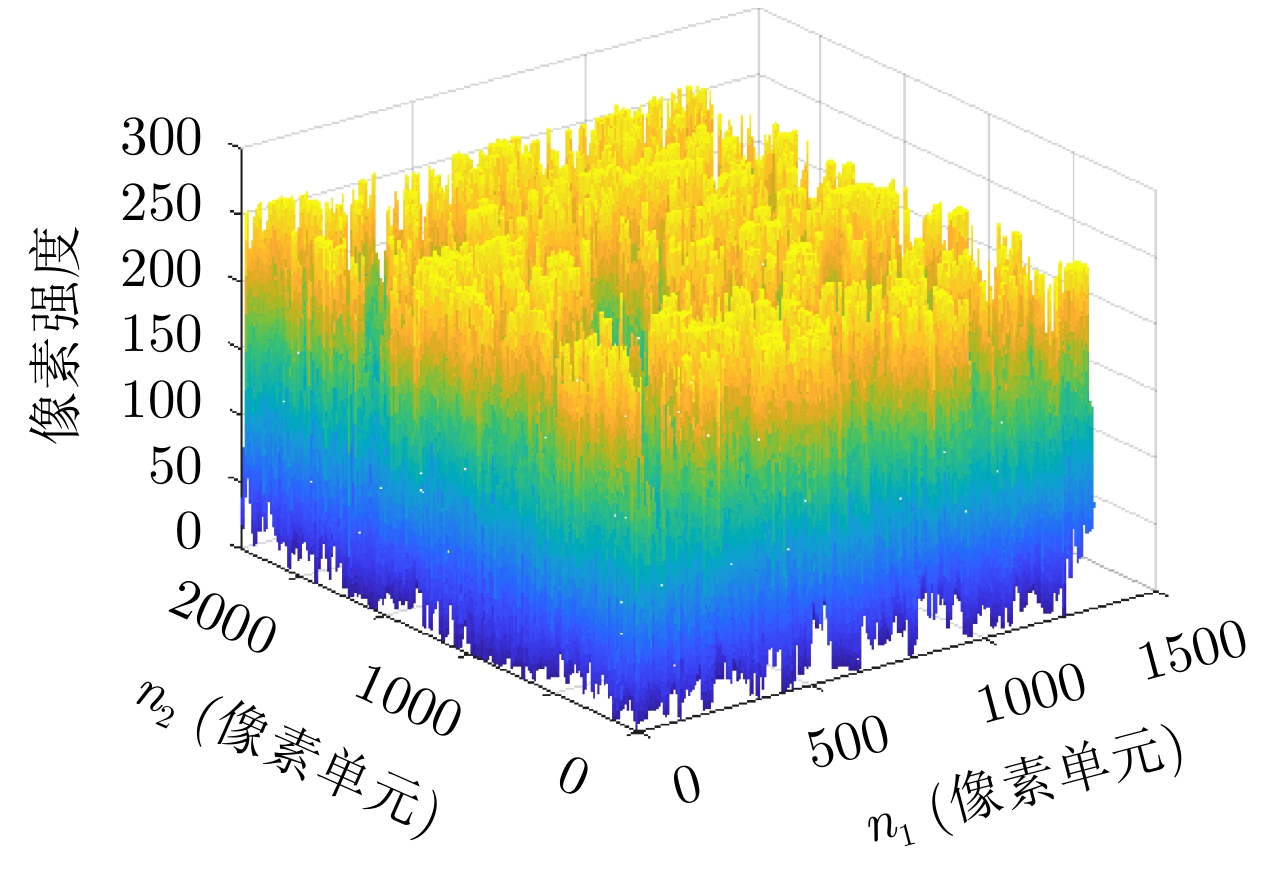
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
解金卫, 李真芳, 王帆, 等. 基于幅相不一致准则的建筑物SAR层析成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 154–165. doi: 12000/JR19062. XIE Jinwei, LI Zhenfang, WANG Fan, et al. SAR tomography imaging for buildings using an inconsistency criterion for amplitude and phase[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 154–165, doi: 12000/JR19062. |
| [3] |
BERNI J A J, ZARCO-TEJADA P J, SUÁREZ L, et al. Thermal and narrowband multispectral remote sensing for vegetation monitoring from an unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(3): 722–738. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010457 |
| [4] |
SAWAYA K E, OLMANSON L G, HEINERT N J, et al. Extending satellite remote sensing to local scales: Land and water resource monitoring using high-resolution imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 88(1/2): 144–156. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2003.04.006 |
| [5] |
DONG Laigen and SHAN Jie. A comprehensive review of earthquake-induced building damage detection with remote sensing techniques[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 84: 85–99. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.06.011 |
| [6] |
SANYAL J and LU X X. Application of remote sensing in flood management with special reference to monsoon Asia: A review[J]. Natural Hazards, 2004, 33(2): 283–301. doi: 10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000037035.65105.95 |
| [7] |
吴一全, 王志来. 基于联合稀疏表示的复Contourlet域SAR图像与红外图像融合(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 349–358. doi: 10.12000/JR17019WU Yiquan and WANG Zhilai. SAR and infrared image fusion in complex contourlet domain based on joint sparse representation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 349–358. doi: 10.12000/JR17019 |
| [8] |
BELL J R, SCHULTZ L A, JONES M, et al. Using optical remote sensing and synthetic aperture radar for near-real-time response to the central U.S. flooding in April-May 2017[C]. The 98th 2018 American Meteorological Society Meeting, Austin, Texas, 2018.
|
| [9] |
KUSSUL N, SHELESTOV A, and SKAKUN S. Flood Monitoring from SAR Data[M]. KOGAN F, POWELL A, and FEDOROV O. Use of Satellite and In-Situ Data to Improve Sustainability. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011: 19-29. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-9618-0_3. |
| [10] |
LIU Zhunga, ZHANG Li, LI Gang, et al. Change detection in heterogeneous remote sensing images based on the fusion of pixel transformation[C]. The 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Xi’an, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.23919/ICIF.2017.8009656. |
| [11] |
LIU Zhunga, LI Gang, MERCIER G, et al. Change detection in heterogenous remote sensing images via homogeneous pixel transformation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(4): 1822–1834. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2784560 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076 |
| [14] |
窦建方, 陈鹰, 翁玉坤. 基于序列非线性滤波SAR影像水体自动提取[J]. 测绘通报, 2008, (9): 37–39, 45.
DOU Jianfang, CHEN Ying, and WENG Yukun. Automatic water body extraction from SAR images based on sequence non-linear filter[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2008(9): 37–39, 45.
|
| [15] |
LEE J S and JURKEVICH I. Coastline detection and tracing in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1990, 28(4): 662–668. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1990.572976 |
| [16] |
DESCOMBES X, MOCTEZUMA M, MAÎTRE H, et al. Coastline detection by a Markovian segmentation on SAR images[J]. Signal Processing, 1996, 55(1): 123–132. doi: 10.1016/S0165-1684(96)00125-9 |
| [17] |
滑文强, 王爽, 郭岩河, 等. 基于邻域最小生成树的半监督极化SAR图像分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 458–470. doi: 10.12000/JR18104HUA Wenqiang, WANG Shuang, GUO Yanhe, et al. Semi-supervised PolSAR image classification based on the neighborhood minimum spanning tree[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 458–470. doi: 10.12000/JR18104 |
| [18] |
赵娟萍, 郭炜炜, 柳彬, 等. 基于概率转移卷积神经网络的含噪标记SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 514–523. doi: 10.12000/JR16140ZHAO Juanping, GUO Weiwei, LIU Bin, et al. Convolutional neural network-based SAR image classification with noisy labels[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 514–523. doi: 10.12000/JR16140 |
| [19] |
HARTIGAN J A and WONG M A. Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C (Applied Statistics) , 1979, 28(1): 100–108.
|
| [20] |
BEZDEK J C, EHRLICH R, and FULL W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1984, 10(2/3): 191–203. doi: 10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7 |
| [21] |
VANNOTE R L, MINSHALL G W, CUMMINS K W, et al. The river continuum concept[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1980, 37(1): 130–137. doi: 10.1139/f80-017 |
| [22] |
FANG Jiajia, WANG Xuan, SUN Tao, et al. Review of research on river connectivity and its impact on eco -hydrological process[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2018, 29(2): 19–26. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2018.02.04 |
| [23] |
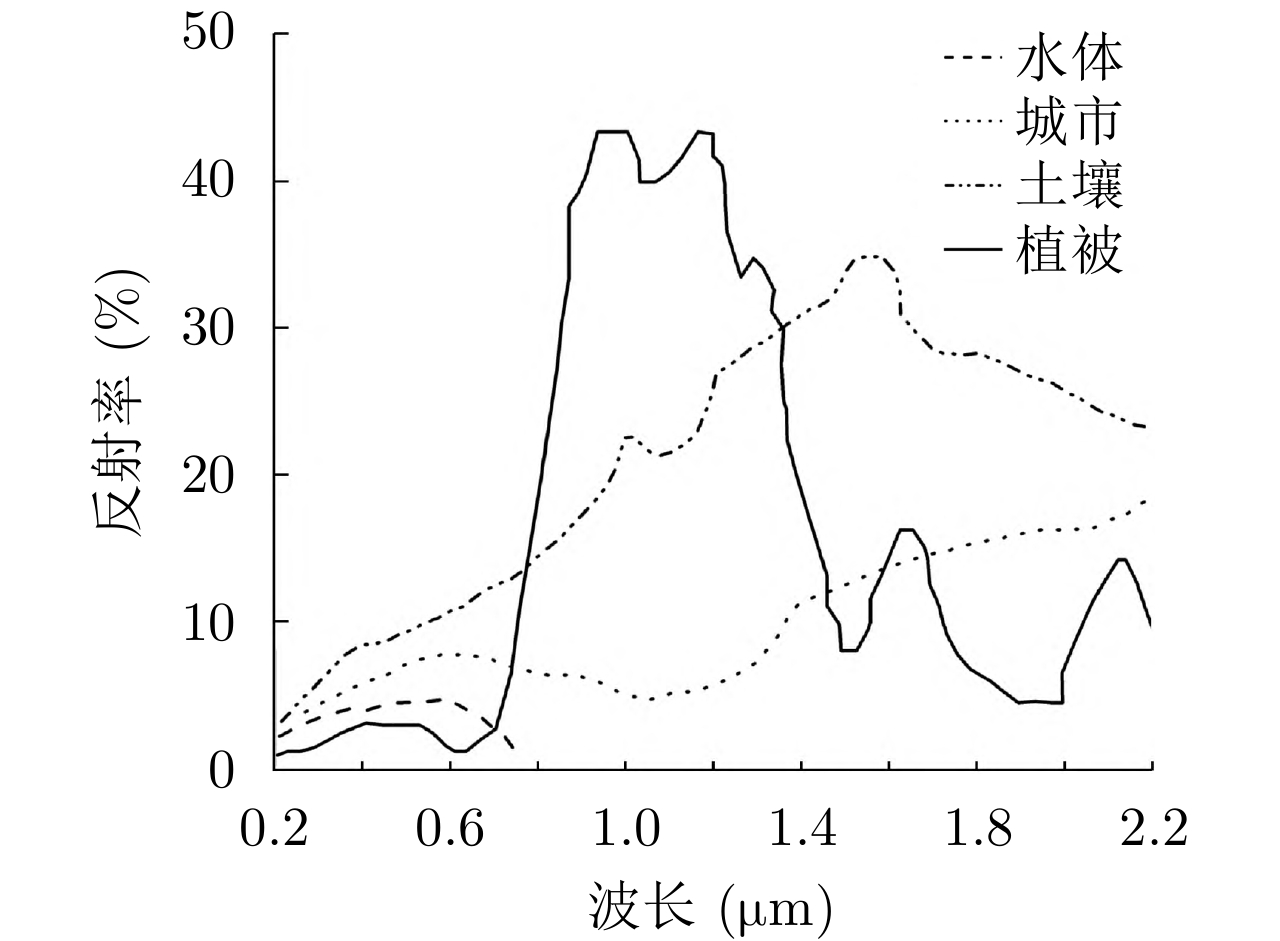
童庆禧, 田国良. 中国典型地物波谱及其特征分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.
TONG Qingxi and TIAN Guoliang. Spectra and Analysis of Typical Earth Objects of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990.
|
| [24] |
CURCIO J A and PETTY C C. The near infrared absorption spectrum of liquid water[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1951, 41(5): 302–304. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.41.000302 |
| [25] |
章毓晋. 图像工程[M]. 4版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2018: 51–53.
ZHANG Yujin. Image Engineering[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018: 51–53.
|
| [26] |
DUDA R O and HART P E. A Generalized Hough Transformation for Detecting Lines in Pictures[M]. Artificial Intelligence Group, SRI International, 1970.
|
| [27] |
XU Hanqiu. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2006, 27(14): 3025–3033. doi: 10.1080/01431160600589179 |
| [28] |
LI Gang and BURKHOLDER R J. Hybrid matching pursuit for distributed through-wall radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(4): 1701–1711. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2398115 |
| [29] |
WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, QUAN Chen, et al. Distributed detection of sparse stochastic signals with quantized measurements: The generalized Gaussian case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(18): 4886–4898. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2932884 |
| [30] |
BATES P D, HORRITT M S, ARONICA G, et al. Bayesian updating of flood inundation likelihoods conditioned on flood extent data[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2004, 18(17): 3347–3370. doi: 10.1002/hyp.1499 |
| [31] |
MCEWEN L J, KRAUSE F, JONES O, et al. Sustainable flood memories, informal knowledge and the development of community resilience to future flood risk[J]. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, 2012, 159(12): 253–264. doi: 10.2495/FRIAR120211 |
| [32] |
RAMBABU C, CHAKRABARTI I, and MAHANTA A. Flooding-based watershed algorithm and its prototype hardware architecture[J]. IEE Proceedings-Vision, Image and Signal Processing, 2004, 151(3): 224–234. doi: 10.1049/ip-vis:20040397 |
| [33] |
DE ROO A, VAN DER KNIJFF J, HORRITT M, et al. Assessing flood damages of the 1997 Oder flood and the 1995 Meuse flood[C]. The 2nd International Symposium on Operationalization of Remote Sensing, Enschede, The Netherlands, 1999: 16–20.
|
| [34] |
LEE J S. Refined filtering of image noise using local statistics[J]. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 1981, 15(4): 380–389. doi: 10.1016/S0146-664X(81)80018-4 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: