② (哈尔滨工业大学信息感知技术协同创新中心 哈尔滨 150001)
③ (哈尔滨工业大学(威海)信息与电气工程学院 威海 264209)
② (Collaborative Innovation Center of Information Sensing and Understanding at Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China)
③ (School of Information and Electronical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology (Weihai), Weihai 264209, China)
作为现代战场侦察、气象观测、资源勘探、环境监测的重要手段之一,雷达在军用、民用领域起着举足轻重的作用。在充分挖掘空间电磁波中包含的信息的基础上,雷达不仅可以获取目标距离、速度、方位等信息,还能对目标的种类、特性、结构做出分析与判断。
极化是继时域、频域、空域信息之后雷达可利用的另一种重要信息,作为电磁波的固有属性,极化反映了波的电场矢量端点随时间变化的规律,按照其形成的空间轨迹形状和旋向又可分为线、圆、椭圆极化和左旋、右旋极化。由于接收电磁波的极化状态既与发射天线辐射电磁波的极化状态有关,还受目标的形状、大小、姿态、物质组成等因素影响[1](目标的去极化效应),因此,将电磁波的极化应用于雷达领域具备巨大的发展潜力[2]。
极化雷达体制的提出最早可以追溯到上世纪50年代,但当时极化信号处理技术仍未成熟,无法带来可观的性能改善,且由于系统、设备相对复杂,受限于硬件水平,其成本也大大增加,因此并未得到广泛应用;而随着软硬件水平的不断提高和极化信号处理技术的逐渐完善,极化雷达开始展现出其显著的优势并逐步成为现代雷达的主流[3]。从世界范围看,美国、俄罗斯、加拿大、意大利、德国、法国、荷兰、日本等国相继开展了极化雷达的研制和系统更新改造,在国内,国防科技大学、哈尔滨工业大学、北京理工大学、西安电子科技大学、电子科技大学等多所高校,以及中科院电子所、中国电子科技集团14所、38所、航天科技704所等多家立足电子或航天科技的科研院所都在极化理论研究、系统研制和工程实现等方面进行了大量的工作[4]。总地来说,极化雷达体制经历了从变/双极化到全极化的漫长发展历程,其全极化测量能力从多脉冲周期分时测量向单脉冲周期同时测量发展,针对的目标也从简单的平稳目标(理想点散射静态目标)推广至复杂的非平稳目标(结构复杂的大型目标或高速机动目标等),应用范围越来越广,并能够适应愈发复杂的电磁环境(宽带信号、部分极化波、各类噪声/杂波/干扰等)。
对极化雷达系统而言,其性能优势一方面来自于系统结构和硬件设备的升级带来的测量精度和稳定性的提高,另一方面则主要归功于成熟的极化信号处理技术,利用适当的信号处理方法对极化信息进行充分的挖掘和利用是其灵魂所在[5]。基本极化信息的获取一般通过直接测量或参数估计实现,而极化分集和编码技术是更全面、更精确、更快速地实现极化数据观测的基础,合理利用获取的基本极化信息或经过进一步处理得到的极化信息,并辅以时域、频域、空域等其他信息,可以大大提高雷达的抗干扰/杂波、目标检测、分类与识别能力,因此,极化信号处理技术已成为预警、监视、跟踪、气象、遥感、成像等各类雷达的关键技术之一。
本文对军用和民用领域涉及的极化雷达信号处理关键技术进行了论述和总结,第2节从目标极化散射矩阵和电磁波极化状态两个方面总结了雷达基本极化信息的测量和获取方法;第3节介绍了极化分集与编码的基本概念、实现方法及其应用;第4节梳理了各类极化抗干扰技术的发展历程、实现方式和优缺点等;第5节从目标极化检测、分类与识别的角度介绍了极化信息在雷达系统中的利用方式及其优势;最后,在第6节对全文进行总结并对雷达极化信号处理技术未来的发展趋势和前景做出了展望。
2 极化信息获取对于雷达系统而言,精确地获取极化信息是雷达抗干扰、目标检测和识别的基础,而通常要获取的基本极化信息有两种:目标的极化散射矩阵和电磁波的极化状态。其中,前者反映了雷达目标的去极化特性,其测量一般需要设计特定的发射/接收体制;后者则反映了雷达接收电磁波电场取向的时变特性,只要接收端为极化天线或极化敏感阵列即可对任意接收信号进行极化参数估计。而其他复杂的极化信息则可在此基础上利用适当的信号处理技术进一步得到。
2.1 目标极化散射矩阵的测量极化散射矩阵[1]的概念最早由G. Sinclair提出,它反映了目标在一定的姿态和观测频率下对电磁波的极化散射效应,可将其记为:
| ${\boldsymbol{S}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{S_{\rm H\!H}}}& {{S_{\rm V\!H}}}\\ {{S_{\rm H\!V}}}& {{S_{\rm V\!V}}} \end{array}} \right]$ | (1) |
鉴于任意极化波都可视为一对正交极化波的幅相加权合成,极化散射矩阵反映了目标对电磁波的全部极化散射信息。因此,完整而精确地测量极化散射矩阵是雷达极化信号处理的关键。
自上世纪五六十年代起,雷达系统开始不再局限于传统的单极化体制,随着极化理论的逐步完善和硬件水平的不断提高,极化雷达测量体制按其出现的时间顺序经历了如下发展历程:变极化、双极化、分时全极化、同时全极化、紧缩极化测量体制。
变极化测量模式一般利用选择开关控制发射信号的极化状态,并在接收端采用相同的极化方式进行接收[6]。通过不同脉冲间的极化切换,该体制可以在两个脉冲周期内测得极化散射矩阵的对角线元素,即同极化分量。然而,该体制对脉冲重复周期、极化转换开关等硬件设备都有严格要求,因此并未得到广泛应用。
双极化测量模式采用单极化发射、正交双极化同时接收的工作方式,仅需在接收端增加一个正交极化通道即可在单个脉冲周期内实现对极化散射矩阵其中一列元素的测量[5, 7],充分利用获取的极化信息能够在一定程度上提高目标检测的信噪比和目标跟踪、抗干扰性能[8, 9]。
在此基础上,分时全极化测量体制[10]被提出,其融合了变极化体制的正交双极化脉间交替发射和双极化体制的正交双极化同时接收方式,使得雷达能够在两个脉冲重复周期内测得完整的极化散射矩阵,因此被广泛应用于气象观测、地理遥感、电子侦察与对抗等[11]。由于获得了完备的目标极化信息,利用目标与环境或干扰的不同极化散射特性即可更好地实现目标检测、分类、识别以及干扰抑制等[2, 4, 6]。但由于极化散射矩阵的两列元素分别是在不同的脉冲重复周期内测得,该体制仍存在一定的缺陷[12]:对于极化散射特性起伏的非平稳目标(如复杂结构或快速运动目标)会出现去相关效应和距离模糊现象;需要精确补偿运动目标的多普勒效应导致的散射矩阵两列之间的相位差;发射通道存在交叉极化耦合。鉴于如今大部分现役极化雷达采用的都是分时极化测量体制,大规模的设备改造代价太大,因此对具有较高极化隔离度的极化捷变天线[13, 14]或极化分集天线[15, 16]的研究仍有较高的实用价值。
为克服分时全极化测量体制的不足,同时全极化测量体制[17, 18]应运而生,该体制利用双极化通道同时发射波形正交的两路编码信号,并在接收端利用发射波形的正交性进行相关接收和两路正交极化发射信号的分离,从而避免了发射端极化切换带来的负面影响,在单个脉冲重复周期内即可实现完整极化散射矩阵的测量。显然,该体制能够在更广泛的应用场景下实现对各类目标极化散射特性的精确测量,大大提高雷达各方面的性能[4]。
当然,尽管同时全极化测量体制在目标检测、分类、识别以及抗干扰等方面都存在显著优势,但仍存在以下问题:系统相对复杂、设备量增大,成本更高;对信号的正交波形设计、编码和处理方法提出了更高的要求。为进一步简化系统结构、降低硬件成本,简缩极化测量体制被提出[19, 20, 21],按照发射和接收极化方式可将其分为两类:45°线极化发射、垂直/水平线极化同时接收的p/4模式[22]和圆极化发射、垂直/水平线极化同时接收的CL-pol模式[23]。简缩极化测量体制功耗低、对通道串扰、不一致性等不敏感,在多数应用场景下其性能基本可以媲美全极化系统[24, 25]。
另外,在发射波形设计和信号处理方面,国内外学者相继提出了正负线性调频信号、相位编码信号、频移脉冲信号等多种极化测量波形[18, 26],并针对动态目标多普勒频移[27]、波形隔离度[28]、目标极化特性起伏[29]、测量误差[30]等对极化散射矩阵测量的影响以及相应的解决方案进行了充分的研究。
值得注意的是,硬件条件、复杂电磁传播环境等不理想因素必然导致极化散射矩阵的测量误差,因此需要进行极化定标[31]。针对通道串扰和幅相不一致性问题,按照极化定标利用的已知极化散射特性目标的种类,可将其分为点目标[32, 33]和分布目标定标方法[34, 35]。前者原理上简单直观,但校正结果一般仅对特定时间内定标体所在的特定空间区域有效且校正精度对定标体误差较为敏感;而后者则具有较高的适应性和稳定性,但选择的定标体散射特性仍对定标精度有一定影响[36, 37]。对于受电离层引起的法拉第旋转效应影响的雷达系统(如星载极化SAR),其参数定标既可在上述通道误差校正后进行[38, 39],也可同时联合求解[40, 41],而各参量的耦合影响往往也不可忽略[42]。
2.2 电磁波的极化状态估计和极化DOA估计在电子对抗中,利用真实目标与干扰的极化差异可以进行分类与识别,通过极化滤波等技术,还可以实现干扰抑制或目标增强[43, 44],因此,精确估计辐射源极化状态[45, 46]同样相当重要。
电磁波的极化状态描述了电场矢量空间取向随时间变化的方式,最为常用的表征方法是Jones矢量法,即将电场幅度表示为:
| ${\boldsymbol{E}} = \left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{E_\theta }}\\ {{E_\varphi }} \end{array}} \right] = {E_0}\left[{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\rm cos}\gamma }\\ {{\rm sin}\gamma {{\rm e}^{{\rm j}\eta }}} \end{array}} \right]$ | (2) |
显然,极化角、极化相差两个参数完全反映了电磁波的极化状态。若接收阵元为完备电磁矢量传感器或部分电磁矢量传感器,则可感知入射信号的极化信息。
由于信号的极化参数与方位信息耦合在阵列流型中,因此目前极化状态估计的过程往往都是与信号的波达方向(DOA)估计联合进行的,一般称之为极化DOA估计。与未考虑极化的传统DOA估计相比,极化DOA估计利用信号极化状态的不同使目标在多维参数空间中的差异性更加明显,因此参数估计的精度和分辨力都有所提升。
一般而言,完备的电磁矢量天线由共相位中心的3根正交偶极子和3个正交电流环构成,能够感知空间电磁信号的全部电场、磁场分量。文献[47, 48]研究了基于单电磁矢量传感器的方位和极化参数联合估计问题,但由于要消除传感器内部各单元之间的互耦影响需要复杂的电磁隔离技术和较高的成本,因此完备的电磁矢量天线仍难以得到广泛的工程应用,但由于硬件水平在不断提高,这方面的研究仍然具有一定的学术意义。
实际上,无论是理论研究还是实际应用,极化DOA估计多数以简化的部分电磁矢量天线/阵列为基础,如交叉偶极子天线。上世纪90年代以来,不断有学者尝试将基于2阶或高阶统计量的MUSIC[49, 50]、矩阵束MUSIC[51]、ESPRIT[52, 53]等经典高分辨参数估计方法推广到极化敏感阵列上来,以实现DOA和极化参数的联合估计。近年来,也有学者引入四元数[54, 55]、几何代数[56]、张量代数[57, 58]等高维代数理论来提升参数估计的鲁棒性;文献[59]引入稀疏表示和压缩感知理论以求带来算法适用性和估计性能上的改善。
针对三极化天线,张国毅等人研究了3维极化滤波[45]的参数估计问题,并给出了高干扰极化度情形下的简化估计方法[60];K.T. Wong等人研究了6维电磁矢量下的极化及DOA估计问题,并对三偶极子条件下矢量叉乘方法的应用进行了分析[61]。随后,Lundback等人对三极化阵列下的参数唯一性进行了研究,认为来自同一方向的不同导向矢量若极化状态不同,则这些导向矢量是相互独立的[62]。徐友根等人对单一三极化天线提出了一种准矢量叉乘算法来估计极化参数及DOA,该算法可对非线极化的移动信源进行参数估计[63]。文献[64]对比并总结了不同组合下的三极化天线下的参数估计性能,并给出参数估计的解析解。孙杰等人在三阵子天线的基础上首先给出了估计波达角的公式,并提出一种滤除地面反射波的方法提高波达角的估计精度,然后利用获得的高精度的波达角估计值和已测的电场强度,计算出电磁波的极化参数[65]。
另外,在接收阵列结构方面,也可采用由单极化天线所组成的共形阵列,既节约了天线设计与制造的成本,又由于天线与载体共形节省了空间。文献[66, 67]分别针对柱面、锥面共形天线研究了方位与极化信息去耦合和联合估计方法,但都要求阵列结构满足一定的对称性。文献[68]则基于秩损理论提出了一种可以适用于任意共形载体的参数联合估计方法,在一定程度上扩大了算法的应用范围。
由于各类电子系统应用场景多种多样,电磁环境越来越复杂,不等功率信号[69]、相干信源[70]、部分极化波[71, 72]及近场[73]条件下的入射信号DOA和极化状态估计也是研究的热点之一。针对任意阵列结构配置,文献[74, 75]基于流形分离技术提出了一种有效的解决方案,利用虚拟阵列转换、快速傅里叶变换或多项式求根等方法实现DOA与极化信息的联合估计,且能够有效克服阵元位置误差、方向图、互耦等非理想因素的影响,具有很好的适用性,但虚拟阵列转换时的内插精度会影响算法的性能。
总之,在电磁波的极化状态估计方面,基础理论和算法已经相当完善,相关技术也渐趋成熟并已得到实际应用。在实现极化参数估计的同时,由于提高了可利用的信息维度,对信号方位等其它参数的估计精度和分辨力也得到明显提高,大大提高了系统性能。显然,处理的信息维度增加必然带来算法复杂度和运算量的提升,如何在更苛刻的条件(如少快拍、低信噪比、信源相干、复杂噪声环境、存在阵列误差等)下以可接受的硬件、时间成本实现稳定、精确的参数估计仍是未来需要努力的方向。
3 极化分集与编码极化分集与极化编码是雷达极化领域的重要概念和技术,对于实际极化雷达系统而言,其工作方式无外乎在时域、频域或空域上进行信号的极化分集或极化编码[21]。极化分集是极化雷达系统设计的出发点,也是极化信息获取和极化信号处理的基础;而极化编码则是在发射信号层面提升雷达系统各方面性能的重要技术手段之一。
3.1 极化分集分集技术是指利用电磁波在时间、频率、空间、极化等特性上的差异,分别进行信号的发射/接收、处理和合并的方法。早在极化分集[76]的概念提出以前,时间分集、频率分集、空间分集技术已经得到了广泛应用,而近年来随着发射分集概念[77]的提出和MIMO技术[78]的逐渐火热,联合收发分集体制也展现出了更广阔的应用前景。
极化分集又可分为极化时间分集、极化频率分集、极化空间分集。前两者在不同的时间或频率上发射不同极化的信号,再在时域或频域上分离接收信号以获取极化信息并加以利用;极化空间分集则一般用于SAR系统,通过在合成孔径时间内的子孔径间切换发射信号极化方式以获取全极化数据。显然,除了单一极化体制以外,双/多极化、分时/同时全极化测量体制都在一定程度上体现了极化分集的概念[79],即利用极化状态正交(垂直/水平极化、左旋/右旋圆极化)的两路信号,通过适当的处理获得电磁波的极化状态或目标完备的极化特性。
极化分集的根本优势在于,引入了信号的极化信息从而提高了雷达获取信息的维度,随着极化分集技术的发展和极化测量体制的改革,获取的极化信息完整性和精度也逐渐提高,为后续信号处理的有效性和可靠性提供了有力保证。以气象雷达为例,降雨量观测[80]、水汽凝结特征识别[81]等都依赖于极化分集技术,由于利用极化信息增加了特征空间的维度,雷达在杂波抑制[82]、目标识别[83, 84]等诸多方面也都有了长足的进步[85]。其次,极化分集能够有效克服雷达RCS起伏,以极化捷变干扰为例,阵元极化特性的差异会导致接收干扰的幅相起伏不同,从而影响干扰抑制效果,而综合利用极化分集获得的干扰极化信息,则可显著提高雷达的探测能力和稳定性。另外,由于其带来的信道容量提升和良好的非相关衰落特性,极化分集技术在通信领域也得到了广泛应用[86, 87, 88]。
3.2 极化编码极化编码是继频率编码(频率捷变)、相位编码后出现的一种新的雷达信号编码方式,其思想是用适当的编码(以M序列、巴克码等为例的固定编码或随机编码)调制雷达发射信号的极化方式,它既可以用于同时极化测量系统以实现极化散射矩阵的精确测量,同样也是低截获概率雷达信号优化设计的技术手段之一。
极化编码技术最早应用于X波段脉内极化捷变雷达[89](IPAR),发射波形采用脉内的左、右旋圆极化进行编码,接收端信号处理部分则利用信号水平、垂直极化分量的相对相位特性实现脉冲压缩。其优势在于:对多普勒频移不敏感,能够识别杂波覆盖下的静止目标、削弱多径干扰、降低截获概率[90, 91]。
为提高雷达系统的生存能力,脉内多次线性调频、随机信号、频率编码、相位编码等复杂调制信号引起了广泛关注,而随着极化编码技术的发展,将之与其他编码方式相结合的复合编码方式逐渐展现出了在检测性能、抗干扰等方面的潜力。鉴于此,国内外学者提出脉内采用其他调制(二进制相位编码[92]、线性调频[93]、非线性调频[94]、频率捷变[95])、脉间采用极化编码的复合编码雷达信号,并对相应的脉冲压缩和相关检测实现方法[93]做出了充分的讨论(如图 1),既保证了较高的距离、速度测量精度和分辨力,又提高了雷达在复杂电磁环境下的抗干扰(如箔条干扰、海杂波等)和抗截获能力。此外,文献[96]提出一种跳频信号与极化编码结合的信号形式,文献[97]介绍了一种极化捷变编码抗干扰雷达系统的简易实现方式,提出利用干扰的极化相对不变性提取干扰波形并准确估计其Jones矢量,以用于后续的抗干扰处理。
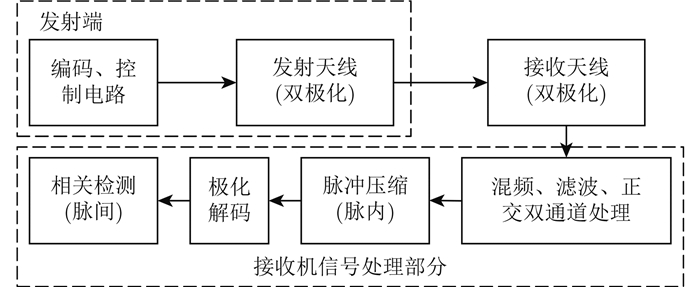
|
图 1 极化编码雷达系统基本框图 Fig.1 Block diagram of polarization-coded radar systems |
雷达极化抗干扰/杂波技术发端于上个世纪70年代的极化研究低潮期,先后经历了从单一极化域滤波到现在的极化域与其他域联合/协同滤波的发展过程,随着时间的推移可以看到整个极化抗干扰技术在逐步提高。其最早被用于抑制雨杂波干扰[98],接着逐渐扩展到气象雷达、航管雷达、对空情报雷达、火控雷达、制导雷达以及雷达导引头等多个应用领域。极化域滤波的本质是对雷达接收端的不同极化天线接收的信号进行调节,使之在保留目标信号的同时,尽可能地抑制干扰信号。其滤波效果取决于对目标与干扰信号极化状态的估计和权值的设定,达到在最优或次优的准则下对接收信号中的目标信号进行无失真保留。主要优化准则有:最大信号干扰噪声比(SINR)准则,最小均方误差准则,主瓣约束准则,多线性约束准则等[99]。一般来说,上述不同的准则适用于不同的环境,但在某些条件下,一些准则是等效的。
以往的综述文献[2, 4, 100]对极化抗干扰已有不同程度的提及和不同侧重点的阐述,故本节结合哈尔滨工业大学在该领域的研究成果,针对单一极化域滤波和包括极化的多域联合/协同滤波,按照时间先后顺序,分别作进一步的补充和阐述。
4.1 单一极化域抗干扰/杂波在单一极化滤波领域,继1975年Nathanson提出自适应极化对消器(APC)[98]后,Poelman于1981年提出虚拟极化自适应滤波器[101]用于干扰抑制。随后其于1984年提出多凹口逻辑积极化滤波器(MLP)[102],用于提高抗干扰能力但实现较复杂;同年其又提出一种基于非线性极化变换的单凹口极化滤波器[103],减小了实现的复杂度;张国毅于2000年提出一种实数加权极化变换法[104],解决了上述算法随非线性程度的增大而越来越复杂的问题。为了进一步提升MLP的自适应能力,Giuli和Gherardelli等人在APC和MLP的基础上分别提出了MLP-APC[105]和MLP-SAPC[106]等算法。
进入20世纪90年代,MLP被用于抑制雨杂波[107],随后极化滤波被逐渐推广应用到整个气象雷达领域,例如在双极化气象雷达上,Moisseev等人先后提出多种在多普勒域上利用极化滤波器抑制地杂波的方法[108, 109]。同时,从这一时期开始,国内科研人员在极化抗干扰方面做出了突出的成果。在宽带极化雷达背景下,文献[110]提出一种横向极化滤波器,以宽带极化滤波和极化增强的方式实现了极化域的检测性能优化;文献[111]则提出待定主瓣约束准则以解决多目标情形下的最优滤波问题;为更全面地分析SINR准则下的极化滤波器性能,王雪松等人给出了完全极化和部分极化情形下的理论性能上界并进行了优化设计[112, 113]。另外,毛兴鹏等从误差成因、优化方法以及信干比提升等方面充分分析了极化滤波技术的有效性[114]。
对于一类新体制雷达--高频地波雷达,由于只能发射垂直极化波,且目标信号的极化形式也以垂直极化为主,故在极化域上抑制干扰引起了研究者的关注。针对该类型雷达背景下的天波电台干扰,利用虚拟极化技术对水平极化通道信号进行加权后再做极化滤波,能够在一定程度上提升极化滤波性能和雷达抗干扰能力[115]。为避免普通极化滤波器可能带来的相位失真,文献[116, 117]提出一种自适应零相移极化滤波器,使得电台干扰被抑制的同时目标相位保持不变。在此基础上,为了抑制相参雷达系统中同时存在的多个干扰,结合线性极化变换、频域极化滤波、幅相补偿和多凹口技术可实现频域零相移多凹口极化滤波[118, 119],既拓展了算法的适用性,又显著提高了滤波性能,以高频地波雷达电台干扰抑制为例,该方法的信干比改善可达28 dB以上;此外,文献[120, 121]从极化子空间的角度提出基于斜投影算子的极化滤波器用于抑制电台干扰。在电离层杂波抑制方面,文献[122]提出一种基于距离-多普勒域(杂波能量较弱)或距离-时间域(杂波能量较强)下的斜投影极化滤波算法。
当前普遍使用的双正交极化天线单元存在极化状态随角度的改变而变化起伏、极化纯度退化等问题,这将制约阵列对接收信号的极化测量及干扰抑制等性能。于是,三极化天线作为一种较双极化天线具有更高自由度的多极化天线,以其可更好地实现极化分集而广受瞩目,近年来在雷达滤波领域得到了广泛应用。
Nehorai等人对三极化天线滤波性能进行了研究[123],理论验证了当目标信号与干扰的极化状态不同时输出信干噪比可获得较理想的效果;在高频地波雷达中,以3维极化天线接收数据为基础,能够联合极化域和空域滤除双正交极化滤波不能抑制的干扰,利用最佳实数加权法还可以进一步提升干扰抑制能力[45]。为了实时处理快速变化的干扰,张国毅等人又提出一种瞬时极化滤波算法,该算法根据单快拍建立滤波极化矢量,且能通过调整采样速率自适应干扰极化状态的变化[124],并提出利用3维正交极化信息改进的2维极化滤波器来降低上述3维极化滤波器的复杂度[125]。另外,为解决传统3维极化滤波造成的目标信号的极化损失,刘爱军等人提出一种基于斜投影的3维极化滤波算法[126],利用目标和干扰的极化矢量分别构建矢量子空间,然后构造斜投影算子作为滤波矢量进行3维极化滤波,该算法实现简便,拓展了极化滤波技术的应用领域。
可以看到,在其他域抗干扰无法取得理想效果时,单一极化域抗干扰能显示出其优点,特别是在对抗主瓣干扰方面,极化域滤波不会造成主瓣波束的畸变,克服了空域等其他抗干扰方法无法解决的问题。在某些特殊的应用领域(如高频地波雷达抗射频电台干扰),其优势显得更加明显。但也能看到,极化域参数受空域信息的影响,且自由度不高,这都制约了单一极化域抗干扰在复杂多变的环境下的应用和效果。
4.2 包括极化的多域联合抗干扰/杂波正如上文所述,复杂的环境往往使得单一极化域抑制干扰/杂波的效果有限,例如当目标信号与干扰/杂波的极化参数较为接近时,单一极化滤波往往性能较差甚至失效[123]。于是极化抗干扰技术逐渐从单一的极化域向包含极化的多域联合转变和发展。
在充分研究天线空域极化特性[127, 128]的基础上,文献[129, 130]分别针对雷达系统中存在的欺骗性干扰和主瓣干扰设计了抑制算法,在一定程度上提高了雷达的工作性能。文献[131, 132, 133]提出了均匀和非均匀杂波背景下极化空时自适应处理技术,通过多域联合处理使雷达的检测和抗干扰能力有所提升[100, 134]。
陶建武先后提出了基于超复数的极化-空域级联滤波算法[135]和空-时-极化联合滤波算法[136],用于机载阵列中的干扰抑制。而对于机载雷达欺骗式的主瓣干扰,文献[137]给出一种基于重叠滑窗子阵合成的空-极化域联合自适应波束形成算法。对于常规的极化敏感阵列,在空-极化域联合自适应处理中引入基于特征空间的广义波束形成算法后[138],可以获得优于传统最优滤波算法的滤波性能并削弱指向误差影响;而对于交替极化敏感阵列,文献[139]分析了其基于特征空间投影算法的抗主瓣干扰能力,并通过与常规极化敏感阵列的比较证明了其在性能和稳健性上的优势。
在高频地波雷达应用领域,针对当前该型雷达的接收阵列以均匀线性阵列为主,结合前述目标信号的极化特性,毛兴鹏、刘爱军、洪泓等先后提出多种基于空-极化域的协同滤波算法[140, 141, 142],用于抑制电离层杂波。此类协同滤波算法可同时抑制多个干扰/杂波,且只有当目标信号与干扰/杂波的空域和极化域参数都完全相同时,上述滤波方法才完全失效;而充分的对比分析也验证了其性能确实优于空域和极化域级联的联合滤波算法。在处理实测数据时,可依据当时的外部干扰环境在多普勒域、距离-多普勒域或距离-时间域上运用协同算法进行干扰/杂波抑制。随后,文献[143]提出基于窄波束的斜投影空域-极化域协同滤波算法,可有效减小主瓣宽度并提升旁瓣抑制比,其算法的基本结构框图[143]如图 2所示。
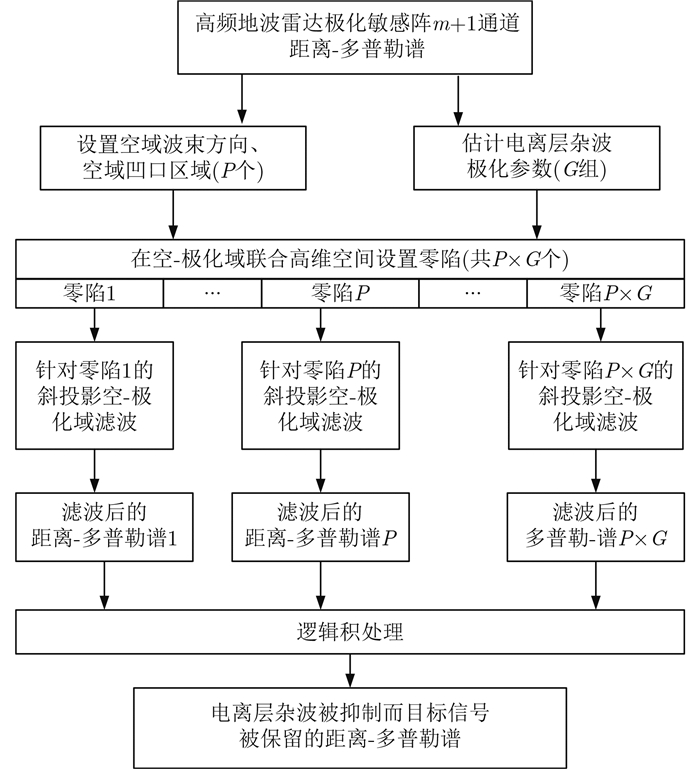
|
图 2 极化域协同抗干扰算法结构框图 Fig.2 Block diagram of narrow beam spatial-polarization collaborative mitigation |
更一般地,当目标信号与干扰/杂波在极化域、空域、时域或频域上参数相差不大时,需要尽可能地将可测参数的多个域联合起来,从而增大目标信号与干扰/杂波的差异性,提升抗干扰能力。例如文献[144]提出一种基于斜投影的多域(包括极化域)协同干扰抑制算法,理论分析表明其性能不仅好于单一极化域滤波,也强于多域级联式的联合抗干扰算法。
总地来看,包括极化的多域联合提供了更多的关于目标信号与干扰/杂波的参数信息及它们之间的差异,使得多域联合抗干扰性能往往明显优于单一极化抗干扰,从而引起了国内外的相关学者对该领域越来越强烈的兴趣和关注。但在具体实现中还需注意:
(1) 相对于单一极化滤波算法,多域联合处理的计算复杂度较高,在具体应用中较难实现实时处理。需要从算法原理和算法的实现过程这两个方面入手,优化算法,降低计算量。
(2) 多域联合处理性能好于单一极化域滤波这一结论,是以各域参数估计精度都较为精准为前提的。例如,若空-极化域中的空域参数估计精度较差,则空-极化域联合滤波性能不一定好于单一极化域滤波。
(3) 在实际应用中,还需考虑极化阵元间的通道一致性、互耦、极化隔离度等非理想因素对干扰/杂波抑制算法的影响。
正是极化抗干扰良好的效果与前景,使得近年来国内外多家单位或对现有雷达进行极化改造[100],或研发具备双极化发射或接收能力的相控阵雷达阵列[145],总地来说,极化抗干扰技术在雷达中的研究与应用越来越广阔。
5 极化检测、分类与识别实际上,无论是极化信息获取还是干扰/杂波抑制,其最终目的都是利用信号的极化信息提高对目标的检测、分类与识别能力。
5.1 目标检测极化作为幅度、相位、频率以外的另一个信息维度,在雷达目标检测中同样起到了相当重要的作用。
一般而言,基于极化信息的目标检测方法可分为最优接收检测和极化统计检测两种。前者的基本思想是:通过控制发射/接收端极化通道的加权,使接收信号中的目标回波相对于噪声或杂波最强以达到目标检测的目的[112, 146],其代表是虚拟极化适配技术[92]及一系列最佳极化检测器[79, 147, 148];后者则建立可靠的目标、噪声或杂波的极化信息模型并基于统计判决准则实现目标检测,如高斯杂波背景下基于广义似然比检验(Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test, GLRT)的自适应极化检测器[131, 149]。
近年来国内外专家学者开始致力于提高目标极化检测方法的性能和适用性[150]。在最优接收检测方面,文献[102]对多干扰条件下的虚拟极化适配进行了推广,文献[151]从雷达波形设计方面讨论了复合高斯杂波背景下的最佳极化自适应问题,文献[152]研究了杂波背景下的收发极化联合优化技术,文献[153]则针对非均匀噪声环境以最大化检测概率为准则设计了最佳极化发射波形,并提出一种恒虚警自适应匹配检测器。对于不同的杂波背景,极化检测器的基本要求是能够在未知杂波统计特性的情况下实现目标的自适应检测,以复合高斯背景为例,基于GLRT[154]、Wald检验[155]、广义匹配子空间准则[156]的一系列次优检测器尽管不能达到一致最优,但仍具有较高的检测性能和良好的鲁棒性。结合特定的极化信息(如极化特征量-联合熵间距、极化聚类中心特征等)和统计检验准则(如GLRT、贝叶斯检验等),极化检测理论逐渐开始在更广泛的场景下得到应用,文献[157]还尝试将极化信息融入检测前跟踪算法,以提高高频地波雷达的目标检测和跟踪性能。
在传统的统计检测的基础上,文献[158]利用多级决策融合思想提高检测概率,而超光谱数据[159]、频谱相干性[160]等信息也可与极化信息融合用于目标检测。实际上,目标检测也是对目标和杂波进行分类与识别的过程,因此同样可以利用极化熵[161]、主散射成分[162]等特征量进行目标检测,相关的极化分解方法将在下一小节有所论述。
显然,目标极化检测技术的渐趋成熟使得雷达在复杂多变的电磁环境下的探测能力大大提高,然而,在更广泛的应用场景下,如何充分利用极化信息实现更好、更快的最佳极化适配和自适应检测仍是极具价值的研究方向。
5.2 目标分类与识别基于极化信息的目标分类与识别是现代雷达提升战场侦察、地理观测等能力的重要技术手段之一,其基本思想是利用从观测数据中提取的目标极化特征进行鉴别,处理流程[163]如图 3。显然,对目标极化特性的研究和极化特征的精确提取技术是整个过程的关键。

|
图 3 极化雷达目标分类与识别流程 Fig.3 Routine of target classification and identification in polarimetric radar systems |
自雷达极化学形成以来,大量的理论研究和实验验证已经极大程度上丰富了对各类目标回波极化特性的了解。分类与识别所利用的目标极化特征一般可分为以下几类:由直接测量数据经简单运算或统计分析构造的目标特征,如极化不变量、瞬态统计特性等;经某些数学变换(如目标极化分解、小波变换)得到的目标特征;其他特征,如SAR图像的纹理特征等。
早期的窄带低分辨雷达主要利用散射矩阵的行列式、迹以及去极化系数、本征极化等“极化不变量[164]”作为衡量指标进行分类与识别,文献[165]又引入了两个新的不变量,即不可逆角度、散射矩阵对称和反对称部分的绝对相位差,进一步丰富了可用的极化特征量。然而,尽管这些“极化不变量”反映了特定取向下的窄带极化散射特性,但据此仅能获得目标结构或特性的粗糙信息[166],因此,目前多应用于具有远距离探测、反隐身功能的窄带雷达进行不同目标及诱饵的区分,以满足防空反导等战场需求[167]。
对于宽带雷达系统而言,目标的分类与识别多基于1维距离像或2维SAR/ISAR图像,结合极化信息与雷达的高分辨能力以提高分类与识别的精细程度。基于1维距离像的分类与识别的基本立足点是回波极化特征随时域[168]、频域[169]或联合域[170]信息呈动态变化,借助瞬态极化特性或散射中心特征实现对各类陆/海/空目标的分类与识别[110, 168, 171]。在2维SAR/ISAR成像中,对目标极化散射矩阵进行特定的数学变换以进一步提取用于分类和识别的目标特征是主要的技术手段之一,其中最为常用的是极化目标分解[172]。
目标极化分解方法最早可追溯到上世纪70年代[166],经过不断地研究和发展,已可用于揭示散射体的奇/偶次散射、面/体(球、二面角、螺旋体)散射、漫散射、交叉散射、布拉格散射等散射机理,其基本思想是:通过将目标散射分解为各种简单散射或各类基本目标的加权组合,即可对各散射分量的成分进行分析并提取有用的极化特征量(如散射矢量[19],散射熵[173, 174],反熵[175],散射角[176],复Wishart距离[177]),从而描述各类复杂目标的特性和几何结构。目前极化分解方法已经相当丰富,其针对的对象可以是相干或非相干目标,利用的信息可以是目标模型或特征矢量等参量,而按照分解针对的目标矩阵不同,可将其分为以下4类:基于Sinclair散射矩阵的相干目标分解法(如Krogager分解[178]以及Cameron分解[175, 179]等)、基于Mueller散射矩阵的Huynen分解法[166, 180]、基于目标协方差矩阵的分解方法[181, 182, 183]、基于相干矩阵的非相干目标分解方法[184](如H/alpha分解方法[176, 185, 186]等)。其中,第1种主要用于单视极化成像数据,后3种则用于多视极化成像数据。鉴于这4种目标矩阵之间存在一定的映射关系,各类目标极化分解方法实际上都可以互相推广。
基于提取的极化特征量和其他有用信息,结合支撑向量机[187]、聚类[188, 189]、小波理论[190, 191]、神经网络[192]等适当的数据处理或图像处理方法即可进行目标分类与识别。按照是否需要训练样本等先验知识可将分类方法分为监督分类[187, 193, 194]和非监督分类[177, 186, 188, 189, 195],前者以贝叶斯方法[194]为代表,其分类精度和复杂度都较高,但由于先验信息的获取难度导致了算法应用上的局限性;后者则以复Wishart分类器[177]为代表,由于不存在训练过程因此相对简单高效。而目标识别就是结合分类结果和已知的目标特征信息进行最终判决的过程[196, 197],随着雷达极化理论的完善,可获得的目标特征量越来越丰富,目标的分类与自动识别结果也更加精确[198, 199],如今已在战场监视、环境监测、地形分析等方面得到广泛应用。
另外,通过极化信号处理技术改善雷达成像质量或对目标材质、结构、姿态等参数反演的精度也是提高分类与识别能力的途径之一。文献[200, 201, 202]利用极化白化滤波等方法对SAR图像固有的相干斑进行了抑制处理,文献[203, 204]利用极化对比增强技术显著提高了SAR图像的信杂比,文献[175, 205]则研究了利用极化信息进行目标特性或几何结构反演的方法。近年来极化干涉SAR[206]逐渐受到重视,该体制根据全局相干最优[207]或子空间相干最优[208]原则优化两幅干涉图像对应的极化状态组合以提高其相干性,从而结合InSAR与PolSAR技术使雷达兼具对散射体空间分布和形状、姿态等的敏感度,因此在地物分类[209]、植被高度估计[210]、隐藏目标检测[211]及舰船目标识别[212]等领域得到广泛应用。为实现3维成像[213, 214],可利用同一场景下不同角度的观测数据进一步结合层析成像技术实现垂直航向的目标分辨,使雷达对目标的分类与识别能力得到质的提升[215, 216, 217, 218]。而除了全极化干涉SAR以外,基于简缩极化干涉SAR[219]的目标分类与识别也成为了近几年的热门研究方向之一,其本质是利用简缩极化测量数据重构伪全极化干涉数据,再通过适当的算法实现目标分类与识别[220, 221],但由于目前简缩极化测量体制应用仍十分有限,因此相关的理论和算法仍处于论证和探索阶段。
6 总结与展望得益于极化信息的充分利用,极化信号处理技术显著地提高了雷达的信息获取、抗各类杂波/干扰、目标检测、分类与识别能力,并已广泛应用于防空反导、战场监视预警、气象观测、地质勘探、环境监测、地理遥感与成像等军用和民用领域。极化雷达的显著优势为其带来了巨大的机遇,使其得以飞速发展,但仍然存在一些亟待解决的问题:
(1) 降低系统软/硬件升级带来的成本。极化分集增加了硬件设备单元的数量和系统结构的复杂性,而为追求各方面更高的性能,复杂的极化信号处理技术带来的大数据量和高时间成本问题也对存储、运算设备提出了更高的要求,因此,必须在系统性能和时间、经济成本之间取得适当的折中。
(2) 复杂目标电磁散射机理的深刻揭示。现有的电磁散射机理建模与表征方法虽然能够适用于典型目标甚至复杂目标[222, 223],但多未考虑极化;而早期对目标极化散射特性的获取方法一般是由现象到本质的总结与验证过程,对于复杂目标(电大尺寸、复杂结构、宽带)全极化散射特性的建模与表征仍不充分,难以为后续信号处理提供有力的理论支撑。
(3) 从提高性能、降低复杂度、减小运算量、扩展适用性等方面对极化信号处理算法进行优化。
尽管如此,随着国内外学者和研究机构对极化雷达重视程度、科研成本投入以及软/硬件水平的不断提高,极化雷达信号处理技术必将得到更强力的推动和更广泛的应用,拥有广阔的发展前景。
| [1] |
Sinclair G. The transmission and reception of elliptically polarized waves[J].
Proceedings of the IRE , 1950, 38 (2) : 148-151 DOI:10.1109/JRPROC.1950.230106 ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
代大海, 廖斌, 肖顺平, 等. 雷达极化信息获取与处理的研究进展[J].
雷达学报 , 2016, 5 (2) : 143-155 Dai Da-hai, Liao Bin, Xiao Shun-ping, et al. Advancements on radar polarization information acquisition and processing[J].
Journal of Radars , 2016, 5 (2) : 143-155 ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
Mott H.
Polarization in Antennas and Radar[M]. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 1986 .
( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J].
雷达学报 , 2016, 5 (2) : 119-131 Wang Xue-song. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J].
Journal of Radars , 2016, 5 (2) : 119-131 ( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
庄钊文, 肖顺平, 王雪松.
雷达极化信息处理及其应用[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1999 .
Zhuang Zhao-wen, Xiao Shun-ping, Wang Xue-song.
Radar Polarization Information Processing and Application[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 1999 .
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
李永祯, 李棉全, 程旭, 等. 雷达极化测量体制研究综述[J].
系统工程与电子技术 , 2013, 35 (9) : 1873-1877 Li Yong-zhen, Li Mian-quan, Cheng Xu, et al. Summarization of radar polarization measurement mode[J].
Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2013, 35 (9) : 1873-1877 ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
McCormick G C. On the completeness of polarization diversity measurements[J].
Radio Science , 1989, 24 (4) : 511-518 DOI:10.1029/RS024i004p00511 ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
Arthur J S, Henry J C, Pettengill G H, et al. The millstone radar in satellite and missile tracking[J].
Planetary and Space Science , 1961, 7 : 81-93 DOI:10.1016/0032-0633(61)90289-6 ( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
Tsunoda R T, Baron M J, and Owen J. ALTAIR:An incoherent scatter radar for equatorial spread-F studies[R]. SRI International Menlo Park CA, 1978.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
Huynen J R. Measurement of the target scattering matrix[J].
Proceedings of the IEEE , 1965, 53 (8) : 936-946 DOI:10.1109/PROC.1965.4072 ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
Santalla V, Antar Y M M. A comparison between different polarimetric measurement schemes[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2002, 40 (5) : 1007-1017 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2002.1010888 ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
常宇亮.瞬态极化雷达测量、检测与抗干扰技术研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2010.
Chang Yu-liang. Study on measurement, detection and interference suppression technologies of instantaneous polarimetric radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2010.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-1011074056.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
Gao S, Sambell A, Zhong S S. Polarization-agile antennas[J].
IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine , 2006, 48 (3) : 28-37 DOI:10.1109/MAP.2006.1703396 ( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
Karabey O H, Bildik S, Bausch S, et al. Continuously polarization agile antenna by using liquid crystal-based tunable variable delay lines[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2013, 61 (1) : 70-76 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2012.2213232 ( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
Row J S, Shih C J. Polarization-diversity ring slot antenna with frequency agility[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2012, 60 (8) : 3953-3957 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2012.2201114 ( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
Ho K M J, Rebeiz G M. A 0.9~1.5 GHz microstrip antenna with full polarization diversity and frequency agility[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2014, 62 (5) : 2398-2406 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2014.2307295 ( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
Sachidananda M and Zrnic D S. Characteristics of echoes from alternately polarized transmission[R]. Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies, 1986.
( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
Giuli D, Facheris L, Fossi M, et al.. Simultaneous scattering matrix measurement through signal coding[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, 1990:258-262.
( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
Howard S D, Calderbank A R, Moran W. A simple signal processing architecture for instantaneous radar polarimetry[J].
IEEE Transactions on Information Theory , 2007, 53 (4) : 1282-1289 DOI:10.1109/TIT.2007.892809 ( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
Nord M E, Ainsworth T L, Lee J S, et al. Comparison of compact polarimetric synthetic aperture radar modes[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2009, 47 (1) : 174-188 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2008.2000925 ( 0) 0)
|
| [21] |
杨汝良, 戴博伟, 李海英. 极化合成孔径雷达极化层次和系统工作方式[J].
雷达学报 , 2016, 5 (2) : 132-142 Yang Ru-liang, Dai Bo-wei, Li Hai-ying. Polarization hierarchy and system operating architecture for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J].
Journal of Radars , 2016, 5 (2) : 132-142 ( 0) 0)
|
| [22] |
Souyris J C, Imbo P, Fjortoft R, et al. Compact polarimetry based on symmetry properties of geophysical media:The p/4 mode[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2005, 43 (3) : 634-646 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2004.842486 ( 0) 0)
|
| [23] |
Raney R K. Hybrid-polarity SAR architecture[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2007, 45 (11) : 3397-3404 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2007.895883 ( 0) 0)
|
| [24] |
Spudis P, Nozette S, Bussey B, et al. Mini-SAR:An imaging radar experiment for the Chandrayaan-1 mission to the Moon[J].
Current Science , 2009, 96 (4) : 533-539 ( 0) 0)
|
| [25] |
Raney R K, Spudis P D, Bussey B, et al. The lunar mini-RF radars:Hybrid polarimetric architecture and initial results[J].
Proceedings of the IEEE , 2011, 99 (5) : 808-823 DOI:10.1109/JPROC.2010.2084970 ( 0) 0)
|
| [26] |
Giuli D, Fossi M, Facheris L. Radar target scattering matrix measurement through orthogonal signals[J].
IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing , 1993, 140 (4) : 233-242 ( 0) 0)
|
| [27] |
王雪松, 王剑, 王涛, 等. 雷达目标极化散射矩阵的瞬时测量方法[J].
电子学报 , 2006, 34 (6) : 1020-1025 Wang Xue-song, Wang Jian, Wang Tao, et al. Instantaneous measurement of radar target polarization scattering matrix[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2006, 34 (6) : 1020-1025 ( 0) 0)
|
| [28] |
Chang Y L, Wang X S, Li Y Z, et al. The signal selection and processing method for polarization measurement radar[J].
Science in China Series F:Information Sciences , 2009, 52 (10) : 1926-1935 DOI:10.1007/s11432-009-0141-6 ( 0) 0)
|
| [29] |
刘勇.动态目标极化特性测量与极化雷达抗干扰新方法研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2011.
Liu Yong. Study on moving target polarization characteristic measurement and polarization radar anti-jamming techniques[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2011.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-1011303268.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [30] |
何密.同时极化测量体制雷达的校准方法研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012.
He Mi. Study on calibration methods for simultaneous measurement polarimetric radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-1013047583.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [31] |
陶利, 曲圣杰, 陈曦. 简述极化SAR定标处理技术研究进展[J].
遥感技术与应用 , 2016, 31 (3) : 459-467 Tao Li, Qu Sheng-jie, Chen Xi. The progress on research of polarimetric SAR calibration[J].
Remote Sensing Technology and Application , 2016, 31 (3) : 459-467 ( 0) 0)
|
| [32] |
Van Zyl J J. Calibration of polarimetric radar images using only image parameters and trihedral corner reflector responses[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1990, 28 (3) : 337-348 DOI:10.1109/36.54360 ( 0) 0)
|
| [33] |
Whitt M W, Ulaby F T, Polatin P, et al. A general polarimetric radar calibration technique[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1991, 39 (1) : 62-67 DOI:10.1109/8.64436 ( 0) 0)
|
| [34] |
Klein J D. Calibration of complex polarimetric SAR imagery using backscatter correlations[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 1992, 28 (1) : 183-194 DOI:10.1109/7.135444 ( 0) 0)
|
| [35] |
Quegan S. A unified algorithm for phase and cross-talk calibration of polarimetric data-theory and observations[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1994, 32 (1) : 89-99 DOI:10.1109/36.285192 ( 0) 0)
|
| [36] |
Ainsworth T L, Ferro-Famil L, Lee J S. Orientation angle preserving a posteriori polarimetric SAR calibration[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2006, 44 (4) : 994-1003 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2005.862508 ( 0) 0)
|
| [37] |
Fore A G, Chapman B D, Hawkins B P, et al. UAVSAR polarimetric calibration[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2015, 53 (6) : 3481-3491 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2014.2377637 ( 0) 0)
|
| [38] |
Freeman A. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to Faraday rotation[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2004, 42 (8) : 1617-1624 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2004.830161 ( 0) 0)
|
| [39] |
Shimada M, Isoguchi O, Tadono T, et al. PALSAR radiometric and geometric calibration[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2009, 47 (12) : 3915-3932 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2009.2023909 ( 0) 0)
|
| [40] |
Fujita M, Murakami C. Polarimetric radar calibration method using polarization-preserving and polarization-selective reflectors[J].
IEICE Transactions on Communications , 2005, 88 (8) : 3428-3435 ( 0) 0)
|
| [41] |
Villa A, Iannini L, Giudici D, et al. Calibration of SAR polarimetric images by means of a covariance matching approach[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2015, 53 (2) : 674-686 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2014.2326955 ( 0) 0)
|
| [42] |
Quegan S, Lomas M R. The interaction between Faraday rotation and system effects in synthetic aperture radar measurements of backscatter and biomass[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2015, 53 (8) : 4299-4312 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2015.2395138 ( 0) 0)
|
| [43] |
Novak L M, Sechtin M B, Cardullo M J. Studies of target detection algorithms that use polarimetric radar data[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 1989, 25 (2) : 150-165 DOI:10.1109/7.18677 ( 0) 0)
|
| [44] |
章力强, 陈信, 李相平, 等. 参数估计误差对极化滤波性能影响分析[J].
雷达科学与技术 , 2012, 10 (2) : 198-202 Zhang Li-qiang, Chen Xin, Li Xiang-ping, et al. Impact of parameter estimation error on polarization filtering performance[J].
Radar Science and Technology , 2012, 10 (2) : 198-202 ( 0) 0)
|
| [45] |
张国毅, 刘永坦. 高频地波雷达的三维极化滤波[J].
电子学报 , 2000, 28 (9) : 114-116 Zhang Guo-yi and Liu Yong-tan. Three dimension polarization filtering of HF ground wave radar[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2000, 28 (9) : 114-116 ( 0) 0)
|
| [46] |
刘爱军, 毛兴鹏, 杨俊炜, 等. 基于FrFT的高频雷达信号极化状态估计方法[J].
电波科学学报 , 2010, 25 (5) : 815-822 Liu Ai-jun, Mao Xin-peng, Yang Jun-wei, et al. Polarized state estimation methods based on FrFT for HF radar[J].
Chinese Journal of Radio Science , 2010, 25 (5) : 815-822 ( 0) 0)
|
| [47] |
Wong K T, Zoltowski M D. Uni-vector-sensor ESPRIT for multisource azimuth, elevation, and polarization estimation[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1997, 45 (10) : 1467-1474 DOI:10.1109/8.633852 ( 0) 0)
|
| [48] |
Yuan X. Estimating the DOA and the polarization of a polynomial-phase signal using a single polarized vector-sensor[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 2012, 60 (3) : 1270-1282 DOI:10.1109/TSP.2011.2177263 ( 0) 0)
|
| [49] |
Wong K T, Zoltowski M D. Self-initiating MUSIC-based direction finding and polarization estimation in spatio-polarizational beamspace[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2000, 48 (8) : 1235-1245 DOI:10.1109/8.884492 ( 0) 0)
|
| [50] |
Xu Y, Liu Z, Wong K T, et al. Virtual-manifold ambiguity in HOS-based direction-finding with electromagnetic vector-sensors[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2008, 44 (4) : 1291-1308 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2008.4667710 ( 0) 0)
|
| [51] |
Hua Y. A pencil-MUSIC algorithm for finding two-dimensional angles and polarizations using crossed dipoles[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1993, 41 (3) : 370-376 DOI:10.1109/8.233122 ( 0) 0)
|
| [52] |
Li J, Compton Jr R T. Angle and polarization estimation using ESPRIT with a polarization sensitive array[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1991, 39 (9) : 1376-1383 DOI:10.1109/8.99047 ( 0) 0)
|
| [53] |
徐友根, 刘志文. 基于累积量的极化敏感阵列信号DOA和极化参数的同时估计[J].
电子学报 , 2004, 32 (12) : 1962-1966 Xu You-gen and Liu Zhi-wen. Cumulant-based two-dimensional DOA and polarization estimation with a polarization sensitive array comprising a spatially stretched tripole[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2004, 32 (12) : 1962-1966 ( 0) 0)
|
| [54] |
Miron S, Le Bihan N, Mars J I. Quaternion-MUSIC for vector-sensor array processing[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 2006, 54 (4) : 1218-1229 DOI:10.1109/TSP.2006.870630 ( 0) 0)
|
| [55] |
赵继超, 陶海红, 计茹, 等. 基于三分量电磁矢量传感器的波达角和极化参数估计[J].
电波科学学报 , 2016, 31 (1) : 39-46 Zhao Ji-chao, Tao Ji-hong, Ji Ru, et al. Joint DOA and polarization parameters estimation based on three-component electromagnetic vector sensor[J].
Chinese Journal of Radio Science , 2016, 31 (1) : 39-46 ( 0) 0)
|
| [56] |
Xiao H K, Zou L, Xu B G, et al.. Direction and polarization estimation with modified quad-quaternion music for vector sensor arrays[C]. IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, 2014:352-357.
( 0) 0)
|
| [57] |
Miron S, Le Bihan N, Mars J I. Vector-sensor MUSIC for polarized seismic sources localization[J].
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing , 2005 (1) : 1-11 ( 0) 0)
|
| [58] |
Gong X F, Liu Z W, Xu Y G. Regularised parallel factor analysis for the estimation of direction-of-arrival and polarisation with a single electromagnetic vector-sensor[J].
IET Signal Processing , 2011, 5 (4) : 390-396 DOI:10.1049/iet-spr.2009.0221 ( 0) 0)
|
| [59] |
Tian Y, Sun X, Zhao S. Sparse-reconstruction-based direction of arrival, polarisation and power estimation using a cross-dipole array[J].
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation , 2015, 9 (6) : 727-731 ( 0) 0)
|
| [60] |
张国毅, 刘永坦. 三维极化滤波及其参数估计[J].
现代雷达 , 2000, 22 (3) : 39-43 Zhang Guo-yi and Liu Yong-tan. Three dimension polarization filtering and its parameter estimation[J].
Modern Radar , 2000, 22 (3) : 39-43 ( 0) 0)
|
| [61] |
Wong K T. Direction finding/polarization estimation-dipole and/or loop triad (s)[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2001, 37 (2) : 679-684 DOI:10.1109/7.937478 ( 0) 0)
|
| [62] |
Lundback J and Nordobo S. On polarization estimation using tripole arrays[C]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, 2003, 1:65-68.
( 0) 0)
|
| [63] |
Xu Y and Liu Z. Adaptive quasi-cross-product algorithm for uni-tripole tracking of moving source[C]. IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, 2006:1-4.
( 0) 0)
|
| [64] |
Yuan X. Diversely polarized antenna-array signal processing[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, 2012.
( 0) 0)
|
| [65] |
孙杰, 张晓娟, 方广有. 近地面三阵子天线估计电磁波到达角和极化参数[J].
物理学报 , 2013, 62 (19) : 1-5 Sun Jie, Zhang Xiao-juan, Fang Guang-you. Direction of arrival of EMW and polarization parameter estimation using tripole near the earth surface[J].
Acta Physica Sinica , 2013, 62 (19) : 1-5 ( 0) 0)
|
| [66] |
Zou L, Lasenby J, He Z. Direction and polarisation estimation using polarised cylindrical conformal arrays[J].
IET Signal Processing , 2012, 6 (5) : 395-403 DOI:10.1049/iet-spr.2011.0287 ( 0) 0)
|
| [67] |
刘帅, 闫锋刚, 金铭, 等. 基于四元数MUSIC的锥面共形阵列极化-DOA联合估计[J].
系统工程与电子技术 , 2016, 38 (1) : 1-7 Liu Shuai, Yan Feng-gang, Jin Ming, et al. Joint polarization-DOA estimation for conical conformal array based on quaternion MUSIC[J].
Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2016, 38 (1) : 1-7 ( 0) 0)
|
| [68] |
齐子森, 郭英, 王布宏, 等. 共形阵列天线信源方位与极化状态的联合估计算法[J].
电子学报 , 2012, 40 (12) : 2562-2566 Qi Zi-sen, Guo Ying, Wang Bu-hong, et al. Joint DOA and polarization estimation algorithm for conformal array antenna[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2012, 40 (12) : 2562-2566 ( 0) 0)
|
| [69] |
Fang Q, Han Y, Jin M, et al. Joint DOA and polarization estimation for unequal power sources[J].
International Journal of Antennas and Propagation , 2015 : 1-9 ( 0) 0)
|
| [70] |
Li J, Compton R T. Angle and polarization estimation in a coherent signal environment[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 1993, 29 (3) : 706-716 DOI:10.1109/7.220922 ( 0) 0)
|
| [71] |
Li J, Stoica P. Efficient parameter estimation of partially polarized electromagnetic waves[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 1994, 42 (11) : 3114-3125 DOI:10.1109/78.330371 ( 0) 0)
|
| [72] |
Ho K C, Tan K C, Tan B T G. Efficient method for estimating directions-of-arrival of partially polarized signals with electromagnetic vector sensors[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 1997, 45 (10) : 2485-2498 DOI:10.1109/78.640714 ( 0) 0)
|
| [73] |
Tao J W, Liu L, Lin Z Y. Joint DOA, range, and polarization estimation in the fresnel region[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2011, 47 (4) : 2657-2672 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2011.6034657 ( 0) 0)
|
| [74] |
Costa M, Richter A, Koivunen V. Unified array manifold decomposition based on spherical harmonics and 2-D Fourier basis[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 2010, 58 (9) : 4634-4645 DOI:10.1109/TSP.2010.2050315 ( 0) 0)
|
| [75] |
Costa M, Richter A, Koivunen V. DoA and polarization estimation for arbitrary array configurations[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 2012, 60 (5) : 2330-2343 DOI:10.1109/TSP.2012.2187519 ( 0) 0)
|
| [76] |
Van Wambeck S H, Ross A H. Performance of diversity receiving systems[J].
Proceedings of the IRE , 1951, 39 (3) : 256-264 DOI:10.1109/JRPROC.1951.231837 ( 0) 0)
|
| [77] |
Alamouti S M. A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications[J].
IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications , 1998, 16 (8) : 1451-1458 DOI:10.1109/49.730453 ( 0) 0)
|
| [78] |
Gesbert D, Shafi M, Shiu D, et al. From theory to practice:An overview of MIMO space-time coded wireless systems[J].
IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications , 2003, 21 (3) : 281-302 DOI:10.1109/JSAC.2003.809458 ( 0) 0)
|
| [79] |
Giuli D. Polarization diversity in radars[J].
Proceedings of the IEEE , 1986, 74 (2) : 245-269 DOI:10.1109/PROC.1986.13457 ( 0) 0)
|
| [80] |
Holt A R, Tan J. Separation of differential propagation phase and differential backscatter phase in polarisation diversity radar[J].
Electronics Letters , 1992, 28 (10) : 943-944 DOI:10.1049/el:19920597 ( 0) 0)
|
| [81] |
Antar Y, Hendry A, Schlesak J, et al. Measurements of ice depolarization at 28.56 GHz using the COMSTAR beacon simultaneously with a 16.5 GHz polarization diversity radar[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1982, 30 (5) : 858-866 DOI:10.1109/TAP.1982.1142911 ( 0) 0)
|
| [82] |
Da Silveira R B, Holt A R. An automatic identification of clutter and anomalous propagation in polarization-diversity weather radar data using neural networks[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2001, 39 (8) : 1777-1788 DOI:10.1109/36.942556 ( 0) 0)
|
| [83] |
Wang Y and Saillard J. Characterization of the scattering centers of a radar target with polarization diversity using polynomial rooting[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 2001, 5:2893-2896.
( 0) 0)
|
| [84] |
Salman R, Willms I, Reichardt L, et al.. On polarization diversity gain in short range UWB-Radar object imaging[C]. IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, 2012:402-406.
( 0) 0)
|
| [85] |
Holt A R, Humphries R G, and McGuinness R. Some advantages of using Polarisation Diversity illustrated through the analysis of radar data from a storm in central Alberta[C]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 1988, 1:237-240.
( 0) 0)
|
| [86] |
Vaughan R G. Polarization diversity in mobile communications[J].
IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology , 1990, 39 (3) : 177-186 DOI:10.1109/25.130998 ( 0) 0)
|
| [87] |
Akhoondzadeh-Asl L, Khan I, Hall P S. Polarisation diversity performance for on-body communication applications[J].
IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation , 2011, 5 (2) : 232-236 ( 0) 0)
|
| [88] |
Ndao P M, Erhel Y, Lemur D, et al. Test of HF (3-30 MHz) MIMO communication system based on polarisation diversity[J].
Electronics Letters , 2012, 48 (1) : 50-51 DOI:10.1049/el.2011.3288 ( 0) 0)
|
| [89] |
Cohen M N and Sjoberg E S. Intrapulse polarization agile radar[C]. Radar-82, 1982:7-11.
( 0) 0)
|
| [90] |
Cohen M N, Perry, and Baden M. Analysis of IPAR field performance[C]. 13th European Microwave Conference, 1983:133-141.
( 0) 0)
|
| [91] |
Efurd R, Cohen M, Sjoberg E. Advanced intrapulse polarization agile radar nears deployment[J].
Microwave System News , 1984, 14 (2) : 67-76 ( 0) 0)
|
| [92] |
乔晓林, 宋立众, 谢新华. 极化编码脉压雷达信号的相关检测[J].
系统工程与电子技术 , 2003, 25 (5) : 550-553 Qiao Xiao-lin, Song Li-zhong, Xie Xin-hua. Correlative detection of pulse-compression radar signal based on polarization coding[J].
Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2003, 25 (5) : 550-553 ( 0) 0)
|
| [93] |
宋立众, 乔晓林, 孟宪德. 圆极化捷变LFM脉冲压缩信号分析[J].
现代雷达 , 2005, 27 (2) : 43-46 Song Li-zhong, Qiao Xiao-lin, Meng Xian-de. Analysis of LFM pulse compression signal with circular polarization agility[J].
Modern Radar , 2005, 27 (2) : 43-46 ( 0) 0)
|
| [94] |
Song Li-zhong and Wang Miao. Study on a nonlinear frequency modulation signal with polarization-coded modulation[C]. IEEE International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, 2007:1-4.
( 0) 0)
|
| [95] |
宋立众, 吴群. 一种极化和频率捷变主动雷达信号处理技术[J].
南京理工大学学报(自然科学版) , 2010, 34 (5) : 668-674 Song Li-zhong and Wu Qun. Signal processing technique for active radar with polarization and frequency agility[J].
Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science) , 2010, 34 (5) : 668-674 ( 0) 0)
|
| [96] |
罗金亮, 党立坤. 极化编码跳频信号在雷达中的应用[J].
兵工自动化 , 2008, 27 (5) : 29-30 Luo Jin-liang and Dang Li-kun. Application of polarize code frequency hopping signal in radar[J].
Ordnance Industry Automation , 2008, 27 (5) : 29-30 ( 0) 0)
|
| [97] |
陈歆炜, 赵建中, 吴文. 基于极化捷变编码技术的雷达抗欺骗干扰研究[J].
南京理工大学学报(自然科学版) , 2011, 35 (5) : 642-645 Chen Xin-wei, Zhao Jian-zhong, Wu Wen. Radar anti-deception based on polarization agile coding technology[J].
Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Natural Science) , 2011, 35 (5) : 642-645 ( 0) 0)
|
| [98] |
Nathanson F E. Adaptive circular polarization[C]. International Radar Conference, 1975, 1:221-225.
( 0) 0)
|
| [99] |
庄钊文, 徐振海, 肖顺平, 等.
极化敏感阵列信号处理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005 .
Zhuang Zhao-wen, Xu Zhen-hai, Xiao Shun-ping, et al.
Signal Processing Based on Polarization Sensitive Array[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2005 .
( 0) 0)
|
| [100] |
施龙飞, 任博, 马佳智, 等. 雷达极化抗干扰技术进展[J].
现代雷达 , 2016, 38 (4) : 1-7 Shi Long-fei, Ren Bo, Ma Jia-zhi, et al. Recent developments of radar anti-interference techniques with polarimetry[J].
Modern Radar , 2016, 38 (4) : 1-7 ( 0) 0)
|
| [101] |
Poelman A J. Virtual polarisation adaptation a method of increasing the detection capability of a radar system through polarisation-vector processing[J].
IEE Proceedings F Communications, Radar and Signal Processing , 1981, 128 (5) : 261-270 DOI:10.1049/ip-f-1.1981.0044 ( 0) 0)
|
| [102] |
Poelman A J, Guy J R F. Multinotch logic-product polarisation suppression filters:A typical design example and its performance in a rain clutter environment[J].
IEE Proceedings F Communications, Radar and Signal Processing , 1984, 131 (4) : 383-396 DOI:10.1049/ip-f-1.1984.0059 ( 0) 0)
|
| [103] |
Poelman A J, Guy J R F. Nonlinear polarisation-vector translation in radar systems[J].
IEE Proceedings F Communications, Radar and Signal Processing , 1984, 131 (5) : 451-465 DOI:10.1049/ip-f-1.1984.0071 ( 0) 0)
|
| [104] |
张国毅, 刘永坦. 实数加权极化变换法[J].
电子学报 , 2000, 28 (3) : 69-72 Zhang Guo-yi and Liu Yong-tan. Real weighting polarization vector translation[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2000, 28 (3) : 69-72 ( 0) 0)
|
| [105] |
Giuli D, Fossi M, and Gherardelli M. A technique for adaptive polarization filtering in radars[C]. International Radar Conference, 1985, 1:213-219.
( 0) 0)
|
| [106] |
Gherardelli M, Giuli D, Fossi M. Suboptimum adative polarisation cancellers for dual-polarisation radars[J].
IEE Proceedings F Communications, Radar and Signal Processing , 1988, 135 (1) : 60-72 DOI:10.1049/ip-f-1.1988.0008 ( 0) 0)
|
| [107] |
Poelman A J, Hilgers C J. Effectiveness of multinotch logic-product polarisation filters in radar for countering rain clutter[J].
IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing , 1991, 138 (5) : 427-437 DOI:10.1049/ip-f-2.1991.0056 ( 0) 0)
|
| [108] |
Unal C M H, Moisseev D N. Combined Doppler and polarimetric radar measurements:Correction for spectrum aliasing and nonsimultaneous polarimetric measurements[J].
Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology , 2004, 21 (3) : 443-456 DOI:10.1175/1520-0426(2004)021<0443:CDAPRM>2.0.CO;2 ( 0) 0)
|
| [109] |
Moisseev D N, Chandrasekar V. Polarimetric spectral filter for adaptive clutter and noise suppression[J].
Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology , 2009, 26 (2) : 215-228 DOI:10.1175/2008JTECHA1119.1 ( 0) 0)
|
| [110] |
王雪松.宽带极化信息处理的研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 1999.
Wang Xue-song. Study on wideband polarization information processing[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 1999.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2006194227.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [111] |
徐振海.极化敏感阵列信号处理的研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2004.
Xu Zhen-hai. Signal processing based on polarization sensitive array[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2004.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2005014455.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [112] |
王雪松, 庄钊文, 肖顺平, 等. 极化信号的优化接收理论:完全极化情形[J].
电子学报 , 1998, 26 (6) : 42-46 Wang Xue-song, Zhuang Zhao-wen, Xiao Shun-ping, et al. The theory of optimal reception of polarized signals:The purley polarized case[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 1998, 26 (6) : 42-46 ( 0) 0)
|
| [113] |
王雪松, 庄钊文, 肖顺平, 等. 极化信号的优化接收理论:部分极化情形[J].
电子科学学刊 , 1998, 20 (4) : 468-473 Wang Xue-song, Zhuang Zhao-wen, Xiao Shun-ping, et al. The theory of optimal reception of polarized signals:The partially polarized case[J].
Journal of Electronics , 1998, 20 (4) : 468-473 ( 0) 0)
|
| [114] |
毛兴鹏, 刘永坦. 极化滤波技术的有效性研究[J].
哈尔滨工业大学学报 , 2002, 34 (4) : 577-580 Mao Xing-peng and Liu Yong-tan. Validity of polarization filtering technique[J].
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology , 2002, 34 (4) : 577-580 ( 0) 0)
|
| [115] |
张国毅, 刘永坦. 高频地波超视距雷达的极化滤波技术研究[J].
系统工程与电子技术 , 2000, 22 (3) : 55-57 Zhang Guo-yi and Liu Yong-tan. Study of the polarization filtering technique of HF ground wave radar[J].
Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2000, 22 (3) : 55-57 ( 0) 0)
|
| [116] |
Xingpeng M, Yongtan L, Weibo D. Radio disturbance of high frequency surface wave radar[J].
Electronics Letters , 2004, 40 (3) : 202-203 DOI:10.1049/el:20040138 ( 0) 0)
|
| [117] |
毛兴鹏, 刘永坦, 邓维波, 等. 零相移瞬时极化滤波器[J].
电子学报 , 2004, 32 (9) : 1495-1498 Mao Xing-peng, Liu Yong-tan, Deng Wei-bo, et al. Null phase-shift instantaneous polarization filter[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2004, 32 (9) : 1495-1498 ( 0) 0)
|
| [118] |
Mao X P, Liu Y T. Null phase-shift polarization filtering for high-frequency radar[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2007, 43 (4) : 1397-1408 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2007.4441747 ( 0) 0)
|
| [119] |
毛兴鹏, 刘永坦, 邓维波. 频域零相移多凹口极化滤波器[J].
电子学报 , 2008, 36 (3) : 537-542 Mao Xing-peng, Liu Yong-tan, Deng Wei-bo. Frequency domain null phase-shift multinotch polarization filter[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2008, 36 (3) : 537-542 ( 0) 0)
|
| [120] |
毛兴鹏, 刘爱军, 邓维波, 等. 斜投影极化滤波器[J].
电子学报 , 2010, 38 (9) : 2003-2008 Mao Xing-peng, Liu Ai-jun, Deng Wei-bo, et al. An oblique projecting polarization filter[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2010, 38 (9) : 2003-2008 ( 0) 0)
|
| [121] |
Mao X P, Liu A J, Hou H J, et al. Oblique projection polarisation filtering for interference suppression in high-frequency surface wave radar[J].
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation , 2012, 6 (2) : 71-80 ( 0) 0)
|
| [122] |
Mao X, Hong H, Deng W, et al. Research on polarization cancellation of nonstationary ionosphere clutter in HF radar system[J].
International Journal of Antennas and Propagation , 2015 : 1-12 ( 0) 0)
|
| [123] |
Nehorai A, Ho K C, Tan B T G. Minimum-noise-variance beamformer with an electromagnetic vector sensor[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 1999, 47 (3) : 601-618 DOI:10.1109/78.747769 ( 0) 0)
|
| [124] |
张国毅, 刘永坦. 三维瞬时极化滤波器[J].
系统工程与电子技术 , 2000, 22 (5) : 55-57 Zhang Guo-yi and Liu Yong-tan. Three dimension instantaneous polarization filter[J].
Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2000, 22 (5) : 55-57 ( 0) 0)
|
| [125] |
Guoyi Z, Zhongji T, Jiantao W. Modification of polarization filtering technique in HF ground wave radar[J].
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2006, 17 (4) : 737-742 DOI:10.1016/S1004-4132(07)60008-5 ( 0) 0)
|
| [126] |
刘爱军, 宋立众, 王季刚, 等. 斜投影三维极化滤波[J].
哈尔滨工业大学学报 , 2012, 44 (3) : 75-80 Liu Ai-jun, Song Li-zhong, Wang Ji-gang, et al. Three-dimensions polarization filtering based on oblique projection[J].
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology , 2012, 44 (3) : 75-80 ( 0) 0)
|
| [127] |
罗佳.天线空域极化特性及应用[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2008.
Luo Jia. Application and analysis of spatial polarization characteristics for antenna[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2009213417.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [128] |
Dai H, Wang X, Luo J, et al. A new polarimetric method by using spatial polarization characteristics of scanning antenna[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2012, 60 (3) : 1653-1656 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2011.2180321 ( 0) 0)
|
| [129] |
Dai H, Wang X, Li Y. Novel discrimination method of digital deceptive jamming in mono-pulse radar[J].
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics , 2011, 22 (6) : 910-916 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4132.2011.06.006 ( 0) 0)
|
| [130] |
Dai H, Wang X, Li Y, et al. Main-lobe jamming suppression method of using spatial polarization characteristics of antennas[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2012, 48 (3) : 2167-2179 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2012.6237586 ( 0) 0)
|
| [131] |
Park H R, Li J, Wang H. Polarization-space-time domain generalized likelihood ratio detection of radar targets[J].
Signal Processing , 1995, 41 (2) : 153-164 DOI:10.1016/0165-1684(94)00097-J ( 0) 0)
|
| [132] |
Showman G A, Melvin W L, and Belenkii M. Performance evaluation of two polarimetric STAP architectures[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, 2003:59-65.
( 0) 0)
|
| [133] |
Park H R, Wang H. Adaptive polarisation-space-time domain radar target detection in inhomogeneous clutter environments[J].
IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation , 2006, 153 (1) : 35-43 DOI:10.1049/ip-rsn:20050018 ( 0) 0)
|
| [134] |
吴迪军.机载雷达极化空时自适应处理技术研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012.
Wu Di-jun. Study on polarization space time adaptive processing for airborne radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-1014048217.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [135] |
Tao J W, Chang W X. A novel combined beamformer based on hypercomplex processes[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2013, 49 (2) : 1276-1289 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2013.6494413 ( 0) 0)
|
| [136] |
Tao J W. Performance analysis for interference and noise canceller based on hypercomplex and spatio-temporal-polarisation processes[J].
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation , 2013, 7 (3) : 277-286 ( 0) 0)
|
| [137] |
文才, 王彤, 吴亿锋, 等. 极化-空域联合抗机载雷达欺骗式主瓣干扰[J].
电子与信息学报 , 2014, 36 (7) : 1552-1559 Wen Cai, Wang Tong, Wu Yi-feng, et al. Deceptive mainlobe jamming suppression for airborne radar based on joint processing in polarizational and spatial domains[J].
Journal of Electronics & Information Technology , 2014, 36 (7) : 1552-1559 ( 0) 0)
|
| [138] |
郭玉华, 常青美, 余道杰, 等. 一种改进的极化域-空域联合的自适应波束形成算法[J].
电子学报 , 2012, 40 (6) : 1279-1283 Guo Yu-hua, Chang Qing-mei, Yu Dao-jie, et al. An improved polarization-space adaptive beamforming algorithm[J].
Acta Electronica Sinica , 2012, 40 (6) : 1279-1283 ( 0) 0)
|
| [139] |
罗章凯, 王华力, 张翼鹏, 等. 极化阵列抗主瓣干扰性能研究[J].
电波科学学报 , 2015, 30 (3) : 504-509 Luo Zhang-kai, Wang Hua-li, Zhang Yi-peng, et al. Mainlobe anti-jamming performance of the polarization sensitive array[J].
Chinese Journal of Radio Science , 2015, 30 (3) : 504-509 ( 0) 0)
|
| [140] |
刘爱军.基于极化信息的高频地波雷达干扰抑制方法研究[D].[博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2011.
Liu Ai-jun. Research on interference mitigation methods based on polarization information for high frequency surface wave radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2011.
( 0) 0)
|
| [141] |
Hong H, Mao X, Hu C, et al.. Joint filtering of space-frequency-polarization domain based on vector sensitive array[C]. IEEE International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, 2011:670-673.
( 0) 0)
|
| [142] |
Hong H, Mao X P, and Hu C. A multi-domain collaborative filter for HFSWR based on oblique projection[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, 2012:907-912.
( 0) 0)
|
| [143] |
洪泓.高频地波雷达多域协同抗电离层杂波干扰方法研究[D].[博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014.
Hong Hong. Research on multidomain collaborative ionosphere clutter mitigation methods for high frequency surface wave radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1015957189.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [144] |
Mao X, Deng W. A multi-domain collaborative filter for interference suppressing[J].
IET Signal Processing , 2016 ( 0) 0)
|
| [145] |
邵春生. 相控阵雷达研究现状与发展趋势[J].
现代雷达 , 2016, 38 (6) : 1-4 Shao Chun-sheng. Study status and development trend of phased array radar[J].
Modern Radar , 2016, 38 (6) : 1-4 ( 0) 0)
|
| [146] |
Yamaguchi Y, Boerner W M, Eom H J, et al. On characteristic polarization states in the cross-polarized radar channel[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1992, 30 (5) : 1078-1080 DOI:10.1109/36.175344 ( 0) 0)
|
| [147] |
Chaney R D, Burl M C, and Novak L M. On the performance of polarimetric target detection algorithms[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, 1990:520-525.
( 0) 0)
|
| [148] |
Wicks M C, Annicola V C, Stiefvater K C, et al.. Polarization radar processing technology[C]. IEEE International Radar Conference, 1990:409-416.
( 0) 0)
|
| [149] |
De Maio A, Ricci G. A polarimetric adaptive matched filter[J].
Signal Processing , 2001, 81 (12) : 2583-2589 DOI:10.1016/S0165-1684(01)00150-5 ( 0) 0)
|
| [150] |
Calderbank R, Howard S D, Moran B. Waveform diversity in radar signal processing[J].
IEEE Signal Processing Magazine , 2009, 26 (1) : 32-41 DOI:10.1109/MSP.2008.930414 ( 0) 0)
|
| [151] |
Wang J, Nehorai A. Adaptive polarimetry design for a target in compound-Gaussian clutter[J].
Signal Processing , 2009, 89 (6) : 1061-1069 DOI:10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.12.018 ( 0) 0)
|
| [152] |
Xiao J J, Nehorai A. Joint transmitter and receiver polarization optimization for scattering estimation in clutter[J].
IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 2009, 57 (10) : 4142-4147 DOI:10.1109/TSP.2009.2022887 ( 0) 0)
|
| [153] |
Lei S, Zhao Z, Nie Z, et al. Adaptive polarimetric detection method for target in partially homogeneous background[J].
Signal Processing , 2015, 106 : 301-311 DOI:10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.07.019 ( 0) 0)
|
| [154] |
Younsi A, Greco M, Gini F, et al. Performance of the adaptive generalised matched subspace constant false alarm rate detector in non-Gaussian noise:An experimental analysis[J].
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation , 2009, 3 (3) : 195-202 ( 0) 0)
|
| [155] |
刘立东, 吴顺君, 孙晓闻. 复合高斯杂波中相干雷达极化自适应检测算法研究[J].
电子与信息学报 , 2006, 28 (2) : 326-329 Liu Li-dong, Wu Shun-Jun, Sun Xiao-wen. Polarimetric adaptive detection algorithm in compound-Gaussian clutter with coherent radar[J].
Journal of Electronics & Information Technology , 2006, 28 (2) : 326-329 ( 0) 0)
|
| [156] |
Alfano G, De Maio A, Conte E. Polarization diversity detection of distributed targets in compound-Gaussian clutter[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2004, 40 (2) : 755-765 DOI:10.1109/TAES.2004.1310021 ( 0) 0)
|
| [157] |
李发宗, 毛兴鹏, 常维国. 利用极化信息的高频地波雷达TBD检测算法[J].
哈尔滨工业大学学报 , 2016, 48 (5) : 36-42 Li Fa-zong, Mao Xing-peng, Chang Wei-guo. TBD algorithm based on polarization information of high frequency surface wave radar[J].
Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology , 2016, 48 (5) : 36-42 ( 0) 0)
|
| [158] |
Liu T and Lampropoulos G. A new polarimetric CFAR ship detection system[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006:137-140.
( 0) 0)
|
| [159] |
Zhao Y Q, Gong P, Pan Q. Object detection by spectropolarimeteric imagery fusion[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2008, 46 (10) : 3337-3345 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2008.920467 ( 0) 0)
|
| [160] |
Souyris J C, Henry C, Adragna F. On the use of complex SAR image spectral analysis for target detection:Assessment of polarimetry[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2003, 41 (12) : 2725-2734 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.817809 ( 0) 0)
|
| [161] |
Touzi R, Charbonneau F, Hawkins R K, et al.. Ship-sea contrast optimization when using polarimetric SARs[C]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2001, 1:426-428.
( 0) 0)
|
| [162] |
Chaoyang N, Debao M, Xiangfeng Z, et al.. Target detection and recognition based on polar decomposition and haugh transform[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2005, 7:4712-4714.
( 0) 0)
|
| [163] |
周晓光.极化SAR图像分类方法研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2008.
Zhou Xiao-guang. Polarimetric SAR image classification[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2009213166.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [164] |
Bickel S H. Some invariant properties of the polarization scattering matrix[J].
Proceedings of the IEEE , 1965, 53 (8) : 1070-1072 DOI:10.1109/PROC.1965.4088 ( 0) 0)
|
| [165] |
Karnychev V, Valery A K, Leo P L, et al. Algorithms for estimating the complete group of polarization invariants of the Scattering Matrix (SM) based on measuring all SM elements[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2004, 42 (3) : 529-539 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.817807 ( 0) 0)
|
| [166] |
Huynen J R. Phenomenological theory of radar targets[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], TU Delft, Delft University of Technology, 1970.
( 0) 0)
|
| [167] |
王涛.弹道中段目标极化域特征提取与识别[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2006.
Wang Tao. Feature extraction and recognition of targets in ballistic midcourse in polarization-domain[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2006.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2007141042.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [168] |
Chamberlain N E, Walton E K, Garber F D. Radar target identification of aircraft using polarization-diverse features[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 1991, 27 (1) : 58-67 DOI:10.1109/7.68148 ( 0) 0)
|
| [169] |
Ferrazzoli P, Guerriero L, Schiavon G. Experimental and model investigation on radar classification capability[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1999, 37 (2) : 960-968 DOI:10.1109/36.752214 ( 0) 0)
|
| [170] |
曾勇虎.极化雷达时频分析与目标识别的研究[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2004.
Zeng Yong-hu. Studies on time-frequency analysis and target recognition with polarimetric radar[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2004.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-90002-2005014452.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [171] |
肖顺平.宽带极化雷达目标识别的理论与应用[D].[博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 1995.
Xiao Shun-ping. Study on wideband polarimetric radar target recognition[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 1995.
( 0) 0)
|
| [172] |
Cloude S R, Pottier E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1996, 34 (2) : 498-518 DOI:10.1109/36.485127 ( 0) 0)
|
| [173] |
Cloude S R, Pottier E. Concept of polarization entropy in optical scattering[J].
Optical Engineering , 1995, 34 (6) : 1599-1610 DOI:10.1117/12.202062 ( 0) 0)
|
| [174] |
Frery A C, Cintra R J, Nascimento A D C. Entropy-based statistical analysis of PolSAR data[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2013, 51 (6) : 3733-3743 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2012.2222029 ( 0) 0)
|
| [175] |
Cameron W L, Youssef N N, Leung L K. Simulated polarimetric signatures of primitive geometrical shapes[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1996, 34 (3) : 793-803 DOI:10.1109/36.499784 ( 0) 0)
|
| [176] |
Lee J S, Grunes M R, Ainsworth T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1999, 37 (5) : 2249-2258 DOI:10.1109/36.789621 ( 0) 0)
|
| [177] |
Lee J S, Grunes M R, Kwok R. Classification of multi-look polarimetric SAR imagery based on complex Wishart distribution[J].
International Journal of Remote Sensing , 1994, 15 (11) : 2299-2311 DOI:10.1080/01431169408954244 ( 0) 0)
|
| [178] |
Krogager E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J].
Electronics Letters , 1990, 26 (18) : 1525-1527 DOI:10.1049/el:19900979 ( 0) 0)
|
| [179] |
Touzi R, Charbonneau F. Characterization of target symmetric scattering using polarimetric SARs[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2002, 40 (11) : 2507-2516 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2002.805070 ( 0) 0)
|
| [180] |
Yang J, Peng Y, Yamaguchi Y, et al. On Huynen's decomposition of a Kennaugh matrix[J].
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters , 2006, 3 (3) : 369-372 DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2006.873229 ( 0) 0)
|
| [181] |
Freeman A, Durden S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1998, 36 (3) : 963-973 DOI:10.1109/36.673687 ( 0) 0)
|
| [182] |
Yamaguchi Y, Moriyama T, Ishido M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2005, 43 (8) : 1699-1706 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084 ( 0) 0)
|
| [183] |
An W, Cui Y, Yang J. Three-component model-based decomposition for polarimetric SAR data[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2010, 48 (6) : 2732-2739 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2010.2041242 ( 0) 0)
|
| [184] |
Yamaguchi Y, Yajima Y, Yamada H. A four-component decomposition of POLSAR images based on the coherency matrix[J].
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters , 2006, 3 (3) : 292-296 DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2006.869986 ( 0) 0)
|
| [185] |
Cloude S R, Pottier E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1997, 35 (1) : 68-78 DOI:10.1109/36.551935 ( 0) 0)
|
| [186] |
Ferro-Famil L, Pottier E, Lee J S. Unsupervised classification of multifrequency and fully polarimetric SAR images based on the H/A/Alpha-Wishart classifier[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2001, 39 (11) : 2332-2342 DOI:10.1109/36.964969 ( 0) 0)
|
| [187] |
Lardeux C, Frison P L, Tison C, et al. Support vector machine for multifrequency SAR polarimetric data classification[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2009, 47 (12) : 4143-4152 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2009.2023908 ( 0) 0)
|
| [188] |
Kersten P R, Lee J S, Ainsworth T L. Unsupervised classification of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images using fuzzy clustering and EM clustering[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2005, 43 (3) : 519-527 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2004.842108 ( 0) 0)
|
| [189] |
Ersahin K, Cumming I G, Ward R K. Segmentation and classification of polarimetric SAR data using spectral graph partitioning[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2010, 48 (1) : 164-174 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2009.2024303 ( 0) 0)
|
| [190] |
Fukuda S, Hirosawa H. A wavelet-based texture feature set applied to classification of multifrequency polarimetric SAR images[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1999, 37 (5) : 2282-2286 DOI:10.1109/36.789624 ( 0) 0)
|
| [191] |
He C, Li S, Liao Z, et al. Texture classification of PolSAR data based on sparse coding of wavelet polarization textons[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2013, 51 (8) : 4576-4590 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2012.2236338 ( 0) 0)
|
| [192] |
Chen C T, Chen K S, Lee J S. The use of fully polarimetric information for the fuzzy neural classification of SAR images[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2003, 41 (9) : 2089-2100 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.813494 ( 0) 0)
|
| [193] |
Nezry E, Lopes A, Ducrot-Gambart D, et al. Supervised classification of K-distributed SAR images of natural targets and probability of error estimation[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1996, 34 (5) : 1233-1242 DOI:10.1109/36.536539 ( 0) 0)
|
| [194] |
Kouskoulas Y, Ulaby F T, Pierce L E. The Bayesian Hierarchical Classifier (BHC) and its application to short vegetation using multifrequency polarimetric SAR[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2004, 42 (2) : 469-477 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.821066 ( 0) 0)
|
| [195] |
Fjortoft R, Delignon Y, Pieczynski W, et al. Unsupervised classification of radar images using hidden Markov chains and hidden Markov random fields[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2003, 41 (3) : 675-686 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.809940 ( 0) 0)
|
| [196] |
Li H J, Lane R Y. Utilization of multiple polarization data for aerospace target identification[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1995, 43 (12) : 1436-1440 DOI:10.1109/8.475934 ( 0) 0)
|
| [197] |
Jones G, Bhanu B. Recognizing occluded objects in SAR images[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 2001, 37 (1) : 316-328 DOI:10.1109/7.913694 ( 0) 0)
|
| [198] |
马林. 雷达目标识别技术综述[J].
现代雷达 , 2011, 33 (6) : 1-7 Ma Lin. Review of radar automatic target recognition[J].
Modern Radar , 2011, 33 (6) : 1-7 ( 0) 0)
|
| [199] |
李丽亚.宽带雷达目标识别技术研究[D].[博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2009.
Li Li-ya. Study on wideband radar target recognition[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2009.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10701-2009195450.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [200] |
Novak L M, Burl M C. Optimal speckle reduction in polarimetric SAR imagery[J].
IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems , 1990, 26 (2) : 293-305 DOI:10.1109/7.53442 ( 0) 0)
|
| [201] |
Lopes A, Séry F. Optimal speckle reduction for the product model in multilook polarimetric SAR imagery and the Wishart distribution[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1997, 35 (3) : 632-647 DOI:10.1109/36.581979 ( 0) 0)
|
| [202] |
Lee J S, Ainsworth T L, Wang Y, et al. Polarimetric SAR speckle filtering and the extended sigma filter[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2015, 53 (3) : 1150-1160 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2014.2335114 ( 0) 0)
|
| [203] |
Kostinski A, Boerner W. On the polarimetric contrast optimization[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 1987, 35 (8) : 988-991 DOI:10.1109/TAP.1987.1144209 ( 0) 0)
|
| [204] |
Yang J, Dong G, Peng Y, et al. Generalized optimization of polarimetric contrast enhancement[J].
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters , 2004, 1 (3) : 171-174 DOI:10.1109/LGRS.2004.830127 ( 0) 0)
|
| [205] |
Potter L C, Moses R L. Attributed scattering centers for SAR ATR[J].
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , 1997, 6 (1) : 79-91 DOI:10.1109/83.552098 ( 0) 0)
|
| [206] |
Papathanassiou K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Technical University GRAZ, 1999.
( 0) 0)
|
| [207] |
Cloude S R, Papathanassiou K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 1998, 36 (5) : 1551-1565 DOI:10.1109/36.718859 ( 0) 0)
|
| [208] |
Sagues L, Lopez-Sanchez J M, Fortuny J, et al. Indoor experiments on polarimetric SAR interferometry[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2000, 38 (2) : 671-684 DOI:10.1109/36.841997 ( 0) 0)
|
| [209] |
Lee J S, Cloude S R, Papathanassiou K P, et al. Speckle filtering and coherence estimation of polarimetric SAR interferometry data for forest applications[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2003, 41 (10) : 2254-2263 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2003.817196 ( 0) 0)
|
| [210] |
Schneider R Z, Papathanassiou K P, Hajnsek I, et al. Polarimetric and interferometric characterization of coherent scatterers in urban areas[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2006, 44 (4) : 971-984 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2005.860950 ( 0) 0)
|
| [211] |
Cloude S R, Corr D G, Williams M L. Target detection beneath foliage using polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J].
Waves in Random Media , 2004, 14 (2) : S393-S414 DOI:10.1088/0959-7174/14/2/015 ( 0) 0)
|
| [212] |
Margarit G, Mallorqui J J, Fabregas X. Single-pass polarimetric SAR interferometry for vessel classification[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2007, 45 (11) : 3494-3502 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2007.897437 ( 0) 0)
|
| [213] |
Xing S, Li Y, Dai D, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of man-made objects using polarimetric tomographic SAR[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2013, 51 (6) : 3694-3705 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2012.2220145 ( 0) 0)
|
| [214] |
Fornaro G, Pauciullo A, Reale D, et al. Multilook SAR tomography for 3-D reconstruction and monitoring of single structures applied to COSMO-SKYMED data[J].
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing , 2014, 7 (7) : 2776-2785 DOI:10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2316323 ( 0) 0)
|
| [215] |
熊涛.极化干涉合成孔径雷达应用的关键技术研究[D].[博士论文], 清华大学, 2009.
Xiong Tao. Study on the key techniques of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2009.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10003-2010214986.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [216] |
卢红喜.极化干涉合成孔径雷达与层析成像技术研究[D].[博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2014.
Lu Hong-xi. Study on polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interferometry and tomography[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2014.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10701-1015437820.htm ( 0) 0)
|
| [217] |
Zhu X X, Bamler R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization-The compressive sensing approach[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2010, 48 (10) : 3839-3846 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 ( 0) 0)
|
| [218] |
Huang Y, Ferro-Famil L, Reigber A. Under-foliage object imaging using SAR tomography and polarimetric spectral estimators[J].
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing , 2012, 50 (6) : 2213-2225 DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2011.2171494 ( 0) 0)
|
| [219] |
Lavalle M, Solimini D, Pottier E, et al. Compact polarimetric SAR interferometry[J].
IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation , 2010, 4 (3) : 449-456 ( 0) 0)
|
| [220] |
Tan L, Huang P, Liu A, et al.. Investigation on unsupervised classification of compact PolInSAR data[C]. European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, 2012:517-520.
( 0) 0)
|
| [221] |
Guo S, Li Y, Yin Q, et al.. Applying the Freeman-Durden decomposition tocompact polarimetric SAR Interferometry[C]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2014:3486-3489.
( 0) 0)
|
| [222] |
Rousseau P R, Pathak P H, Chou H T. A time domain formulation of the uniform geometrical theory of diffraction for scattering from a smooth convex surface[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2007, 55 (6) : 1522-1534 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2007.897204 ( 0) 0)
|
| [223] |
Ergul Ö Ü, Gurel L. Efficient parallelization of the multilevel fast multipole algorithm for the solution of large-scale scattering problems[J].
IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation , 2008, 56 (8) : 2335-2345 DOI:10.1109/TAP.2008.926757 ( 0) 0)
|




