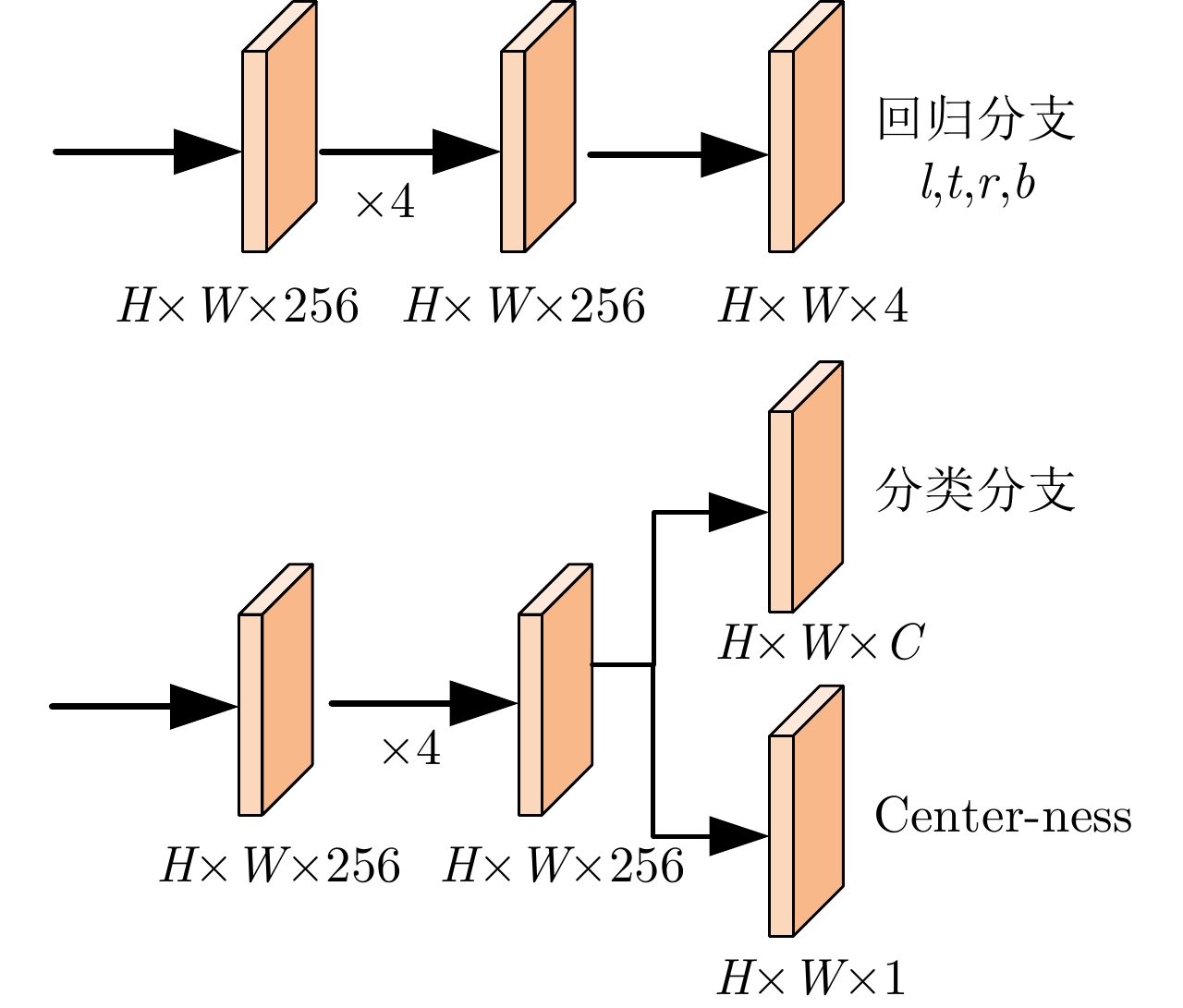
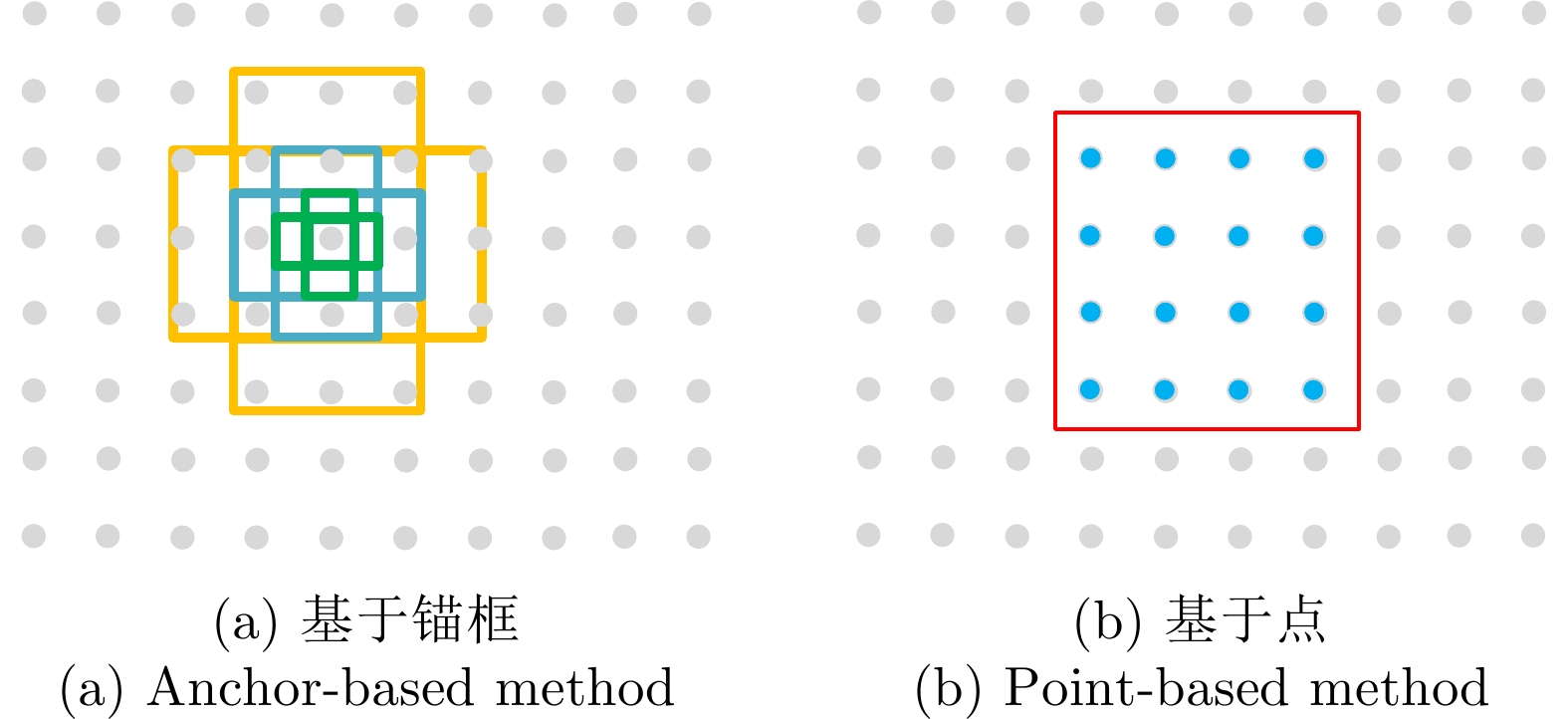
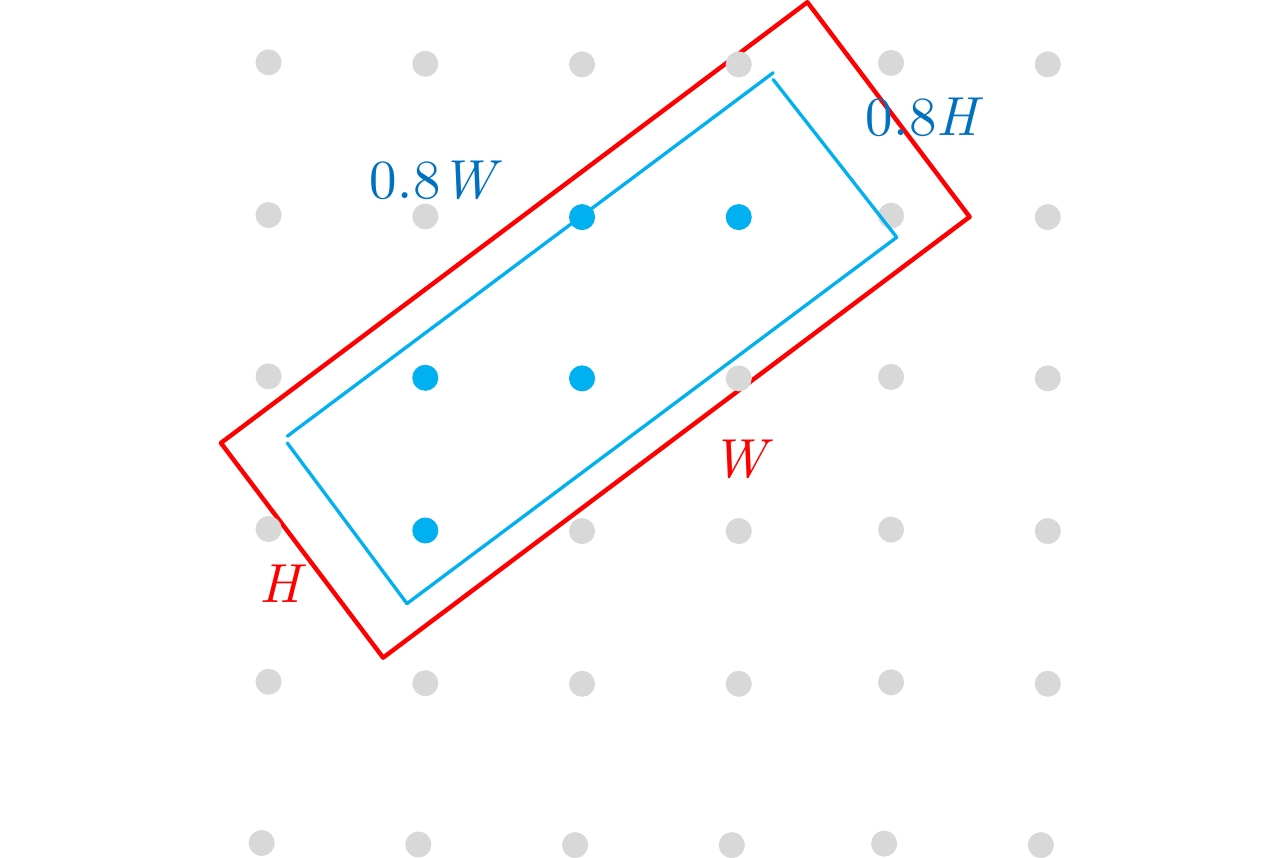
| [1] |
郭倩, 王海鹏, 徐丰. SAR图像飞机目标检测识别进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Research progress on aircraft detection and recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020 |
| [2] |
FAN Haiwei, SHI Shuang, LIN Qi, et al. Research on ship target detection algorithm in complex background SAR image[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2021, 31(10): 49–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2021.10.009 |
| [3] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and PENG Shujuan. A ship detection method based on cascade CNN in SAR images[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2191–2197. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0168 |
| [4] |
CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988 |
| [5] |
张晓玲, 张天文, 师君, 等. 基于深度分离卷积神经网络的高速高精度SAR舰船检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, SHI Jun, et al. High-speed and high-accurate SAR ship detection based on a depthwise separable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111 |
| [6] |
陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 |
| [7] |
WANG Zhen, WANG Buhong, and XU Nan. SAR ship detection in complex background based on multi-feature fusion and non-local channel attention mechanism[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(19): 7519–7550. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2021.1963003 |
| [8] |
WANG Yuanyuan, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, et al. Automatic ship detection based on RetinaNet using multi-resolution Gaofen-3 imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 531. doi: 10.3390/rs11050531 |
| [9] |
ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, XIONG Boli, et al. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2738–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997081 |
| [10] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, and KE Xiao. Quad-FPN: A novel quad feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(14): 2771. doi: 10.3390/rs13142771 |
| [11] |
LAW H and DENG Jia. CornerNet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(3): 642–656. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01204-1 |
| [12] |
ZHOU Xingyi, WANG Dequan, and KRÄHENBÜHL P. Objects as points[C]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1904.07850, 2019.
|
| [13] |
TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9626–9635.
|
| [14] |
KONG Tao, SUN Fuchun, LIU Huaping, et al. FoveaBox: Beyound anchor-based object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7389–7398. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3002345 |
| [15] |
CUI Zongyong, WANG Xiaoya, LIU Nengyuan, et al. Ship detection in large-scale SAR images via spatial shuffle-group enhance attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 379–391. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2997200 |
| [16] |
GUO Haoyuan, YANG Xi, WANG Nannan, et al. A CenterNet++ model for ship detection in SAR images[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 112: 107787. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107787 |
| [17] |
SUN Zhongzhen, DAI Muchen, LENG Xiangguang, et al. An anchor-free detection method for ship targets in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7799–7816. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3099483 |
| [18] |
FU Jiamei, SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, et al. An anchor-free method based on feature balancing and refinement network for multiscale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1331–1344. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3005151 |
| [19] |
MA Jianqi, SHAO Weiyuan, YE Hao, et al. Arbitrary-oriented scene text detection via rotation proposals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(11): 3111–3122. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2818020 |
| [20] |
JIANG Yingying, ZHU Xiangyu, WANG Xiaobing, et al. R2CNN: Rotational region CNN for orientation robust scene text detection[C]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.09579, 2017.
|
| [21] |
YANG Xue, YANG Jirui, YAN Junchi, et al. SCRDet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8231–8240.
|
| [22] |
YANG Xue, LIU Qingqing, YAN Junchi, et al. R3Det: Refined single-stage detector with feature refinement for rotating object[C]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1908.05612, 2019.
|
| [23] |
HAN Jiaming, DING Jian, XUE Nan, et al. ReDet: A rotation-equivariant detector for aerial object detection[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 2785–2794.
|
| [24] |
WANG Jizhou, LU Changhua, and JIANG Weiwei. Simultaneous ship detection and orientation estimation in SAR images based on attention module and angle regression[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 2851. doi: 10.3390/s18092851 |
| [25] |
LIU Lei, CHEN Guowei, PAN Zongxu, et al. Inshore ship detection in SAR images based on deep neural networks[C]. IGARSS 2018 - 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 25–28.
|
| [26] |
AN Quanzhi, PAN Zongxu, LIU Lei, et al. DRBox-v2: An improved detector with rotatable boxes for target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8333–8349. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2920534 |
| [27] |
CHEN Chen, HE Chuan, HU Changhua, et al. MSARN: A deep neural network based on an adaptive recalibration mechanism for multiscale and arbitrary-oriented SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 159262–159283. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951030 |
| [28] |
PAN Zhenru, YANG Rong, and ZHANG Zhimin. MSR2N: Multi-stage rotational region based network for arbitrary-oriented ship detection in SAR images[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 2340. doi: 10.3390/s20082340 |
| [29] |
CHEN Shiqi, ZHANG Jun, and ZHAN Ronghui. R 2FA-Det: Delving into high-quality rotatable boxes for ship detection in SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(12): 2031. doi: 10.3390/rs12122031 |
| [30] |
YANG Rong, WANG Gui, PAN Zhenru, et al. A novel false alarm suppression method for CNN-based SAR ship detector[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(8): 1401–1405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2999506 |
| [31] |
DAI Jifeng, QI Haozhi, XIONG Yuwen, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 764–773.
|
| [32] |
ZHANG Shifeng, CHI Cheng, YAO Yongqiang, et al. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 9756–9765.
|
| [33] |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 |
| [34] |
LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6.
|
| [35] |
WEI Shunjun, ZENG Xiangfeng, QU Qizhe, et al. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234–120254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005861 |
| [36] |
XIA Guisong, BAI Xiang, DING Jian, et al. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3974–3983.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: