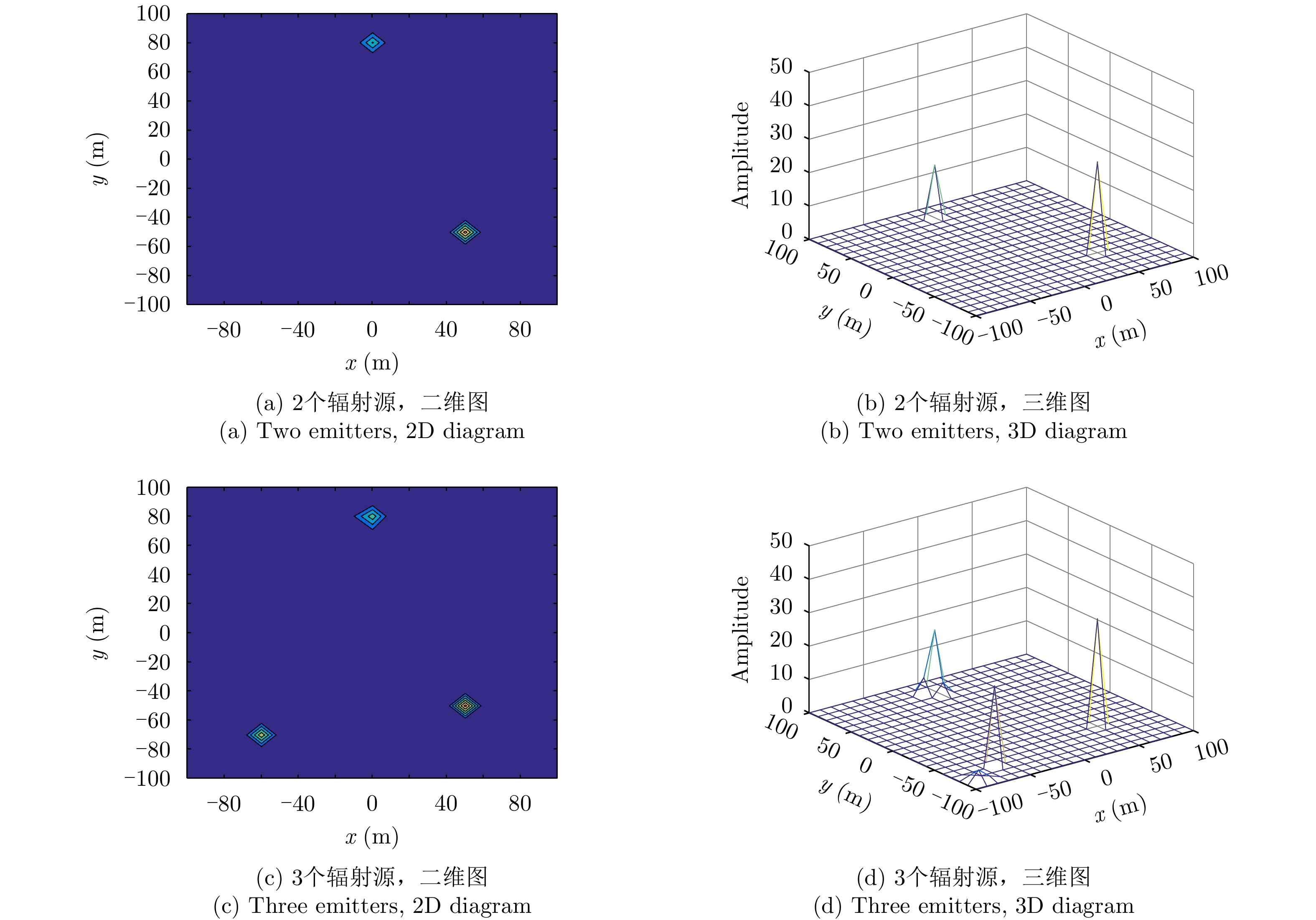
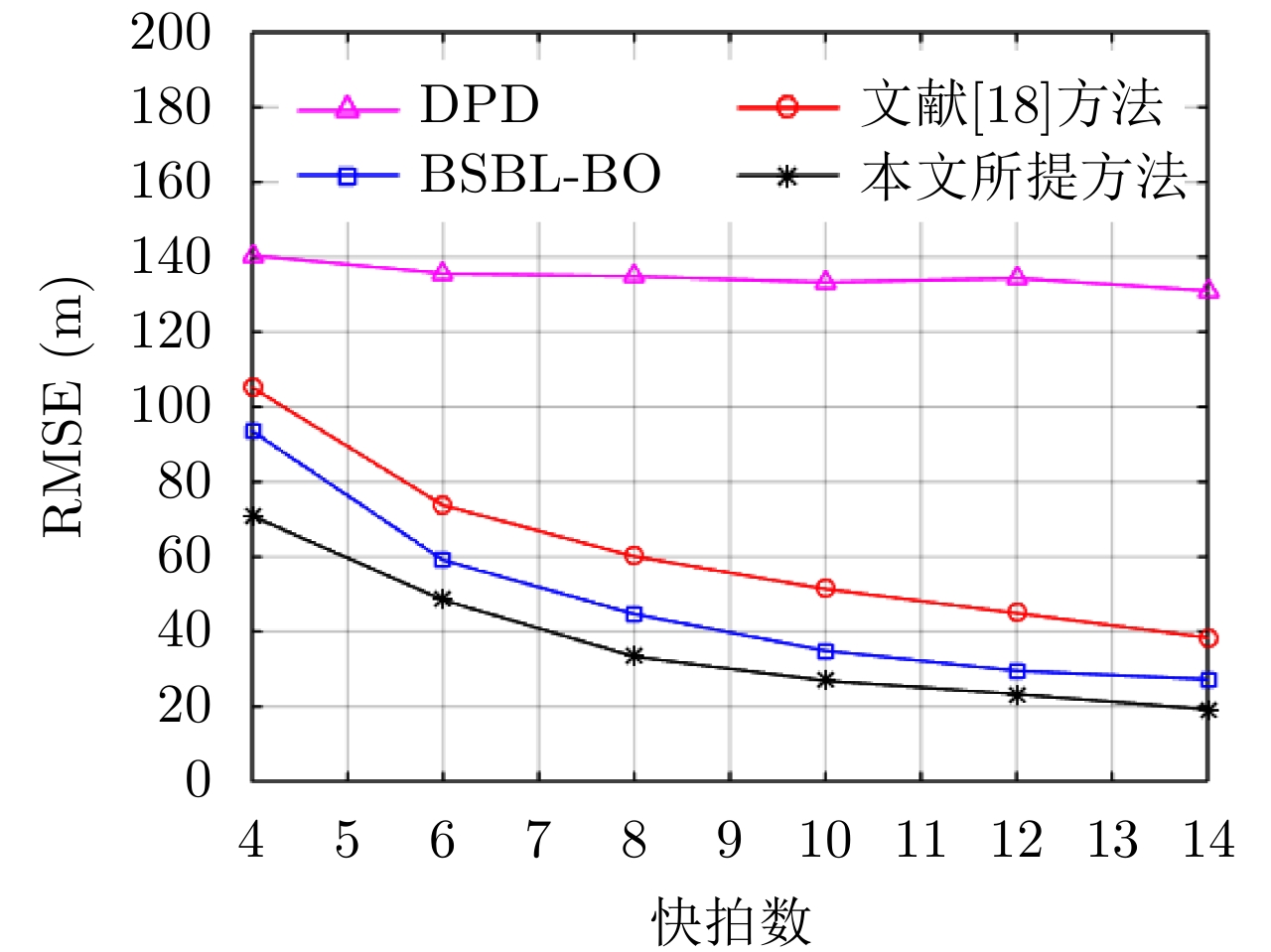
| [1] |
GUO Ying, FENG Mingyang, SUN Yuxi, et al. An improved algorithm of Bayesian fingerprint localization based on Bluetooth[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(5): 1–6. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2019.0138 |
| [2] |
SUN Sibo, ZHANG Xinyu, ZHENG Ce, et al. Underwater acoustical localization of the black box utilizing single autonomous underwater vehicle based on the second-order time difference of arrival[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(4): 1268–1279. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2950954 |
| [3] |
SUN Sibo, QIN Shasha, HAO Yu, et al. Underwater acoustic localization of the black box based on generalized second-order time difference of arrival (GSTDOA)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7245–7255. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3032982 |
| [4] |
WEISS A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 |
| [5] |
MALIOUTOV D, CETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 |
| [6] |
TIBSHIRANI R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: A retrospective[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B ( Statistical Methodology) , 2011, 73(3): 273–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x |
| [7] |
TIPPING M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1(3): 211–244. doi: 10.1162/15324430152748236 |
| [8] |
WIPF D P and RAO B D. Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2153–2164. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831016 |
| [9] |
ZHANG Zhilin and RAO B D. Sparse signal recovery with temporally correlated source vectors using sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2011, 5(5): 912–926. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2011.2159773 |
| [10] |
ZHANG Zhilin and RAO B D. Extension of SBL algorithms for the recovery of block sparse signals with intra-block correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(8): 2009–2015. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2241055 |
| [11] |
BABACAN S D, MOLINA R, and KATSAGGELOS A K. Bayesian compressive sensing using Laplace priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(1): 53–63. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2032894 |
| [12] |
NANNURU S, GEMBA K L, GERSTOFT P, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning with multiple dictionaries[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 159: 159–170. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.02.003 |
| [13] |
SUN Baoming, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Multiple target counting and localization using variational Bayesian EM algorithm in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(7): 2985–2998. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2695198 |
| [14] |
游康勇, 杨立山, 刘玥良, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的网格自适应多源定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238YOU Kangyong, YANG Lishan, LIU Yueliang, et al. Adaptive grid multiple sources localization based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238 |
| [15] |
CHEN Minqiu, MAO Xingpeng, and ZHAO Chunlei. Direct localization of emitters based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5769–5781. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2910831 |
| [16] |
YOU Kangyong, GUO Wenbin, PENG Tao, et al. Parametric sparse Bayesian dictionary learning for multiple sources localization with propagation parameters uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4194–4209. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3009875 |
| [17] |
SCHMITZ J, MATHAR R, and DORSCH D. Compressed time difference of arrival based emitter localization[C]. The 3rd International Workshop on Compressed Sensing Theory and its Applications to Radar, Sonar and Remote Sensing (CoSeRa), Pisa, Italy, 2015. doi: 10.1109/CoSeRa.2015.7330305. |
| [18] |
HINCAPIE R, GOMEZ C, BETANCUR L, et al. Sparse framework for hybrid TDoA/DoA multiple emitter localization[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Bilbao, Spain, 2017. doi: 10.1109/ISSPIT.2017.8388637. |
| [19] |
CARLIN M, ROCCA P, OLIVERI G, et al. Directions-of-arrival estimation through Bayesian compressive sensing strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(7): 3828–3838. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2256093 |
| [20] |
ZHANG Zhengchao and TONG Li. Precision analysis of passive location of 4-stations based on TDOA[J]. Journal of China Acadewy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2010, 5(6): 582–585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2010.06.007 |
| [21] |
TIRER T and WEISS A J. High resolution direct position determination of radio frequency sources[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(2): 192–196. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2503921 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: