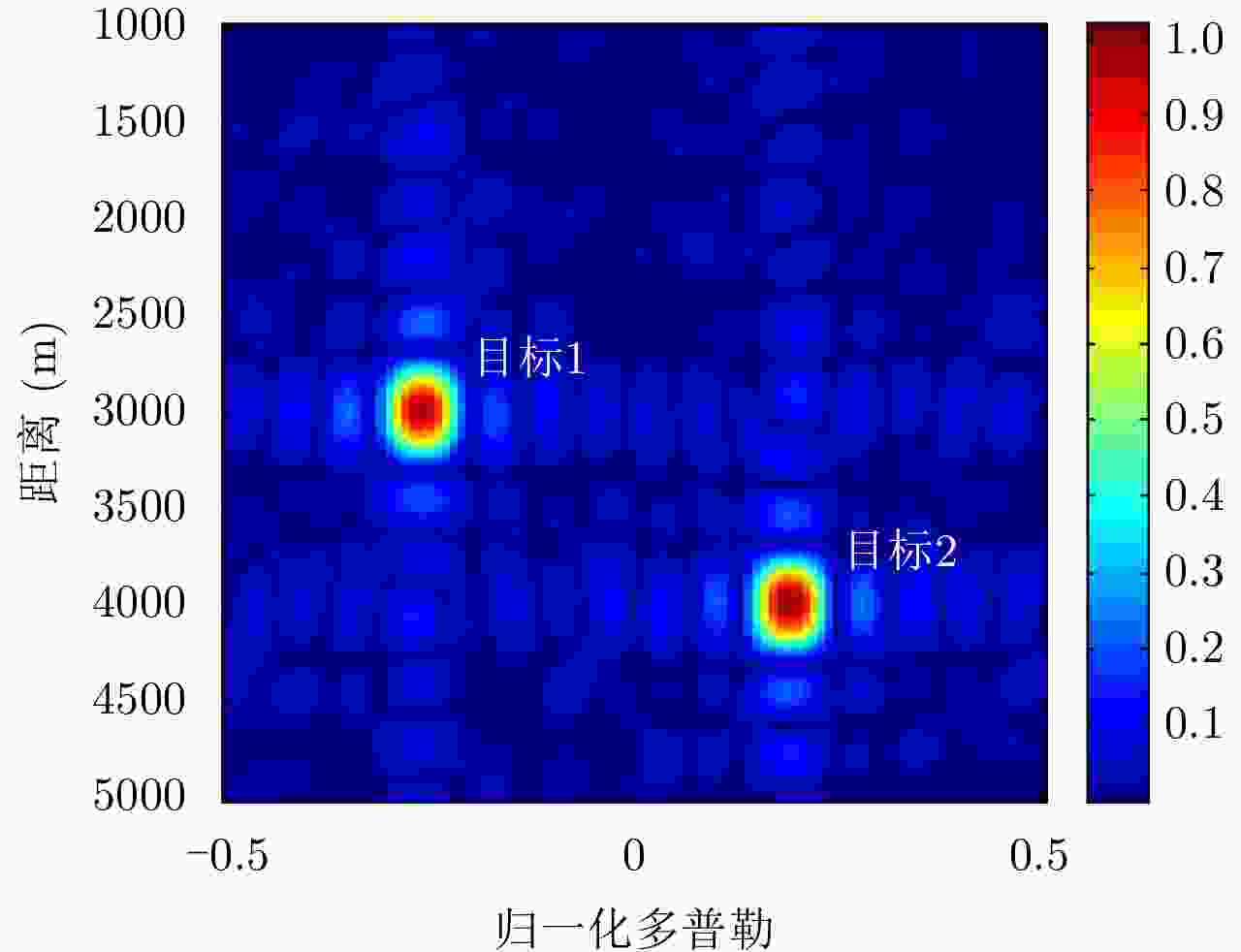
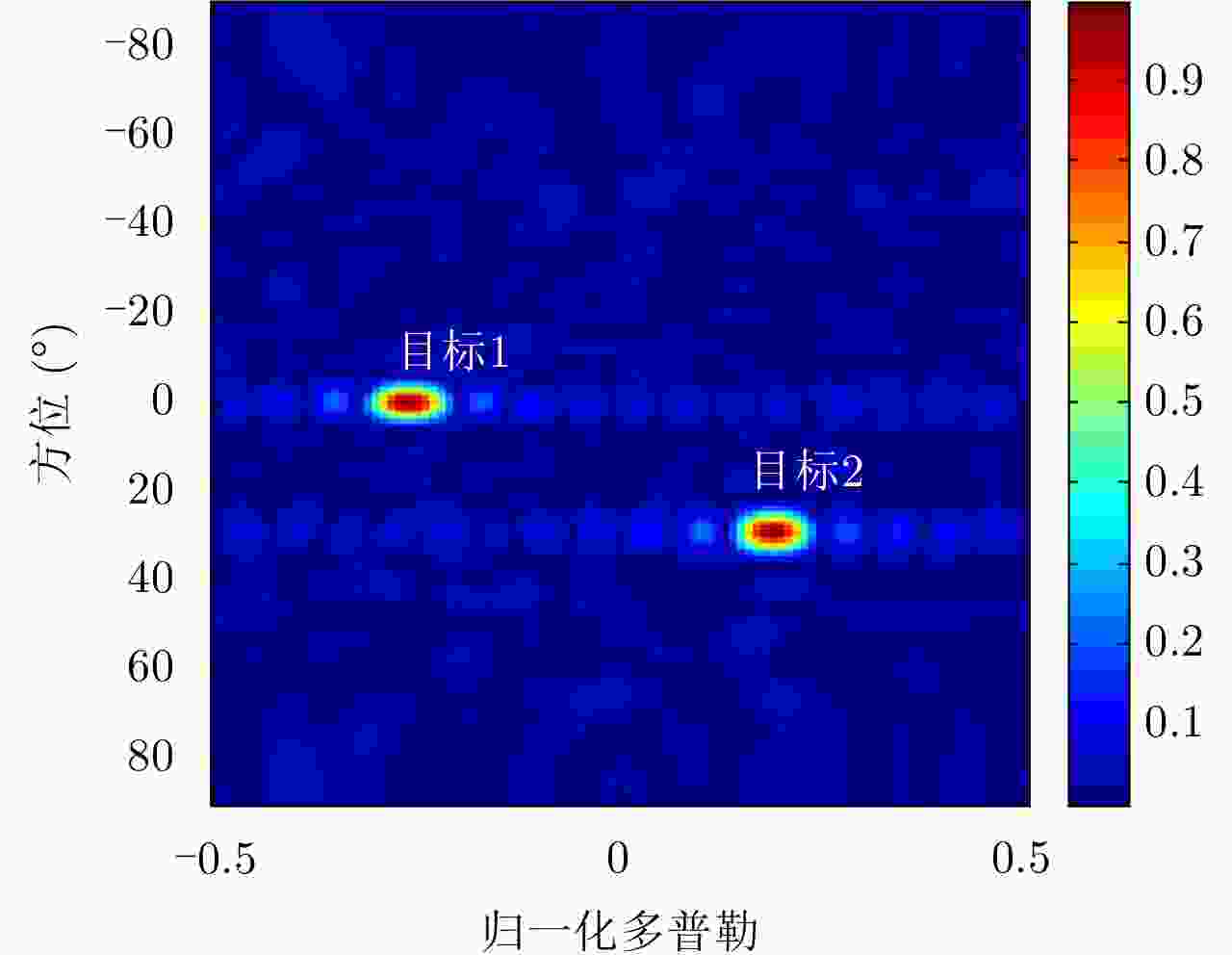
| [1] |
陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 19–27Chen Xiao-long, Guan Jian, Huang Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science&Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27
|
| [2] |
陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测目标探测技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(11): 30–38Chen Xiao-long, Guan Jian, Huang Yong, et al. Radar low-observable target detection[J]. Science&Technology Review, 2017, 35(11): 30–38
|
| [3] |
许稼, 彭应宁, 夏香根, 等. 空时频检测前聚焦雷达信号处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 129–141. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14023Xu Jia, Peng Ying-ning, Xia Xiang-gen, et al. Radar signal processing method of space-time-frequency focus-before-detects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 129–141. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14023
|
| [4] |
Haimovich A M, Blum R S, and Cimini L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. DOI: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448
|
| [5] |
Antonik P, Wicks M C, Griffiths H D, et al.. Range dependent beamforming using element level waveform diversity[C]. Proceedings of Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, LasVegas, 2006.
|
| [6] |
Zhang Z and Kayama H. Dynamic space-frequency-division multiple-access over frequency-selective slow-fading channels[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 63rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 2006: 2119–2124.
|
| [7] |
Farooq J, Temple M A, and Saville M A. Application of frequency diverse arrays to synthetic aperture radar imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2007 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Torino, Italy, 2007: 447–449.
|
| [8] |
Higgins T and Blunt S D. Analysis of range-angle coupled beamforming with frequency-diverse chirps[C]. Proceedings of 2009 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 2009: 140–144.
|
| [9] |
Huang J J. Frequency diversity array: Theory and design[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University College London, 2010.
|
| [10] |
Weber J, Oruklu E, and Saniie J. FPGA-based configurable frequency-diverse ultrasonic target-detection system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(3): 871–879. DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2030214
|
| [11] |
Wang W Q. Phased-MIMO radar with frequency diversity for range-dependent beamforming[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(4): 1320–1328. DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2012.2232909
|
| [12] |
Secmen M, Demir S, Hizal A, et al.. Frequency diverse array antenna with periodic time modulated pattern in range and angle[C]. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2007: 427–430.
|
| [13] |
Jones A M and Rigling B D. Frequency diverse array radarreceiver architectures[C]. Proceedings of 2012 InternationalWaveform Diversity & Design Conference, Kauai, HI, USA,2012: 211–217.
|
| [14] |
Basit A, Qureshi I M, Khan W, et al.. Cognitive frequency offset calculation for frequency diverse array radar[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2015: 641–645.
|
| [15] |
Khan W, Qureshi I M, Basit A, et al. Range-bins-based MIMO frequency diverse array radar with logarithmic frequency offset[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 885–888. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2478964
|
| [16] |
Wang W Q, So H C, and Farina A. An overview on time/frequency modulated array processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 228–246. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627182
|
| [17] |
So H C, Amin M G, Blunt S, et al. Introduction to the special issue on time/frequency modulated array signal processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 225–227. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2017.2652098
|
| [18] |
Xu J W, Liao G S, Zhang Y H, et al. An adaptive range-angle-Doppler processing approach for FDA-MIMO radar using three-dimensional localization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 309–320. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2615269
|
| [19] |
Qin S, Zhang Y D, Amin M G, et al. Frequency diverse coprime arrays with coprime frequency offsets for multitarget localization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 321–335. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627184
|
| [20] |
Liu Y M, Ruan H, Wang L, et al. The random frequency diverse array: A new antenna structure for uncoupled direction-range indication in active sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 295–308. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627183
|
| [21] |
Wang W Q. Range-angle dependent transmit beampattern synthesis for linear frequency diverse arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2013, 61(8): 4073–4081. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2260515
|
| [22] |
Wang W Q and So H C. Transmit subaperturing for range and angle estimation in frequency diverse array radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(8): 2000–2011. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2305638
|
| [23] |
Xu Y H, Shi X W, Xu J W, et al. Range-angle-dependent beamforming of pulsed frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(7): 3262–3267. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2423698
|
| [24] |
Xu J W, Liao G S, Zhu S Q, et al. Joint range and angle estimation using MIMO radar with frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(13): 3396–3410. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422680
|
| [25] |
Li Y. Dynamic waveform design for sensor systems with novel estimation of sensing environment characteristics[D]. Arizona State University, 2010.
|
| [26] |
Deng H and Himed B. Optimum waveform design and clutter rejection processing for MIMO radar[C]. Proceedings of the 2010 18th European Signal Processing Conference, Aalborg, Denmark, 2010: 1249–1251.
|
| [27] |
Friedlander B. Waveform design for MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(3): 1227–1238. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4383615
|
| [28] |
Naghibi T and Behnia F. MIMO radar waveform design in the presence of clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 770–781. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751224
|
| [29] |
Rabideau D J. MIMO radar aperture optimization[Z]. Lexington, Massachusetts: Lincoln Laboratory, 2011.
|
| [30] |
Bliss D W, Forsythe K W, and Richmond C D. MIMO radar: Joint array and waveform optimization[C]. Proceedings of 2007 Conference Record of the Forty-First Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2007: 207–211.
|
| [31] |
Xue Y H, Li X Y, and Sun Y L. Knowledge-aided target detection in sea clutter for distributed MIMO sky-wave radar[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–5.
|
| [32] |
李秀友, 薛永华, 黄勇, 等. 基于不确定集的稳健MIMO雷达波形设计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(10): 2445–2452. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT151425Li Xiu-you, Xue Yong-hua, Huang Yong, et al. Robust MIMO radar waveform design algorithm based on uncertainty set[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(10): 2445–2452. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT151425
|
| [33] |
关键, 黄勇, 何友. 基于自适应脉冲压缩-Capon滤波器的MIMO阵列雷达CFAR检测器[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2011, 54(11): 2411–2424Guan Jian, Huang Yong, and He You. A CFAR detector for MIMO array radar based on adaptive pulse compression-capon filter[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2011, 54(11): 2411–2424
|
| [34] |
关键, 黄勇, 何友. MIMO阵列雷达检测器的性能分析[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(9): 2107–2111Guan Jian, Huang Yong, and He You. Performance analysis of the detector for MIMO array radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(9): 2107–2111
|
| [35] |
关键, 黄勇. Gauss色噪声中MIMO分布孔径雷达检测性能分析[J]. 中国科学 F辑: 信息科学, 2009, 52(9): 1688–1696Guan Jian and Huang Yong. Detection performance analysis for MIMO radar with distributed apertures in Gaussian colored noise[J]. Science in China Series F-Information Sciences, 2009, 52(9): 1688–1696
|
| [36] |
Xu J, Zhou X, Qian L C, et al. Hybrid integration for highly maneuvering radar target detection based on generalized radon-Fourier transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(5): 2554–2561. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2016.150076
|
| [37] |
Huang P H, Liao G S, Yang Z W, et al. Long-time coherent integration for weak maneuvering target detection and high-order motion parameter estimation based on keystone transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(15): 4013–4026. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2558161
|
| [38] |
Chen X L, Guan J, Liu N B, et al. Maneuvering target detection via radon-fractional Fourier transform-based long-time coherent integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(4): 939–953. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2297682
|
| [39] |
Chen X L, Guan J, Huang Y, et al. Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function-based detection and estimation method for marine target with micromotion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2225–2240. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2358456
|
| [40] |
Chen X L, Guan J, Liu N B, et al. Detection of a low observable sea-surface target with micromotion via the radon-linear canonical transform[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(7): 1225–1229. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2290024
|
| [41] |
Chen X L, Huang Y, Liu N B, et al. Radon-fractional ambiguity function-based detection method of low-observable maneuvering target[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 815–833. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130791
|
| [42] |
Xu J, Yu J, Peng Y N, et al. Radon-Fourier transform for radar target detection, I: Generalized Doppler filter bank[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1186–1202. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751251
|
| [43] |
Li X L, Cui G L, Kong L J, et al. Fast non-searching method for maneuvering target detection and motion parameters estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(9): 2232–2244. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2515066
|
| [44] |
Zheng J B, Su T, Zhu W T, et al. ISAR imaging of nonuniformly rotating target based on a fast parameter estimation algorithm of cubic phase signal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4727–4740. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2408350
|
| [45] |
Wang H W, Fan X Y, Chen Y, et al. Wigner-Hough transform based on slice's entropy and its application to multi-LFM signal detection[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28(4): 634–642.
|
| [46] |
Yang L S, Zhang Z J, and Guo F Y. Fast algorithm for Radon-ambiguity transform[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2016, 10(3): 553–559. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0297
|
| [47] |
Wang Y, Zhao B, and Jiang Y C. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of targets with complex motion based on cubic Chirplet decomposition[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2015, 9(5): 419–429. DOI: 10.1049/iet-spr.2014.0086
|
| [48] |
Tao R, Li Y L, and Wang Y. Short-time fractional Fourier transform and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(5): 2568–2580. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2028095
|
| [49] |
Chen X L, Wang G Q, Dong Y L, et al. Sea clutter suppression and micromotion marine target detection via Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(6): 622–631. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0318
|
| [50] |
Chen X L, Guan J, Li X Y, et al. Effective coherent integration method for marine target with micromotion via phase differentiation and Radon-Lv’s distribution[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1284–1295. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0100
|
| [51] |
Sammartino P F and Baker C J. The frequency diverse bistatic system[C]. Proceedings of 2009 International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Kissimmee, FL, USA, 2009: 155–159. DOI: 10.1109/WDDC.2009.4800336.
|
| [52] |
Khan W, Qureshi I M, and Saeed S. Frequency diverse array radar with logarithmically increasing frequency offset[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 499–502. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2014.2368977
|
| [53] |
Chen H and Shao H Z. Sparse reconstruction based target localization with frequency diverse array MIMO radar[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing, Chengdu, China, 2015: 94–98.
|
| [54] |
Gao K D, Shao H Z, Chen H, et al. Impact of frequency increment errors on frequency diverse array MIMO in adaptive beamforming and target localization[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2015, 44: 58–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsp.2015.05.005
|
| [55] |
Chen B X, Chen X L, Huang Y, et al. Transmit beampattern synthesis for the FDA radar[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(1): 98–101. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2017.2776957
|
| [56] |
Wang W Q and Shao H Z. Range-angle localization of targets by a double-pulse frequency diverse array radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(1): 106–114. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.4200690
|
| [57] |
Wang W Q. Subarray-based frequency diverse array radar for target range-angle estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(4): 3057–3067. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120804
|
| [58] |
Xiong J, Wang W Q, and Gao K D. FDA-MIMO radar range-angle estimation: CRLB, MSE, and resolution analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 284–294. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756498
|
| [59] |
Li J J, Li H B, and Ouyang S. Identifying unambiguous frequency pattern for target localisation using frequency diverse array[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(19): 1331–1333. DOI: 10.1049/el.2017.2355
|
| [60] |
Gui R H, Wang W Q, Pan Y, et al. Cognitive target tracking via angle-range-Doppler estimation with transmit subaperturing FDA radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 76–89. DOI: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2793761
|
| [61] |
陈小龙, 关键, 何友, 等. 高分辨稀疏表示及其在雷达动目标检测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. DOI: 10.12000/JR16110Chen Xiao-long, Guan Jian, He You, et al. High-resolution sparse representation and its applications in radar moving target detection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. DOI: 10.12000/JR16110
|
| [62] |
陈小龙, 关键, 于晓涵, 等. 雷达动目标短时稀疏分数阶傅里叶变换域检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2017, 45(12): 3030–3036Chen Xiao-long, Guan Jian, Yu Xiao-han, et al. Radar detection for moving target in short-time sparse fractional Fourier transform domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2017, 45(12): 3030–3036
|
| [63] |
Liu S S, Shan T, Tao R, et al. Sparse discrete fractional Fourier transform and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(24): 6582–6595. DOI: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2366719
|
| [64] |
刘永军, 廖桂生, 杨志伟, 等. 一种超分辨OFDM雷达通信一体化设计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(2): 425–433. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150320Liu Yong-jun, Liao Gui-sheng, Yang Zhi-wei, et al. A super-resolution design method for integration of OFDM radar and communication[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2016, 38(2): 425–433. DOI: 10.11999/JEIT150320
|



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: